Research Methods in Toxicology and Insecticide Resistance ...
Research Methods in Toxicology and Insecticide Resistance ...
Research Methods in Toxicology and Insecticide Resistance ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
H<br />
H<br />
H C O<br />
H C OH ATP ADP H C OH<br />
H CH O<br />
HO C H<br />
H<br />
C OH H C<br />
H C OH<br />
HO C C<br />
OH<br />
H C OHO<br />
H OH<br />
H C<br />
H<br />
–<br />
O –O<br />
OP<br />
H C<br />
C<br />
HO C<br />
H C<br />
C<br />
C<br />
H<br />
H O<br />
H C OPO<br />
C O O<br />
H O<br />
OH<br />
HO C H<br />
H C OPO<br />
O<br />
H<br />
C O O<br />
H<br />
HO C H<br />
OH<br />
H C OH<br />
H OH –<br />
O H C OH<br />
H OPO<br />
H<br />
H<br />
C OPO<br />
H<br />
H<br />
C O<br />
H C OH<br />
H C OPO<br />
H<br />
OPO<br />
O O ATP ADP<br />
C O<br />
OPO<br />
H C OH<br />
OPO<br />
H C OPO<br />
H<br />
–<br />
O<br />
C<br />
H C OH<br />
H C<br />
H<br />
–<br />
O<br />
C<br />
C<br />
C<br />
O<br />
C<br />
H C<br />
H C OH<br />
H<br />
–<br />
O<br />
ATP ADP O<br />
H<br />
H H<br />
–<br />
Dihydroxyacetone<br />
phosphate<br />
Glyceraldehyde<br />
Glucose Glucose 6-phosphate Fructose 6-phosphate Fructose 1, 6-phosphate<br />
3-phosphate<br />
2×<br />
NAD<br />
O<br />
C<br />
H C O<br />
H C H<br />
H<br />
OPO<br />
H2O Pyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate<br />
(PEP)<br />
2-phosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate<br />
+<br />
NADH + H +<br />
ATP ADP<br />
Fructose<br />
Triose<br />
bisphosphate phosphate<br />
Hexok<strong>in</strong>ase Phosphoglucose<br />
Phosphofructo<br />
aldose<br />
isomerase<br />
isomerase<br />
k<strong>in</strong>ase<br />
O<br />
Glycolysis<br />
Glyceraldehyde<br />
3-phosphate<br />
dehydrogenase<br />
+ Pi Pyruvate<br />
k<strong>in</strong>ase<br />
Enolase<br />
Phosphoglycerate<br />
Phosphoglycerate<br />
mutase<br />
k<strong>in</strong>ase<br />
–<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
O –<br />
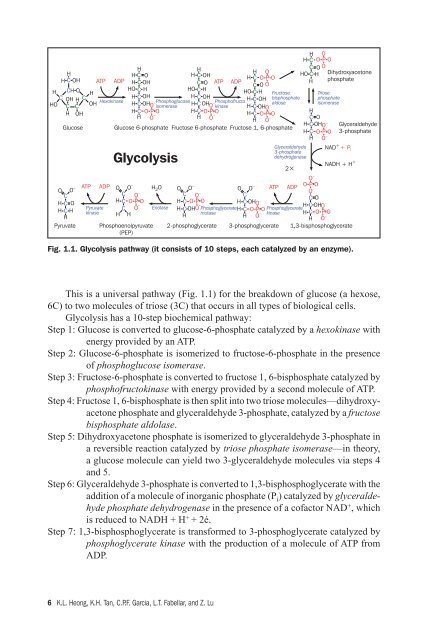
Fig. 1.1. Glycolysis pathway (it consists of 10 steps, each catalyzed by an enzyme).<br />
This is a universal pathway (Fig. 1.1) for the breakdown of glucose (a hexose,<br />
6C) to two molecules of triose (3C) that occurs <strong>in</strong> all types of biological cells.<br />
Glycolysis has a 10-step biochemical pathway:<br />
Step 1: Glucose is converted to glucose-6-phosphate catalyzed by a hexok<strong>in</strong>ase with<br />
energy provided by an ATP.<br />
Step 2: Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate <strong>in</strong> the presence<br />
of phosphoglucose isomerase.<br />
Step 3: Fructose-6-phosphate is converted to fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate catalyzed by<br />
phosphofructok<strong>in</strong>ase with energy provided by a second molecule of ATP.<br />
Step 4: Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate is then split <strong>in</strong>to two triose molecules—dihydroxyacetone<br />
phosphate <strong>and</strong> glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, catalyzed by a fructose<br />
bisphosphate aldolase.<br />
Step 5: Dihydroxyacetone phosphate is isomerized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate <strong>in</strong><br />
a reversible reaction catalyzed by triose phosphate isomerase—<strong>in</strong> theory,<br />
a glucose molecule can yield two 3-glyceraldehyde molecules via steps 4<br />
<strong>and</strong> 5.<br />
Step 6: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is converted to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate with the<br />
addition of a molecule of <strong>in</strong>organic phosphate (P i ) catalyzed by glyceraldehyde<br />
phosphate dehydrogenase <strong>in</strong> the presence of a cofactor NAD + , which<br />
is reduced to NADH + H + + 2é.<br />
Step 7: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is transformed to 3-phosphoglycerate catalyzed by<br />
phosphoglycerate k<strong>in</strong>ase with the production of a molecule of ATP from<br />
ADP.<br />
6 K.L. Heong, K.H. Tan, C.P.F. Garcia, L.T. Fabellar, <strong>and</strong> Z. Lu