- Page 3: Broadband Strategies Handbook
- Page 6 and 7: © 2012 International Bank for Reco
- Page 8 and 9: Access to Infrastructure 111 Openin
- Page 10 and 11: 4.5 Regional Communications Infrast
- Page 12 and 13: 7.1 Global Broadband Subscriptions
- Page 15 and 16: FOREWORD The world is shifting from
- Page 17 and 18: ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This report was pro
- Page 19 and 20: ABOUT THE AUTHORS This report was p
- Page 21 and 22: CCK Communications Commission of Ke
- Page 23 and 24: IMT-2000 International Mobile Telec
- Page 25 and 26: SIDA Swedish International Developm
- Page 27 and 28: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Broadband Str
- Page 29: esources to support private supply
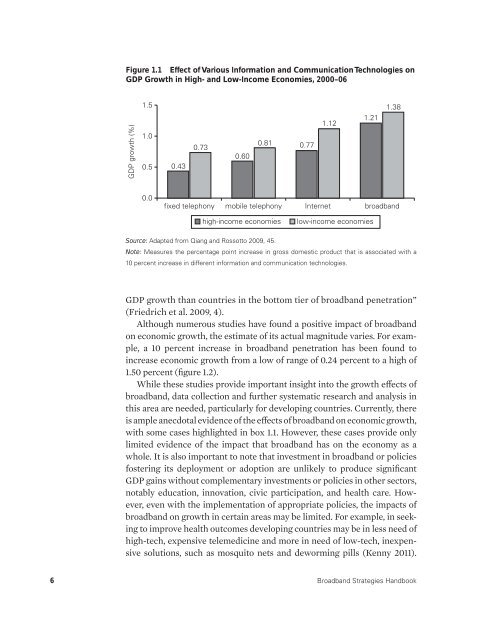
- Page 32 and 33: health, transportation, energy, and
- Page 34 and 35: users, so the speeds advertised by
- Page 38 and 39: Box 1.1 continued they did not have
- Page 40 and 41: on the employment creation rate. Fo
- Page 42 and 43: As broadband’s potential as a GPT
- Page 44 and 45: isks associated with cloud computin
- Page 46 and 47: individuals generally have a better
- Page 48 and 49: Table 1.2 Upstream and Downstream S
- Page 50 and 51: Figure 1.3 Global Fixed and Mobile
- Page 52 and 53: Figure 1.4 Average Broadband Speed
- Page 54 and 55: substantial benefi ts. The use of b
- Page 56 and 57: such, the many demand-side componen
- Page 58 and 59: Figure 1.6 Examples of the Elements
- Page 60 and 61: The Role of Governments in Broadban
- Page 62 and 63: state_of_internet_q32010.pdf?curl=/
- Page 64 and 65: Katz, Raúl. 2009. “Estimating Br
- Page 66 and 67: 1 (May): 7-18. http://www.springerl
- Page 68 and 69: of term contract), a pay-as-you-go
- Page 70 and 71: Supply: Reaching Unserved and Under
- Page 72 and 73: cost to be a larger issue. Therefor
- Page 74 and 75: (which will also increase private s
- Page 76 and 77: Table 2.1 Publicly Stated Policy Go
- Page 78 and 79: over other countries. For example,
- Page 80 and 81: secretary housed within the Ministr
- Page 82 and 83: once networks are available. For th
- Page 84 and 85: ollout through regulatory measures
- Page 86 and 87:
potential. The same can happen if a
- Page 88 and 89:
(and the associated civil works cos
- Page 90 and 91:
Table 2.3 Checklist of Policies to
- Page 92 and 93:
and medium enterprises (SMEs). Eff
- Page 94 and 95:
policies that support and encourage
- Page 96 and 97:
and e-education projects relying on
- Page 98 and 99:
The principles for estimating econo
- Page 100 and 101:
Box 2.4: Expe rience in the Europea
- Page 102 and 103:
essential to the fi nancial sustain
- Page 104 and 105:
Box 2.5: Munic ipal Broadband Initi
- Page 106 and 107:
Measurem ent, Monitoring, and Evalu
- Page 108 and 109:
uptake or adoption of wireline and
- Page 110 and 111:
Figure 2.6 Wireline Broadband (ADSL
- Page 112 and 113:
Competitive broadband markets typic
- Page 114 and 115:
Table 2.7 Sources of Offi cial Broa
- Page 116 and 117:
International Mauritania Telecom, O
- Page 118 and 119:
EUROSTAT (Statistical Offi ce of th
- Page 121 and 122:
CHAPTER 3 Law and Regulation for a
- Page 123 and 124:
the principles of technology and se
- Page 125 and 126:
Figure 3.1 General Elements of a Un
- Page 127 and 128:
Spectrum Licensing Regimes The proc
- Page 129 and 130:
and (b) spectrum blocks are confi g
- Page 131 and 132:
investment and the technological up
- Page 133 and 134:
signifi cant strain on available re
- Page 135 and 136:
Box 3.1: Summa ry of the Digital Te
- Page 137 and 138:
exclusive rights for the provision
- Page 139 and 140:
single entity has the ability to co
- Page 141 and 142:
data services become increasingly d
- Page 143 and 144:
landing in Nigeria, the NCC recentl
- Page 145 and 146:
implemented or proposed in countrie
- Page 147 and 148:
works). However, in developing coun
- Page 149 and 150:
fl exible use of spectrum, such com
- Page 151 and 152:
of ICT infrastructure, reducing dup
- Page 153 and 154:
working for both divisions) and the
- Page 155 and 156:
during congested periods. Another i
- Page 157 and 158:
and according to a set of standards
- Page 159 and 160:
Similarly, in France net neutrality
- Page 161 and 162:
developing those standards. General
- Page 163 and 164:
authorities, while others like the
- Page 165 and 166:
personal data. Also, due to the cro
- Page 167 and 168:
individuals to know when their data
- Page 169 and 170:
Freedom of Opinion and Expression O
- Page 171 and 172:
commercial vendors have developed p
- Page 173 and 174:
An alternative solution involves co
- Page 175 and 176:
19. Independent Communications Auth
- Page 177 and 178:
Covenant on Civil and Political Rig
- Page 179 and 180:
———. 2009b. “Main Elements
- Page 181 and 182:
GSA (Global Mobile Suppliers Associ
- Page 183 and 184:
Protecting Privacy.” OECD, Paris.
- Page 185 and 186:
CHAPTER 4 Extending Universal Broad
- Page 187 and 188:
and services throughout the populat
- Page 189 and 190:
In Denmark, Canada, and Ireland, go
- Page 191 and 192:
Box 4.1: Rural Broadband Connectivi
- Page 193 and 194:
Society Universal Access Policy. Th
- Page 195 and 196:
• Finland. The government’s app
- Page 197 and 198:
Box 4.3 continued lower-than-expect
- Page 199 and 200:
defi nitions. 14 The following are
- Page 201 and 202:
population, specifi cally because o
- Page 203 and 204:
ural pay phones. Since then, it has
- Page 205 and 206:
Table 4.3 Competition among Firms f
- Page 207 and 208:
simple, transparent, expeditious, a
- Page 209 and 210:
governments, and other federal and
- Page 211 and 212:
Finance Corporation, have also foun
- Page 213 and 214:
support widespread deployment of pu
- Page 215 and 216:
for improving, streamlining, or rea
- Page 217 and 218:
a manual or handbook for recipients
- Page 219 and 220:
Notes 1. An alternative interpretat
- Page 221 and 222:
23. Some categories of providers mi
- Page 223 and 224:
León, Laura. 2009. “Informe de a
- Page 225 and 226:
CHAPTER 5 Technologies to Support D
- Page 227 and 228:
The Broadband Supply Chain The broa
- Page 229 and 230:
Figure 5.2 Design of IP Next-Genera
- Page 231 and 232:
Basic Technologies for Broadband Co
- Page 233 and 234:
From a geosynchronous vantage point
- Page 235 and 236:
media, but it can often suffi ce fo
- Page 237 and 238:
(that is, where the cable makes lan
- Page 239 and 240:
F igure 5.4 Internet Protocol Packe
- Page 241 and 242:
Box 5.1: Connecting the Maldives to
- Page 243 and 244:
agreements. In many developed count
- Page 245 and 246:
Figure 5.6 Internet Exchange Point
- Page 247 and 248:
The average cost of a backbone netw
- Page 249 and 250:
portion of the broadband supply cha
- Page 251 and 252:
oadband widely with the reality tha
- Page 253 and 254:
and data streams and to route data
- Page 255 and 256:
Figure 5.10 Cable Modem Connection
- Page 257 and 258:
Figure 5.11 Diagram of Various FTTx
- Page 259 and 260:
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multi
- Page 261 and 262:
Figure 5.12 Frequenc y Bands Used b
- Page 263 and 264:
family of standards. Despite the go
- Page 265 and 266:
Box 5.3: Three 3G Technolog ies in
- Page 267 and 268:
Wi-Fi Wi-Fi refers to the IEEE 802.
