You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
abstracts<br />
<strong>Annals</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Oncology</strong><br />
Conclusions: This study provides evidence that functional germline polymorphisms in<br />
the VEGF pathway may be helpful as prognostic biomarkers in colon cancer.<br />
Legal entity responsible for the study: Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (Barcelona)<br />
Funding: Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (Barcelona)<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts <strong>of</strong> interest.<br />
99P<br />
Clinical characteristics in colorectal cancer harboring BRAF<br />
V600E and non-V600E mutations<br />
E. Shinozaki 1 , Y. Miki 2 , M. Ueno 3 , M. Igarashi 4 , K. Chin 1 , D. Takahari 1 , M. Ogura 1 ,<br />
T. Ichimura 1 , I. Nakayama 1 , H. Osumi 1 , T. Wakatsuki 1 , T. Matsushima 1 ,<br />
K. Yamaguchi 1<br />
1 Department <strong>of</strong> GI <strong>Oncology</strong>, Cancer Institute Hospital <strong>of</strong> JFCR, Tokyo, Japan,<br />
2 Lab <strong>of</strong> Genetic Diagnosis, Cancer Institute Hospital <strong>of</strong> JFCR, Tokyo, Japan,<br />
3 Department <strong>of</strong> Gastroenterological Surgery, Cancer Institute Hospital <strong>of</strong> JFCR,<br />
Tokyo, Japan, 4 Department <strong>of</strong> Gastroenterology, Cancer Institute Hospital <strong>of</strong><br />
JFCR, Tokyo, Japan<br />
Background: BRAF V600E mutation (MT) in metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) has<br />
been known thoroughly as a prognostic biomarker, and as a negative predictive<br />
biomarker for anti-EGFR treatment. On the other hand, the feature <strong>of</strong> BRAF MTs<br />
other than BRAF V600E still remains unclear. This study aimed to reveal the clinical<br />
characteristics <strong>of</strong> BRAF non-V600E MTs compared with the EGFR signaling pathway<br />
MTs status including BRAF V600E MT.<br />
Methods: Consecutive patients from June 2012 to November 2013 were enrolled in this<br />
study. Multiplex genotyping <strong>of</strong> EGFR signaling pathway was performed on archival<br />
samples using Luminex Assay (MABGEN, GENOSEARCH Mu-PACK and<br />
GENOSEARCH BRAF, MBL) for BRAF V600E / BRAF non-V600E , KRAS including exon<br />
2, 3 and 4, NRAS, and PIK3CA. We analyzed the correlation among MTs pr<strong>of</strong>ile,<br />
clinical data and location <strong>of</strong> CRC.<br />
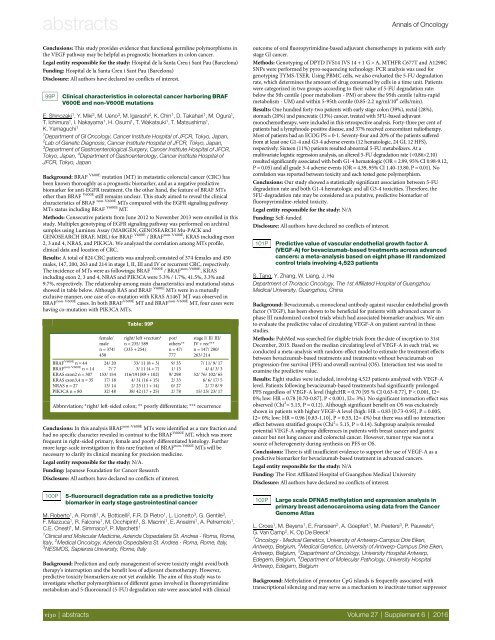
Results: A total <strong>of</strong> 824 CRC patients was analyzed; consisted <strong>of</strong> 374 females and 450<br />
males, 147, 200, 263 and 214 in stage I, II, III and IV or recurrent CRC, respectively.<br />
The incidence <strong>of</strong> MTs were as followings; BRAF V600E / BRAF non-V600E , KRAS<br />
including exon 2, 3 and 4, NRAS and PIK3CA were 5.3% / 1.7%, 41.5%, 3.3% and<br />
9.7%, respectively. The relationship among main characteristics and mutational status<br />
showed in table below. Although RAS and BRAF V600E MTs were in a mutually<br />
exclusive manner, one case <strong>of</strong> co-mutation with KRAS A146T MT was observed in<br />
BRAF non-V600E cases. In both BRAF V600E MT and BRAF non-V600E MT, four cases were<br />
having co-mutation with PIK3CA MTs.<br />
female/<br />
male<br />
n = 374/<br />
450<br />
Table: 99P<br />
right/ left +rectum*<br />
n = 235/ 589<br />
(335 + 254)<br />
por/<br />
others**<br />
n = 47/<br />
777<br />
stage I/ II/ III/<br />
IV + rec***<br />
n = 147/ 200/<br />
263/ 214<br />
BRAF V600E n = 44 24/ 20 33/ 11 (8 + 3) 9/ 35 7/ 11/ 9/ 17<br />
BRAF non-V600E n = 14 7/ 7 3/ 11 (4 + 7) 1/ 13 4/ 4/ 3/ 3<br />
KRAS exon2 n = 307 153/ 154 116/191(89 + 102) 9/ 298 52/ 76/ 102/ 65<br />
KRAS exon3,4 n = 35 17/ 18 4/ 31 (16 + 15) 2/ 33 6/ 6/ 17/ 5<br />
NRAS n = 27 13/ 14 2/ 25 (11 + 14) 0/ 27 2/ 7/ 8/ 9<br />
PIK3CA n = 80 32/ 48 38/ 42 (17 + 25) 2/ 78 15/ 25/ 23/ 17<br />
