Agar as a medium for removing soil from earthworm ... - Directory UMM
Agar as a medium for removing soil from earthworm ... - Directory UMM
Agar as a medium for removing soil from earthworm ... - Directory UMM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1316<br />
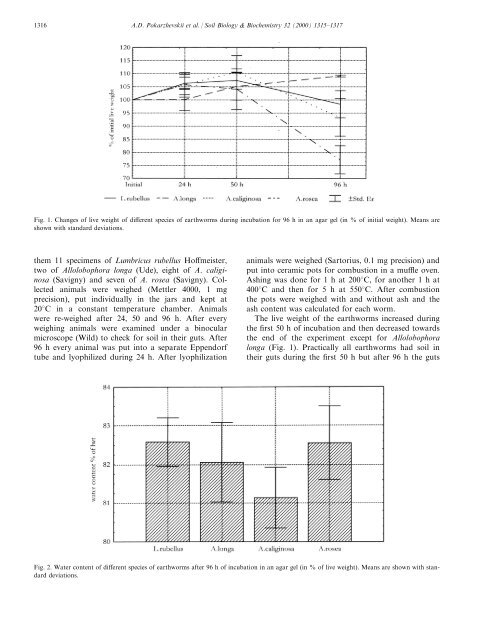
Fig. 1. Changes of live weight of di€erent species of <strong>earthworm</strong>s during incubation <strong>for</strong> 96 h in an agar gel (in % of initial weight). Means are<br />
shown with standard deviations.<br />
them 11 specimens of Lumbricus rubellus Ho€meister,<br />
two of Allolobophora longa (Ude), eight of A. caliginosa<br />
(Savigny) and seven of A. rosea (Savigny). Collected<br />
animals were weighed (Mettler 4000, 1 mg<br />
precision), put individually in the jars and kept at<br />
208C in a constant temperature chamber. Animals<br />
were re-weighed after 24, 50 and 96 h. After every<br />
weighing animals were examined under a binocular<br />
microscope (Wild) to check <strong>for</strong> <strong>soil</strong> in their guts. After<br />
96 h every animal w<strong>as</strong> put into a separate Eppendorf<br />
tube and lyophilized during 24 h. After lyophilization<br />
A.D. Pokarzhevskii et al. / Soil Biology & Biochemistry 32 (2000) 1315±1317<br />
animals were weighed (Sartorius, 0.1 mg precision) and<br />
put into ceramic pots <strong>for</strong> combustion in a mu‚e oven.<br />
Ashing w<strong>as</strong> done <strong>for</strong> 1 h at 2008C, <strong>for</strong> another 1 h at<br />
4008C and then <strong>for</strong> 5 h at 5508C. After combustion<br />
the pots were weighed with and without <strong>as</strong>h and the<br />
<strong>as</strong>h content w<strong>as</strong> calculated <strong>for</strong> each worm.<br />
The live weight of the <strong>earthworm</strong>s incre<strong>as</strong>ed during<br />
the ®rst 50 h of incubation and then decre<strong>as</strong>ed towards<br />
the end of the experiment except <strong>for</strong> Allolobophora<br />
longa (Fig. 1). Practically all <strong>earthworm</strong>s had <strong>soil</strong> in<br />
their guts during the ®rst 50 h but after 96 h the guts<br />
Fig. 2. Water content of di€erent species of <strong>earthworm</strong>s after 96 h of incubation in an agar gel (in % of live weight). Means are shown with standard<br />
deviations.