Cyber Security and IoT
Explaining why IoT (Internet of Things) devices must be secure by design. Published by CENSIS, the Innovation Centre for sensing, imaging and IoT. censis.org.uk
Explaining why IoT (Internet of Things) devices must be secure by design. Published by CENSIS, the Innovation Centre for sensing, imaging and IoT.
censis.org.uk
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
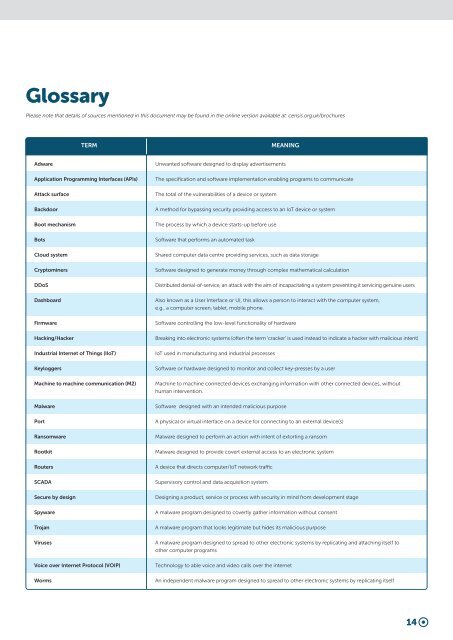
Glossary<br />
Please note that details of sources mentioned in this document may be found in the online version available at: censis.org.uk/brochures<br />
TERM MEANING<br />
Adware<br />
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)<br />
Attack surface<br />
Backdoor<br />
Boot mechanism<br />
Bots<br />
Cloud system<br />
Cryptominers<br />
DDoS<br />
Dashboard<br />
Firmware<br />
Hacking/Hacker<br />
Industrial Internet of Things (I<strong>IoT</strong>)<br />
Keyloggers<br />
Machine to machine communication (M2)<br />
Malware<br />
Port<br />
Ransomware<br />
Rootkit<br />
Routers<br />
SCADA<br />
Secure by design<br />
Spyware<br />
Trojan<br />
Viruses<br />
Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP)<br />
Worms<br />
Unwanted software designed to display advertisements<br />
The specification <strong>and</strong> software implementation enabling programs to communicate<br />
The total of the vulnerabilities of a device or system<br />
A method for bypassing security providing access to an <strong>IoT</strong> device or system<br />
The process by which a device starts-up before use<br />
Software that performs an automated task<br />
Shared computer data centre providing services, such as data storage<br />
Software designed to generate money through complex mathematical calculation<br />
Distributed denial-of-service, an attack with the aim of incapacitating a system preventing it servicing genuine users<br />
Also known as a User Interface or UI, this allows a person to interact with the computer system,<br />
e.g., a computer screen, tablet, mobile phone.<br />
Software controlling the low-level functionality of hardware<br />
Breaking into electronic systems (often the term ‘cracker’ is used instead to indicate a hacker with malicious intent)<br />
<strong>IoT</strong> used in manufacturing <strong>and</strong> industrial processes<br />
Software or hardware designed to monitor <strong>and</strong> collect key-presses by a user<br />
Machine to machine connected devices exchanging information with other connected devices, without<br />
human intervention.<br />
Software designed with an intended malicious purpose<br />
A physical or virtual interface on a device for connecting to an external device(s)<br />
Malware designed to perform an action with intent of extorting a ransom<br />
Malware designed to provide covert external access to an electronic system<br />
A device that directs computer/<strong>IoT</strong> network traffic<br />
Supervisory control <strong>and</strong> data acquisition system<br />
Designing a product, service or process with security in mind from development stage<br />
A malware program designed to covertly gather information without consent<br />
A malware program that looks legitimate but hides its malicious purpose<br />
A malware program designed to spread to other electronic systems by replicating <strong>and</strong> attaching itself to<br />
other computer programs<br />
Technology to able voice <strong>and</strong> video calls over the internet<br />
An independent malware program designed to spread to other electronic systems by replicating itself<br />
14