Abbreviation; *right/ left-sided colon; ** poorly differentiate; *** recurrence<br />
Conclusions: In this analysis BRAF non-V600E MTs were identified as a rare fraction and<br />
had no specific character revealed in contrast to the BRAF V600E MT, which was more<br />
frequent in right-sided primary, female and poorly differentiated histology. Further<br />
more large-scale investigation in this rare fraction <strong>of</strong> BRAF non-V600E MTs will be<br />
necessary to clarify its clinical meaning for precision medicine.<br />
Legal entity responsible for the study: N/A.<br />
Funding: Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts <strong>of</strong> interest.<br />
100P<br />
5-fluorouracil degradation rate as a predictive toxicity<br />
biomarker in early stage gastrointestinal cancer<br />
M. Roberto 1 , A. Romiti 1 , A. Botticelli 2 , F.R. Di Pietro 1 , L. Lionetto 3 , G. Gentile 3 ,<br />
F. Mazzuca 1 , R. Falcone 1 , M. Occhipinti 1 , S. Macrini 1 , E. Anselmi 1 , A. Petremolo 1 ,<br />
C.E. Onesti 1 , M. Simmaco 3 , P. Marchetti 1<br />
1 Clinical and Molecular Medicine, Azienda Ospedaliera St. Andrea - Roma, Rome,<br />
Italy, 2 Medical <strong>Oncology</strong>, Azienda Ospedaliera St. Andrea - Roma, Rome, Italy,<br />
3 NESMOS, Sapienza University, Rome, Italy<br />
Background: Prediction and early management <strong>of</strong> severe toxicity might avoid both<br />
therapy’s interruption and the benefit loss <strong>of</strong> adjuvant chemotherapy. However,<br />
predictive toxicity biomarkers are not yet available. The aim <strong>of</strong> this study was to<br />
investigate whether polymorphisms <strong>of</strong> different genes involved in fluoropyrimidine<br />
metabolism and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) degradation rate were associated with clinical<br />
outcome <strong>of</strong> oral fluoropyrimidine-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early<br />
stage GI cancer.<br />
Methods: Genotyping <strong>of</strong> DPYD IVS14 IVS 14 + 1 G > A, MTHFR C677T and A1298C<br />
SNPs were performed by pyro-sequencing technology. PCR analysis was used for<br />
genotyping TYMS-TSER. Using PBMC cells, we also evaluated the 5-FU degradation<br />
rate, which determines the amount <strong>of</strong> drug consumed by cells in a time unit. Patients<br />
were categorized in two groups according to their value <strong>of</strong> 5-FU degradation rate:<br />
below the 5th centile (poor metabolism - PM) or above the 95th centile (ultra-rapid<br />
metabolism - UM) and within 5-95th centile (0.85-2.2 ng/ml/10 6 cells/min).<br />
Results: One hundred forty-two patients with early stage colon (39%), rectal (28%),<br />
stomach (20%) and pancreatic (13%) cancer, treated with 5FU-based adjuvant<br />
monochemotherapy, were included in this retrospective analysis. Forty-three per cent <strong>of</strong><br />
patients had a lymphnode-positive disease, and 37% received concomitant radiotherapy.<br />
Most <strong>of</strong> patients had an ECOG PS = 0-1. Seventy-four and 20% <strong>of</strong> the patients suffered<br />
from at least one G1-4 and G3-4 adverse events (12 hematologic, 24 GI, 12 HFS),<br />
respectively. Sixteen (11%) patients resulted abnormal 5-FU metabolizers. At a<br />
multivariate logistic regression analysis, an altered 5-FU degradation rate (2.10)<br />
resulted significantly associated with both G1-4 hematologic (OR = 2.99, 95% CI 0.98-9.12,<br />
P = 0.05) and all grade 3-4 adverse events (OR = 4.39, 95% CI 1.40-13.80, P = 0.01). No<br />
correlation was reported between toxicity and each tested gene polymorphism.<br />
Conclusions: Our study showed a statistically significant association between 5-FU<br />
degradation rate and both G1-4 hematologic and all G3-4 toxicities. Therefore, the<br />
5FU-degradation rate may be considered as a putative, predictive biomarker <strong>of</strong><br />
