Sewerage - Nagar Nigam Raipur
Sewerage - Nagar Nigam Raipur
Sewerage - Nagar Nigam Raipur
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Project Management Consultancy Services for <strong>Sewerage</strong>, Storm, Surface Water Drains and Lake<br />
Protection Works For <strong>Raipur</strong> City<br />
Detailed Design Report - <strong>Sewerage</strong><br />
Chapter 9: Design of Sewage Treatment Plant<br />
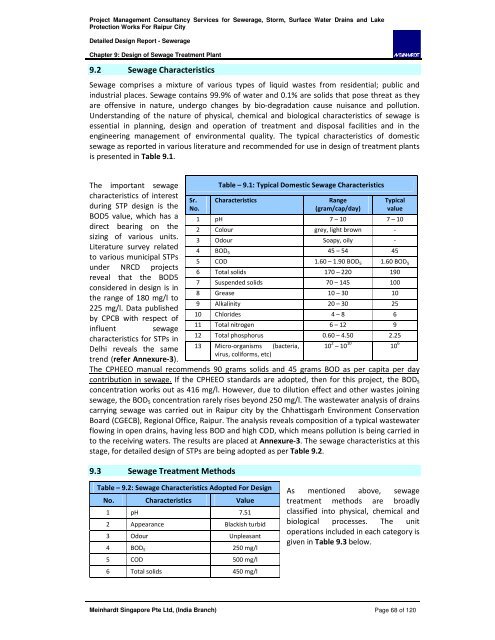
9.2 Sewage Characteristics<br />
Sewage comprises a mixture of various types of liquid wastes from residential; public and<br />
industrial places. Sewage contains 99.9% of water and 0.1% are solids that pose threat as they<br />
are offensive in nature, undergo changes by bio-degradation cause nuisance and pollution.<br />
Understanding of the nature of physical, chemical and biological characteristics of sewage is<br />
essential in planning, design and operation of treatment and disposal facilities and in the<br />
engineering management of environmental quality. The typical characteristics of domestic<br />
sewage as reported in various literature and recommended for use in design of treatment plants<br />
is presented in Table 9.1.<br />
The important sewage<br />
characteristics of interest<br />
during STP design is the<br />
BOD5 value, which has a<br />
direct bearing on the<br />
sizing of various units.<br />
Literature survey related<br />
to various municipal STPs<br />
under NRCD projects<br />
reveal that the BOD5<br />
considered in design is in<br />
the range of 180 mg/l to<br />
225 mg/l. Data published<br />
by CPCB with respect of<br />
influent sewage<br />
characteristics for STPs in<br />
Delhi reveals the same<br />
trend (refer Annexure-3).<br />
Sr.<br />
No.<br />
The CPHEEO manual recommends 90 grams solids and 45 grams BOD as per capita per day<br />
contribution in sewage. If the CPHEEO standards are adopted, then for this project, the BOD5<br />
concentration works out as 416 mg/l. However, due to dilution effect and other wastes joining<br />
sewage, the BOD5 concentration rarely rises beyond 250 mg/l. The wastewater analysis of drains<br />
carrying sewage was carried out in <strong>Raipur</strong> city by the Chhattisgarh Environment Conservation<br />
Board (CGECB), Regional Office, <strong>Raipur</strong>. The analysis reveals composition of a typical wastewater<br />
flowing in open drains, having less BOD and high COD, which means pollution is being carried in<br />
to the receiving waters. The results are placed at Annexure-3. The sewage characteristics at this<br />
stage, for detailed design of STPs are being adopted as per Table 9.2.<br />
9.3 Sewage Treatment Methods<br />
Table – 9.2: Sewage Characteristics Adopted For Design<br />
No. Characteristics Value<br />
1 pH 7.51<br />
2 Appearance Blackish turbid<br />
3 Odour Unpleasant<br />
4 BOD 5 250 mg/l<br />
5 COD 500 mg/l<br />
6 Total solids 450 mg/l<br />
Table – 9.1: Typical Domestic Sewage Characteristics<br />
Characteristics Range<br />
(gram/cap/day)<br />
Typical<br />
value<br />
1 pH 7 – 10 7 – 10<br />
2 Colour grey, light brown -<br />
3 Odour Soapy, oily -<br />
4 BOD 5 45 – 54 45<br />
5 COD 1.60 – 1.90 BOD 5 1.60 BOD 5<br />
6 Total solids 170 – 220 190<br />
7 Suspended solids 70 – 145 100<br />
8 Grease 10 – 30 10<br />
9 Alkalinity 20 – 30 25<br />
10 Chlorides 4 – 8 6<br />
11 Total nitrogen 6 – 12 9<br />
12 Total phosphorus 0.60 – 4.50 2.25<br />
13 Micro-organisms (bacteria, 10<br />
virus, coliforms, etc)<br />
2 – 10 10 10 6<br />
As mentioned above, sewage<br />
treatment methods are broadly<br />
classified into physical, chemical and<br />
biological processes. The unit<br />
operations included in each category is<br />
given in Table 9.3 below.<br />
Meinhardt Singapore Pte Ltd, (India Branch) Page 68 of 120