Experiences with Novel Secondary Conductivity Sensors within the ...
Experiences with Novel Secondary Conductivity Sensors within the ...
Experiences with Novel Secondary Conductivity Sensors within the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
TECHNICAL PAPERS<br />
G, µS<br />
838.00<br />
836.00<br />
834.00<br />
832.00<br />
830.00<br />
828.00<br />
826.00<br />
nificant frequencies were determined.<br />
1.4 Temperature Measurement<br />
Constant temperature of <strong>the</strong> measuring<br />
cells is an important precondition for <strong>the</strong><br />
determination of reproducible measurement<br />
results <strong>with</strong> low uncertainties.<br />
The homogeneity of <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmostatic<br />
bath must be assured. Usually <strong>the</strong>rmometers<br />
<strong>with</strong> platinum elements of<br />
100 Ω (Pt100) or 25 Ω (Pt25)resistance<br />
1/f, Hz –1<br />
y = 970.1x + 837.7<br />
R 2 = 0.9995<br />
0.0000 0.0020 0.0040 0.0060 0.0080 0.0100 0.0120<br />
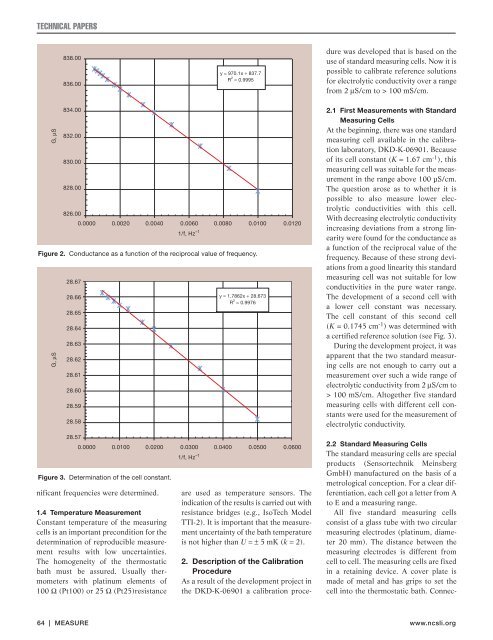
Figure 2. Conductance as a function of <strong>the</strong> reciprocal value of frequency.<br />
G, µS<br />
28.67<br />
28.66<br />
28.65<br />
28.64<br />
28.63<br />
28.62<br />
28.61<br />
28.60<br />
28.59<br />
28.58<br />
28.57<br />
0.0000 0.0100 0.0200 0.0300 0.0400 0.0500 0.0600<br />
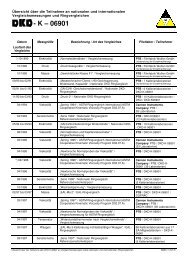
Figure 3. Determination of <strong>the</strong> cell constant.<br />
1/f, Hz –1<br />
y = 1.7862x + 28.673<br />
R 2 = 0.9976<br />
are used as temperature sensors. The<br />
indication of <strong>the</strong> results is carried out <strong>with</strong><br />
resistance bridges (e.g., IsoTech Model<br />
TTI-2). It is important that <strong>the</strong> measurement<br />
uncertainty of <strong>the</strong> bath temperature<br />
is not higher than U = ± 5 mK (k = 2).<br />
2. Description of <strong>the</strong> Calibration<br />
Procedure<br />
As a result of <strong>the</strong> development project in<br />
<strong>the</strong> DKD-K-06901 a calibration proce-<br />
dure was developed that is based on <strong>the</strong><br />
use of standard measuring cells. Now it is<br />
possible to calibrate reference solutions<br />
for electrolytic conductivity over a range<br />
from 2 µS/cm to > 100 mS/cm.<br />
2.1 First Measurements <strong>with</strong> Standard<br />
Measuring Cells<br />
At <strong>the</strong> beginning, <strong>the</strong>re was one standard<br />
measuring cell available in <strong>the</strong> calibration<br />
laboratory, DKD-K-06901. Because<br />
of its cell constant (K = 1.67 cm -1 ), this<br />
measuring cell was suitable for <strong>the</strong> measurement<br />
in <strong>the</strong> range above 100 µS/cm.<br />
The question arose as to whe<strong>the</strong>r it is<br />
possible to also measure lower electrolytic<br />
conductivities <strong>with</strong> this cell.<br />
With decreasing electrolytic conductivity<br />
increasing deviations from a strong linearity<br />
were found for <strong>the</strong> conductance as<br />
a function of <strong>the</strong> reciprocal value of <strong>the</strong><br />
frequency. Because of <strong>the</strong>se strong deviations<br />
from a good linearity this standard<br />
measuring cell was not suitable for low<br />
conductivities in <strong>the</strong> pure water range.<br />
The development of a second cell <strong>with</strong><br />
a lower cell constant was necessary.<br />
The cell constant of this second cell<br />
(K = 0.1745 cm -1 ) was determined <strong>with</strong><br />
a certified reference solution (see Fig. 3).<br />
During <strong>the</strong> development project, it was<br />
apparent that <strong>the</strong> two standard measuring<br />
cells are not enough to carry out a<br />
measurement over such a wide range of<br />
electrolytic conductivity from 2 µS/cm to<br />
> 100 mS/cm. Altoge<strong>the</strong>r five standard<br />
measuring cells <strong>with</strong> different cell constants<br />
were used for <strong>the</strong> measurement of<br />
electrolytic conductivity.<br />
2.2 Standard Measuring Cells<br />
The standard measuring cells are special<br />
products (Sensortechnik Meinsberg<br />
GmbH) manufactured on <strong>the</strong> basis of a<br />
metrological conception. For a clear differentiation,<br />
each cell got a letter from A<br />
to E and a measuring range.<br />
All five standard measuring cells<br />
consist of a glass tube <strong>with</strong> two circular<br />
measuring electrodes (platinum, diameter<br />
20 mm). The distance between <strong>the</strong><br />
measuring electrodes is different from<br />
cell to cell. The measuring cells are fixed<br />
in a retaining device. A cover plate is<br />
made of metal and has grips to set <strong>the</strong><br />
cell into <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmostatic bath. Connec-<br />
64 | MEASURE www.ncsli.org