fluoropyrimidine-related toxicity.<br />
Legal entity responsible for the study: N/A<br />
Funding: Self-funded<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts <strong>of</strong> interest.<br />
101P<br />
Predictive value <strong>of</strong> vascular endothelial growth factor A<br />
(VEGF-A) for bevacizumab-based treatments across advanced<br />
cancers: a meta-analysis based on eight phase III randomized<br />
control trials involving 4,523 patients<br />
S. Tang, Y. Zhang, W. Liang, J. He<br />
Department <strong>of</strong> Thoracic <strong>Oncology</strong>, The 1st Affiliated Hospital <strong>of</strong> Guangzhou<br />
Medical University, Guangzhou, China<br />
Background: Bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth<br />
factor (VEGF), has been shown to be beneficial for patients with advanced cancer in<br />
phase III randomized control trials which had associated biomarker analyses. We aim<br />
to evaluate the predictive value <strong>of</strong> circulating VEGF-A on patient survival in these<br />
studies.<br />
Methods: PubMed was searched for eligible trials from the date <strong>of</strong> inception to 31st<br />
December, 2015. Based on the median circulating level <strong>of</strong> VEGF-A in each trial, we<br />
conducted a meta-analysis with random-effect model to estimate the treatment effects<br />
between bevacizumab-based treatments and treatments without bevacizumab on<br />
progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Interaction test was used to<br />
examine the predictive value.<br />
Results: Eight studies were included, involving 4,523 patients analyzed with VEGF-A<br />
level. Patients following bevacizumab-based treatments had significantly prolonged<br />
PFS regardless <strong>of</strong> VEGF-A level (high:HR = 0.70 [95 % CI 0.63-0.77], P < 0.001, I2=<br />
0%; low: HR = 0.78 [0.70-0.87], P < 0.001, I2= 3%). No significant interaction effect was<br />
observed (Chi 2 = 5.15, P = 0.12). Although significant benefit on OS was exclusively<br />
shown in patients with higher VEGF-A level (high: HR = 0.83 [0.73-0.95], P = 0.005,<br />
I2= 0%; low: HR = 0.96 [0.83-1.10], P = 0.55, I2= 4%) but there was still no interaction<br />
effect between stratified groups (Chi 2 = 5.15, P = 0.14). Subgroup analysis revealed<br />
potential VEGF-A subgroup differences in patients with breast cancer and gastric<br />
cancer but not lung cancer and colorectal cancer. However, tumor type was not a<br />
source <strong>of</strong> heterogeneity during synthesis on PFS or OS.<br />
Conclusions: There is still insufficient evidence to support the use <strong>of</strong> VEGF-A as a<br />
predictive biomarker for bevacizumab-based treatment in advanced cancers.<br />
Legal entity responsible for the study: N/A<br />
Funding: The First Affiliated Hospital <strong>of</strong> Guangzhou Medical University<br />
Disclosure: All authors have declared no conflicts <strong>of</strong> interest.<br />
102P<br />
Large scale DFNA5 methylation and expression analysis in<br />
primary breast adenocarcinoma using data from the Cancer<br />
Genome Atlas<br />
L. Croes 1 , M. Beyens 1 , E. Franssen 2 , A. Goepfert 1 , M. Peeters 3 , P. Pauwels 4 ,<br />
G. Van Camp 2 , K. Op De Beeck 1<br />
1 <strong>Oncology</strong> - Medical Genetics, University <strong>of</strong> Antwerp-Campus Drie Eiken,<br />
Antwerp, Belgium, 2 Medical Genetics, University <strong>of</strong> Antwerp-Campus Drie Eiken,<br />
Antwerp, Belgium, 3 Department <strong>of</strong> <strong>Oncology</strong>, University Hospital Antwerp,<br />
Edegem, Belgium, 4 Department <strong>of</strong> Molecular Pathology, University Hospital<br />
Antwerp, Edegem, Belgium<br />
Background: Methylation <strong>of</strong> promotor CpG islands is frequently associated with<br />
transcriptional silencing and may serve as a mechanism to inactivate tumor suppressor<br />
vi30 | abstracts Volume 27 | Supplement 6 | 2016