African Forest Biodiversity - Earthwatch Institute
African Forest Biodiversity - Earthwatch Institute
African Forest Biodiversity - Earthwatch Institute
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
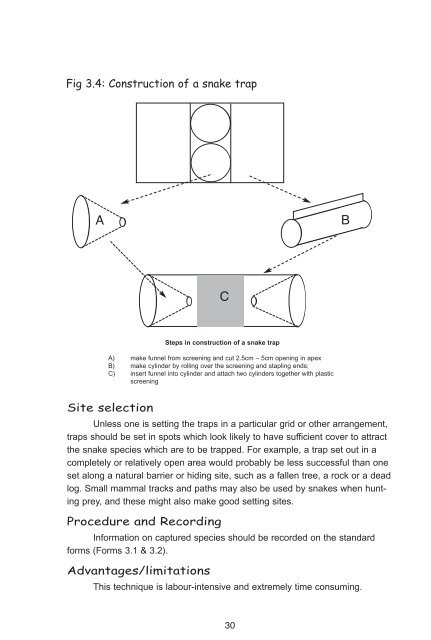
Fig 3.4: Construction of a snake trap<br />
A B<br />
Site selection<br />
Unless one is setting the traps in a particular grid or other arrangement,<br />
traps should be set in spots which look likely to have sufficient cover to attract<br />
the snake species which are to be trapped. For example, a trap set out in a<br />
completely or relatively open area would probably be less successful than one<br />
set along a natural barrier or hiding site, such as a fallen tree, a rock or a dead<br />
log. Small mammal tracks and paths may also be used by snakes when hunting<br />
prey, and these might also make good setting sites.<br />
Procedure and Recording<br />
Information on captured species should be recorded on the standard<br />
forms (Forms 3.1 & 3.2).<br />
Advantages/limitations<br />
C<br />
Steps in construction of a snake trap<br />
A) make funnel from screening and cut 2.5cm – 5cm opening in apex<br />
B) make cylinder by rolling over the screening and stapling ends;<br />
C) insert funnel into cylinder and attach two cylinders together with plastic<br />
screening<br />
This technique is labour-intensive and extremely time consuming.<br />
30