The Role of Cell-Free Rabbit Reticulocyte Expression ... - Promega
The Role of Cell-Free Rabbit Reticulocyte Expression ... - Promega
The Role of Cell-Free Rabbit Reticulocyte Expression ... - Promega
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Role</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Cell</strong>-<strong>Free</strong> <strong>Rabbit</strong> <strong>Reticulocyte</strong> <strong>Expression</strong> Systems in Functional Proteomics<br />
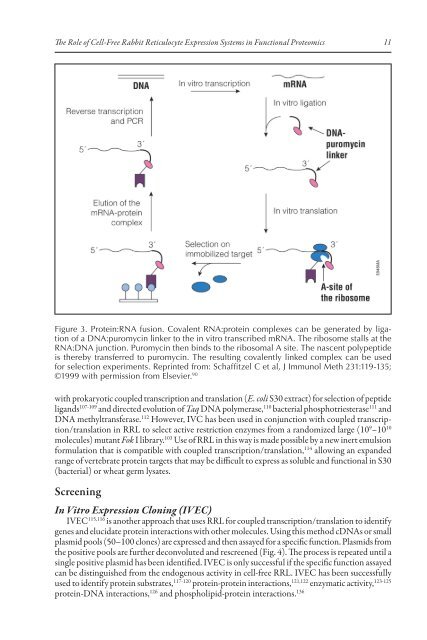
Figure 3. �rotein:�NA fusion. Co���ent �NA:protein �o�p�exes ��n �e gener�ted �y �ig�tion<br />
<strong>of</strong> � �NA:puro�y�in �inker to the in �itro tr�ns�ri�ed ��NA. <strong>The</strong> ri�oso�e st���s �t the<br />
�NA:�NA jun�tion. �uro�y�in then �inds to the ri�oso��� A site. <strong>The</strong> n�s�ent po�ypeptide<br />
is there�y tr�nsferred to puro�y�in. <strong>The</strong> resu�ting �o���ent�y �inked �o�p�ex ��n �e used<br />
for se�e�tion experi�ents. �eprinted fro�: S�h�ffitze� C et ���� J I��uno� Meth 231:119-135;<br />
©1999 with per�ission fro� ��se�ier. 90<br />
with prokaryotic coupled transcription and translation (E. coli S30 extract) for selection <strong>of</strong> peptide<br />
ligands 107‑109 and directed evolution <strong>of</strong> Taq DNA polymerase, 110 bacterial phosphotriesterase 111 and<br />
DNA methyltransferase. 112 However, IVC has been used in conjunction with coupled transcrip‑<br />
tion/translation in RRL to select active restriction enzymes from a randomized large (10 9 –10 10<br />
molecules) mutant Fok I library. 103 Use <strong>of</strong> RRL in this way is made possible by a new inert emulsion<br />
formulation that is compatible with coupled transcription/translation, 114 allowing an expanded<br />
range <strong>of</strong> vertebrate protein targets that may be difficult to express as soluble and functional in S30<br />
(bacterial) or wheat germ lysates.<br />
Screening<br />
In Vitro <strong>Expression</strong> Cloning (IVEC)<br />
IVEC 115,116 is another approach that uses RRL for coupled transcription/translation to identify<br />
genes and elucidate protein interactions with other molecules. Using this method cDNAs or small<br />
plasmid pools (50–100 clones) are expressed and then assayed for a specific function. Plasmids from<br />
the positive pools are further deconvoluted and rescreened (Fig. 4). <strong>The</strong> process is repeated until a<br />
single positive plasmid has been identified. IVEC is only successful if the specific function assayed<br />
can be distinguished from the endogenous activity in cell‑free RRL. IVEC has been successfully<br />
used to identify protein substrates, 117‑120 protein‑protein interactions, 121,122 enzymatic activity, 123‑125<br />
protein‑DNA interactions, 126 and phospholipid‑protein interactions. 136<br />
11