Rolling Revision of the WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality ...
Rolling Revision of the WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality ...
Rolling Revision of the WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
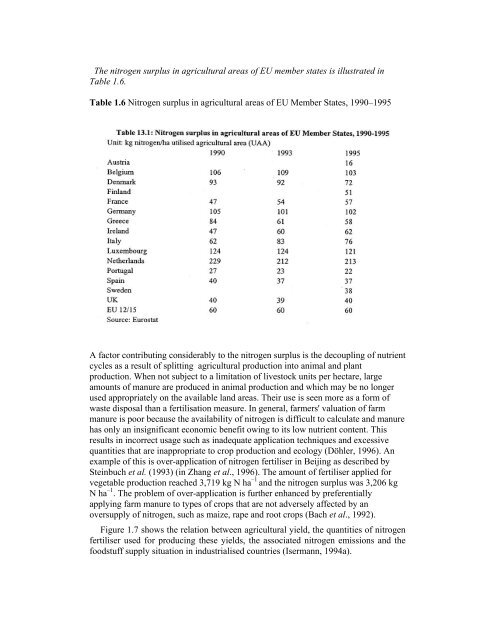
The nitrogen surplus in agricultural areas <strong>of</strong> EU member states is illustrated in<br />
Table 1.6.<br />
Table 1.6 Nitrogen surplus in agricultural areas <strong>of</strong> EU Member States, 1990–1995<br />
A factor contributing considerably to <strong>the</strong> nitrogen surplus is <strong>the</strong> decoupling <strong>of</strong> nutrient<br />
cycles as a result <strong>of</strong> splitting agricultural production into animal and plant<br />
production. When not subject to a limitation <strong>of</strong> livestock units per hectare, large<br />
amounts <strong>of</strong> manure are produced in animal production and which may be no longer<br />
used appropriately on <strong>the</strong> available land areas. Their use is seen more as a <strong>for</strong>m <strong>of</strong><br />
waste disposal than a fertilisation measure. In general, farmers' valuation <strong>of</strong> farm<br />
manure is poor because <strong>the</strong> availability <strong>of</strong> nitrogen is difficult to calculate and manure<br />
has only an insignificant economic benefit owing to its low nutrient content. This<br />
results in incorrect usage such as inadequate application techniques and excessive<br />
quantities that are inappropriate to crop production and ecology (Döhler, 1996). An<br />
example <strong>of</strong> this is over-application <strong>of</strong> nitrogen fertiliser in Beijing as described by<br />
Steinbuch et al. (1993) (in Zhang et al., 1996). The amount <strong>of</strong> fertiliser applied <strong>for</strong><br />
vegetable production reached 3,719 kg N ha –1 and <strong>the</strong> nitrogen surplus was 3,206 kg<br />
N ha –1 . The problem <strong>of</strong> over-application is fur<strong>the</strong>r enhanced by preferentially<br />
applying farm manure to types <strong>of</strong> crops that are not adversely affected by an<br />
oversupply <strong>of</strong> nitrogen, such as maize, rape and root crops (Bach et al., 1992).<br />
Figure 1.7 shows <strong>the</strong> relation between agricultural yield, <strong>the</strong> quantities <strong>of</strong> nitrogen<br />
fertiliser used <strong>for</strong> producing <strong>the</strong>se yields, <strong>the</strong> associated nitrogen emissions and <strong>the</strong><br />
foodstuff supply situation in industrialised countries (Isermann, 1994a).