TAPIR FIELD VETERINARY MANUAL - Tapir Specialist Group
TAPIR FIELD VETERINARY MANUAL - Tapir Specialist Group
TAPIR FIELD VETERINARY MANUAL - Tapir Specialist Group
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2. <strong>Tapir</strong> Anatomy: General Information<br />
The internal anatomy and physiology of tapirs is similar to that of the domestic horse and other<br />
Perissodactyla. When specific data is not available for tapirs, it is recommended to adapt the<br />
doses and therapeutics from protocols used for equids and rhinos.<br />
The tapirs have a solid and massive body structure, and their body weight is around 150-300 kg,<br />
or above 300 kg for the Malayan tapir (Further details on TABLE 1). Females tend to be larger<br />
than males, but there is no evident sexual dimorphism. <strong>Tapir</strong>s have a proboscis derived from<br />
muscle and soft tissues from the nose and upper lip. The proboscis is highly mobile and sensitive<br />
to touch, and is very important for the manipulation and ingestion of food. Lowland tapirs have<br />
an exuberant crest on the back of the neck, which is derived from fat and soft tissues and<br />
covered by very long black hair.<br />
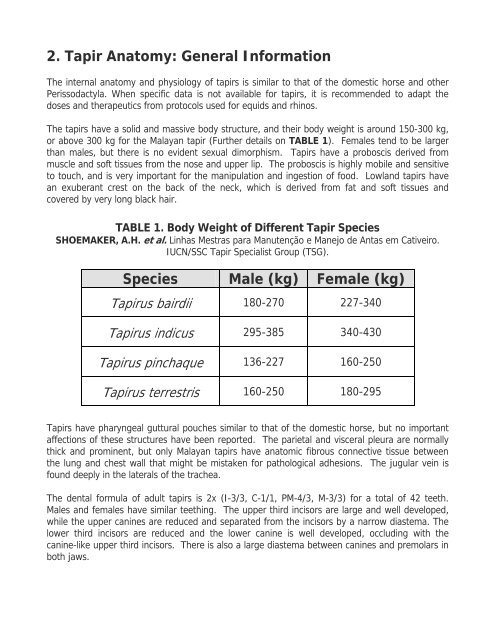
TABLE 1. Body Weight of Different <strong>Tapir</strong> Species<br />
SHOEMAKER, A.H. et al. Linhas Mestras para Manutenção e Manejo de Antas em Cativeiro.<br />
IUCN/SSC <strong>Tapir</strong> <strong>Specialist</strong> <strong>Group</strong> (TSG).<br />
Species Male (kg) Female (kg)<br />
<strong>Tapir</strong>us bairdii<br />
<strong>Tapir</strong>us indicus<br />
<strong>Tapir</strong>us pinchaque<br />
<strong>Tapir</strong>us terrestris<br />
180-270<br />
295-385<br />
136-227<br />
160-250<br />
227-340<br />
340-430<br />
160-250<br />
180-295<br />
<strong>Tapir</strong>s have pharyngeal guttural pouches similar to that of the domestic horse, but no important<br />
affections of these structures have been reported. The parietal and visceral pleura are normally<br />
thick and prominent, but only Malayan tapirs have anatomic fibrous connective tissue between<br />
the lung and chest wall that might be mistaken for pathological adhesions. The jugular vein is<br />
found deeply in the laterals of the trachea.<br />
The dental formula of adult tapirs is 2x (I-3/3, C-1/1, PM-4/3, M-3/3) for a total of 42 teeth.<br />
Males and females have similar teething. The upper third incisors are large and well developed,<br />
while the upper canines are reduced and separated from the incisors by a narrow diastema. The<br />
lower third incisors are reduced and the lower canine is well developed, occluding with the<br />
canine-like upper third incisors. There is also a large diastema between canines and premolars in<br />
both jaws.