You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
lsetse<br />
THE COINCIDENCE OF VIRt'S-.IKE PARTICI.1. INIHtCEI)<br />
SALIVARY GLAND HYPIFR ROPIIY )' AND ') tPANOhM.Il<br />
INFECTION IN GIOS.SIA.V. PI.I'1>5 A'S II.N<br />
T K. Goh'r.S A. hirin,. R.1 I)Irufid<br />
The virus-like particles (VI.Ps) which cause saliarty gland<br />
hypertrophy (SGH) in Ghlos.%ina oallidipes have been<br />
considered as possinle biological-control agents, because of<br />
the high incidence of sterility in infected rialc,. It has been<br />
suggested that flies it h S(i H might he particularly vell<br />
suited for trypanosotne infection,. Iherefore, we have<br />
collected atlar e sample (12,330)) of G. pallidipw Irot our<br />
,tady site at Nguruman to elucidate tile relationship<br />
betx een VI.IP and trVpanosone-infectin rntcs. Flics %%ere<br />
dissected for trypanosome infection. Si'll and age<br />
determination. [he ox.erall trypanosonc-infection rate (I<br />
tiv5, i: (oigo'li.w, and T: brui''i)in Ilies vith to;mal<br />
lixarvgland:.,(hothi sexes was 4. 9' (n- 12,14). Inflies<br />
%sithSI-IG, the overall tr,.panosonie-itilectii rate was<br />
L'. -. ,it Si'5,) [lie ditticitCC in trxpansoieinlecti<br />
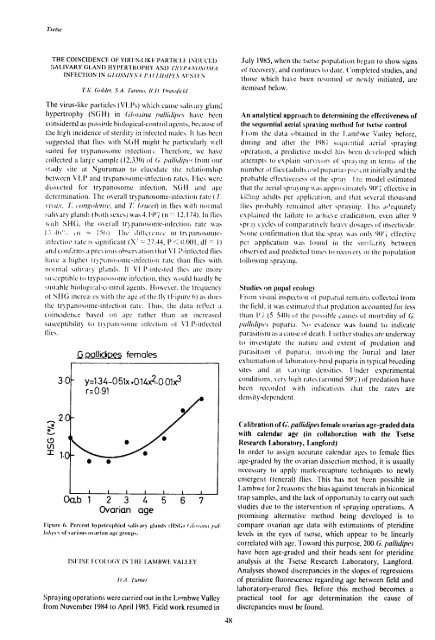
' rate is ignificant (X 27.44, 1