- Page 269 and 270:
• Line sharing. The copper local
- Page 271 and 272:
spectrum that can be made available
- Page 273 and 274:
30. According to the GSMA, “GPRS
- Page 275 and 276:
———. 2010. “Annual Report 2
- Page 277 and 278:
CHAPTER 6 Driving Demand for Broadb
- Page 279 and 280:
Figure 6.1 The Three Pillars of Fac
- Page 281 and 282:
Figure 6.3 How People Obtain ICT Tr
- Page 283 and 284:
Box 6.1: Sri Lanka’s Approach to
- Page 285 and 286:
Table 6.1 Exa mples of Funding for
- Page 287 and 288:
Internet access centers in various
- Page 289 and 290:
To help SMEs to use broadband netwo
- Page 291 and 292:
• Establishing locations for shar
- Page 293 and 294:
Figure 6.4 Cost of Us er Devices Re
- Page 295 and 296:
A business model that has contribut
- Page 297 and 298:
e used between midnight and 5 a.m.
- Page 299 and 300:
the basis of household surveys cond
- Page 301 and 302:
overall broadband experience (see t
- Page 303 and 304:
Table 6.2 Subscriptions to Bu ndled
- Page 305 and 306:
that since 2005 many countries have
- Page 307 and 308:
In addition, a greater range of ser
- Page 309 and 310:
services as a result. As applicatio
- Page 311 and 312:
ising to 40 Mbit/s (Indosat 2010).
- Page 313 and 314:
such as Flat World Knowledge’s op
- Page 315 and 316:
Figure 6.6 Number of Internet Users
- Page 317 and 318:
8. ITU, “Connect a School, Connec
- Page 319 and 320:
Press_Releases/2010/8/Indonesia_Bra
- Page 321 and 322:
Hernandez, Janet, Daniel Leza, and
- Page 323:
Stats).” Institute for Statistics
- Page 326 and 327:
Figure 7.1 Global Broadband Subscri
- Page 328 and 329:
Box 7.2: The 10 WSIS Targets Connec
- Page 330 and 331:
deploy any wireline infrastructure.
- Page 332 and 333:
Figure 7.4 Broadband and Human Deve
- Page 334 and 335:
Box 7.3 continued “It is not an e
- Page 336 and 337:
Malaysia’s 2006 Information, Comm
- Page 338 and 339:
2009). Results of the study were is
- Page 340 and 341:
For the countries of Latin America
- Page 342 and 343:
wireline telephone network (measure
- Page 344 and 345:
able to deploy local access broadba
- Page 346 and 347:
development due to a wide range of
- Page 348 and 349:
In Afghanistan, for example, years
- Page 350 and 351:
320 Table 7.2 Examples of Policies
- Page 352 and 353:
networking services. At the other e
- Page 354 and 355:
Morocco Mor occo is a lower-middle-
- Page 356 and 357:
The deployment of a second submarin
- Page 358 and 359:
E-government initiatives have been
- Page 360 and 361:
variety of technologies, aff ecting
- Page 362 and 363:
Cagatay, Telli. 2011. “Broadband
- Page 364 and 365:
Telkom Indonesia. 2010. “Info Mem
- Page 366 and 367:
Country Title of the plan Weblink S
- Page 368 and 369:
Table B.1 Infrastructure Policies a
- Page 370 and 371:
Table B.1 (continued) 340 Supply an
- Page 372 and 373:
Table B.2 Services Policies and Pro
- Page 374 and 375:
Table B.3 Applications and Content
- Page 376 and 377:
346 Table B.4 Policies and Procedur
- Page 378 and 379:
References Aphiphunya, Prasert. 201
- Page 380 and 381:
Anatel, Brazil, 167-68 ANSI-95, 230
- Page 382 and 383:
Chile, 19, 141 bidding for subsidie
- Page 384 and 385:
data caps, 267, 270-71 data control
- Page 386 and 387:
economies of scale, 121 ecosystem m
- Page 388 and 389:
freedom of opinion and expression,
- Page 390 and 391:
individual users, and access to bro
- Page 392 and 393:
Kenya Power and Lighting Company Li
- Page 394 and 395:
mobile operators and backbone servi
- Page 396 and 397:
policies and policy making (continu
- Page 398 and 399:
service contracts, 265-66, 287n20 s
- Page 400 and 401:
supply-side components (continued)
- Page 402 and 403:
universal mobile service, 317 Unive
- Page 404:
ECO-AUDIT Environmental Benefits St