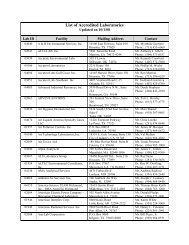
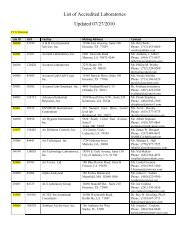
Bayou Lafourche
Bayou Lafourche - LDEQ Nonpoint 319 Projects
Bayou Lafourche - LDEQ Nonpoint 319 Projects
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
population explosion of these microscopic organisms can quickly consume nearly all<br />
available oxygen, greatly impacting fisheries and potentially resulting in fish kills.<br />
Insecticides used to target agricultural pests can also decimate aquatic insects vital to<br />
the productivity of the <strong>Bayou</strong> <strong>Lafourche</strong> ecosystem. Insects often provide the primary<br />
source of nourishment to larval fish. Some of these fish will mature to become part of a<br />
lucrative sport fishing industry. Others will be consumed by other small fish, which will,<br />
in-turn, be consumed by larger sport fish. The introduction of pesticides threatens to<br />
collapse this food chain by eliminating the base on which it is built. The impact is not<br />
limited to aquatic organisms. This community of insects and fish supports countless<br />
larger terrestrial communities of amphibians, birds, reptiles, and mammals.<br />
When agricultural herbicides enter water bodies, they often execute their largest impact<br />
on native vegetation. Native aquatic plants are a food source to many species and act<br />
as shelter to others. When native plant species are weakened by herbicides, they are<br />
often replaced by exotic or introduced species. Exotic species are not as well suited to<br />
fulfill the roll as food and shelter to aquatic animals. The result is a decline in<br />
productivity at every level similar to the impact of insecticides as discussed above.<br />
Perhaps the greatest potential impact from agriculture is sedimentation. As raindrops<br />
impact bare soil, they dislodge sediment particles that are carried by runoff over fields,<br />
into drainage channels, and eventually into receiving waters. Sediments can fill<br />
channels and limit their ability to convey water. This ability is especially important in<br />
<strong>Bayou</strong> <strong>Lafourche</strong>. The water conveyed by the bayou is used to irrigate fields and to<br />
provide drinking water to thousands of homes. Sediment clouds water and limits the<br />
production of food sources for aquatic animals. Sediment can also carry pesticides,<br />
herbicides, fertilizers, and other potentially harmful chemicals. Sedimentation potential<br />
is increased by eroding channel walls and improper agricultural practices.<br />
Urban Runoff<br />
Urban NPS pollution has severely impacted many of the water bodies receiving runoff<br />
from major cities in Louisiana, but urban NPS pollution is not limited only to large<br />
communities. Rural areas such as those near <strong>Bayou</strong> <strong>Lafourche</strong> contribute to urban NPS<br />
pollution as well. The <strong>Bayou</strong> <strong>Lafourche</strong> Watershed is also home to Louisiana Highways<br />
1 and 308. These roads are heavily utilized for commercial transport, agricultural<br />
27