You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
positively charged<br />
cations or negatively<br />
charged anions that<br />
have varying levels<br />
of impact on overall<br />
salinity stress, with<br />
more or less effort<br />
to manage. Soil<br />
chloride (Cl) and<br />
sodium (Na) levels<br />
>30 milliequivalents<br />
per liter (meq/L),<br />
and B levels above 3<br />
mg/L are problematic<br />
for the<br />
long-term health<br />
and productivity<br />
of pistachios. Cl<br />
can be reduced<br />
with clean water<br />
alone, however<br />
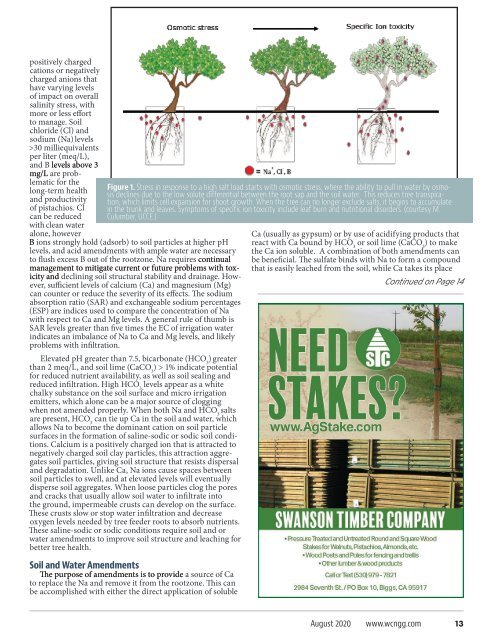
Figure 1. Stress in response to a high salt load starts with osmotic stress, where the ability to pull in water by osmosis<br />
declines due to the low solute differential between the root sap and the soil water. This reduces tree transpiration,<br />
which limits cell expansion for shoot growth. When the tree can no longer exclude salts, it begins to accumulate<br />
in the FIGURE trunk 1and leaves. Symptoms of specific ion toxicity include leaf burn and nutritional disorders. (courtesy M.<br />
Culumber, UCCE.)<br />
B ions strongly hold (adsorb) to soil particles at higher pH<br />
levels, and acid amendments with ample water are necessary<br />
to flush excess B out of the rootzone. Na requires continual<br />
management to mitigate current or future problems with toxicity<br />
and declining soil structural stability and drainage. However,<br />
sufficient levels of calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg)<br />
can counter or reduce the severity of its effects. The sodium<br />
absorption ratio (SAR) and exchangeable sodium percentages<br />
(ESP) are indices used to compare the concentration of Na<br />
with respect to Ca and Mg levels. A general rule of thumb is<br />
SAR levels greater than five times the EC of irrigation water<br />
indicates an imbalance of Na to Ca and Mg levels, and likely<br />
problems with infiltration.<br />
Elevated pH greater than 7.5, bicarbonate (HCO 3<br />
) greater<br />
than 2 meq/L, and soil lime (CaCO 3<br />
) > 1% indicate potential<br />
for reduced nutrient availability, as well as soil sealing and<br />
reduced infiltration. High HCO 3<br />
levels appear as a white<br />
chalky substance on the soil surface and micro irrigation<br />
emitters, which alone can be a major source of clogging<br />
when not amended properly. When both Na and HCO 3<br />
salts<br />
are present, HCO 3<br />
can tie up Ca in the soil and water, which<br />
allows Na to become the dominant cation on soil particle<br />
surfaces in the formation of saline-sodic or sodic soil conditions.<br />
Calcium is a positively charged ion that is attracted to<br />
negatively charged soil clay particles, this attraction aggregates<br />
soil particles, giving soil structure that resists dispersal<br />
and degradation. Unlike Ca, Na ions cause spaces between<br />
soil particles to swell, and at elevated levels will eventually<br />
disperse soil aggregates. When loose particles clog the pores<br />
and cracks that usually allow soil water to infiltrate into<br />
the ground, impermeable crusts can develop on the surface.<br />
These crusts slow or stop water infiltration and decrease<br />
oxygen levels needed by tree feeder roots to absorb nutrients.<br />
These saline-sodic or sodic conditions require soil and or<br />
water amendments to improve soil structure and leaching for<br />
better tree health.<br />
Soil and Water Amendments<br />
The purpose of amendments is to provide a source of Ca<br />
to replace the Na and remove it from the rootzone. This can<br />
be accomplished with either the direct application of soluble<br />
Ca (usually as gypsum) or by use of acidifying products that<br />
react with Ca bound by HCO 3<br />
or soil lime (CaCO 3<br />
) to make<br />
the Ca ion soluble. A combination of both amendments can<br />
be beneficial. The sulfate binds with Na to form a compound<br />
that is easily leached from the soil, while Ca takes its place<br />
Continued on Page 14<br />
<strong>August</strong> <strong>2020</strong> www.wcngg.com 13