Bioinformatics Biocomputing - Ercim
Bioinformatics Biocomputing - Ercim
Bioinformatics Biocomputing - Ercim
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
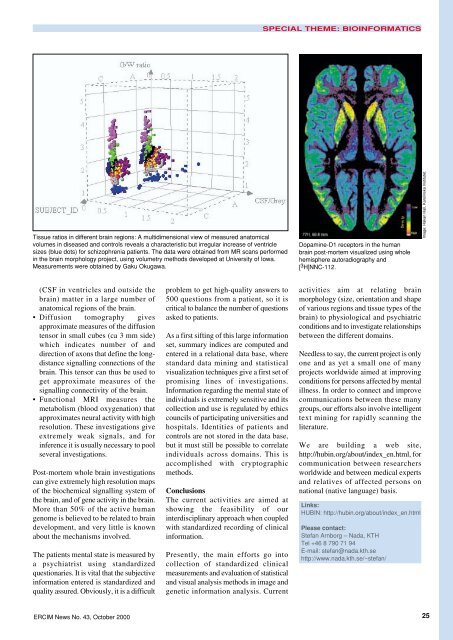
Tissue ratios in different brain regions: A multidimensional view of measured anatomical<br />
volumes in diseased and controls reveals a characteristic but irregular increase of ventricle<br />
sizes (blue dots) for schizophrenia patients. The data were obtained from MR scans performed<br />
in the brain morphology project, using volumetry methods developed at University of Iowa.<br />
Measurements were obtained by Gaku Okugawa.<br />
(CSF in ventricles and outside the<br />
brain) matter in a large number of<br />
anatomical regions of the brain.<br />
• Diffusion tomography gives<br />
approximate measures of the diffusion<br />
tensor in small cubes (ca 3 mm side)<br />
which indicates number of and<br />
direction of axons that define the longdistance<br />
signalling connections of the<br />
brain. This tensor can thus be used to<br />
get approximate measures of the<br />
signalling connectivity of the brain.<br />
• Functional MRI measures the<br />
metabolism (blood oxygenation) that<br />
approximates neural activity with high<br />
resolution. These investigations give<br />
extremely weak signals, and for<br />
inference it is usually necessary to pool<br />
several investigations.<br />
Post-mortem whole brain investigations<br />
can give extremely high resolution maps<br />
of the biochemical signalling system of<br />
the brain, and of gene activity in the brain.<br />
More than 50% of the active human<br />
genome is believed to be related to brain<br />
development, and very little is known<br />
about the mechanisms involved.<br />
The patients mental state is measured by<br />
a psychiatrist using standardized<br />
questionaries. It is vital that the subjective<br />
information entered is standardized and<br />
quality assured. Obviously, it is a difficult<br />
ERCIM News No. 43, October 2000<br />
problem to get high-quality answers to<br />
500 questions from a patient, so it is<br />
critical to balance the number of questions<br />
asked to patients.<br />
As a first sifting of this large information<br />
set, summary indices are computed and<br />
entered in a relational data base, where<br />
standard data mining and statistical<br />
visualization techniques give a first set of<br />
promising lines of investigations.<br />
Information regarding the mental state of<br />
individuals is extremely sensitive and its<br />
collection and use is regulated by ethics<br />
councils of participating universities and<br />
hospitals. Identities of patients and<br />
controls are not stored in the data base,<br />
but it must still be possible to correlate<br />
individuals across domains. This is<br />
accomplished with cryptographic<br />
methods.<br />
Conclusions<br />
The current activities are aimed at<br />
showing the feasibility of our<br />
interdisciplinary approach when coupled<br />
with standardized recording of clinical<br />
information.<br />
Presently, the main efforts go into<br />
collection of standardized clinical<br />
measurements and evaluation of statistical<br />
and visual analysis methods in image and<br />
genetic information analysis. Current<br />
SPECIAL THEME: BIOINFORMATICS<br />
Dopamine-D1 receptors in the human<br />
brain post-mortem visualized using whole<br />
hemisphere autoradiography and<br />
[ 3 H]NNC-112.<br />
activities aim at relating brain<br />
morphology (size, orientation and shape<br />
of various regions and tissue types of the<br />
brain) to physiological and psychiatric<br />
conditions and to investigate relationships<br />
between the different domains.<br />
Needless to say, the current project is only<br />
one and as yet a small one of many<br />
projects worldwide aimed at improving<br />
conditions for persons affected by mental<br />
illness. In order to connect and improve<br />
communications between these many<br />
groups, our efforts also involve intelligent<br />
text mining for rapidly scanning the<br />
literature.<br />
We are building a web site,<br />
http://hubin.org/about/index_en.html, for<br />
communication between researchers<br />
worldwide and between medical experts<br />
and relatives of affected persons on<br />
national (native language) basis.<br />
Links:<br />
HUBIN: http://hubin.org/about/index_en.html<br />
Please contact:<br />
Stefan Arnborg – Nada, KTH<br />
Tel +46 8 790 71 94<br />
E-mail: stefan@nada.kth.se<br />
http://www.nada.kth.se/~stefan/<br />
Image: Håkan Hall, Karolinska Institutet.<br />
25