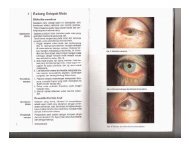
Clinical Pathways in Neuro-ophthalmology : An ... - E-Lib FK UWKS
Clinical Pathways in Neuro-ophthalmology : An ... - E-Lib FK UWKS
Clinical Pathways in Neuro-ophthalmology : An ... - E-Lib FK UWKS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
112 <strong>Cl<strong>in</strong>ical</strong> <strong>Pathways</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Neuro</strong>-Ophthalmology, second edition<br />
Cullen JF. (1967). Occult temporal arteritis. A common cause of bl<strong>in</strong>dness <strong>in</strong> old age. Br J Ophthalmol 51:513–525.<br />
Cullen JF, Coleiro JA. (1976). Ophthalmic complications of giant cell arteritis. Surv Ophthalmol 20:247–260.<br />
Currey J. (1997). Scalp necrosis <strong>in</strong> giant cell arteritis and review of the literature. Br J Rheumatol 36:814–816.<br />
Danesh-Meyer HV, Sav<strong>in</strong>o PJ, Eagle RC Jr, et al. (2000). Low diagnostic yield with second biopsies <strong>in</strong> suspected<br />
giant cell arteritis. J <strong>Neuro</strong>-ophthalmol 20:213–215.<br />
Danesh-Meyer HV, Sav<strong>in</strong>o PJ, Sergott RC. (2001). The prevalence of cupp<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> end-stage arteritic and nonarteritic<br />
anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 108:593–598.<br />
de Heide LJ, Talsma MA. (1999). Giant-cell arteritis present<strong>in</strong>g as an orbital pseudotumor. Neth J Med 55:196–198.<br />
Delecoeullerie G, Joly P, DeLara AC, et al. (1988). Polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritis: a retrospective<br />
analysis of prognostic features and different corticosteroid regimens (11 year survey of 210 patients). <strong>An</strong>n<br />
Rheum Dis 47:733–739.<br />
Dennis RH II, Ransome JR. (1996). Giant cell arteritis present<strong>in</strong>g as a carpal tunnel syndrome. J Natl Med Assoc<br />
88:524–525.<br />
DeSilva M, Hazleman BL. (1986). Azathiopr<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> giant cell arteritis=polymyalgia rheumatica: a double-bl<strong>in</strong>d<br />
study. <strong>An</strong>n Rheum Dis 45:136–138.<br />
Desmet GD, Knockaert DC, Bobbaers HJ. (1990). Temporal arteritis: the silent presentation and delay <strong>in</strong> diagnosis.<br />
J Intern Med 227:237–240.<br />
Desmond J, Hussa<strong>in</strong> ST, Col<strong>in</strong> JF. (1999). Giant cell arteritis as a cause of <strong>in</strong>termittent claudications. Hosp Med<br />
60:302.<br />
de Vita S, Tavoni A, Jeracitano G, Gemignani G, Dolcher MP, Bombardieri S. (1992). Treatment of giant cell<br />
arteritis with cyclophosphamide pulses (letter). J Intern Med 232:373–375.<br />
Diamond JP. (1991). Treatable bl<strong>in</strong>dness <strong>in</strong> temporal arteritis. Br J Ophthalmol 75:432.<br />
Diamond JP. (1993). IV steroid treatment <strong>in</strong> giant cell arteritis (letter). Ophthalmology 100:291–292.<br />
DiBartolomeo AG, Brick JE. (1992). Giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Postgrad Med 91:107–109.<br />
Dick AD, Millar A, Johnson N. (1991). Bra<strong>in</strong>stem vascular accidents and cranial arteritis. Scott Med J 36:85.<br />
Diego M, Margo CE. (1998). Postural vision loss <strong>in</strong> giant cell arteritis. J <strong>Neuro</strong>-ophthalmol 18:124–126.<br />
Egge K, Midtbo A, Westby R. (1996). Arteritis temporalis. Acta Ophthalmol 44:49–56.<br />
Eggenberger E. (1998). Eight-and-a-half syndrome: one-and-a-half syndrome plus cranial nerve VII palsy.<br />
J <strong>Neuro</strong>ophthalmol 18:114–116.<br />
Ellis JD, Munro P, McGettrick P. (1994). Bl<strong>in</strong>dness with a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate <strong>in</strong> giant cell<br />
arteritis. Br J Hosp Med 52:358–359.<br />
Evans JM, Batts KP, Hunder GG. (1994). Persistent giant cell arteritis despite corticosteroid treatment. Mayo Cl<strong>in</strong><br />
Proc 69:1060–1061.<br />
Evans JM, O’Fallon WM, Hunder GG. (1995). Increased <strong>in</strong>cidence of aortic aneurysm and dissection <strong>in</strong> giant cell<br />
(temporal) arteritis. A population-based study. <strong>An</strong>n Intern Med 122:502–507.<br />
Evans JM, Vukov LF, Hunder GG. (1993). Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis <strong>in</strong> emergency<br />
department patients. <strong>An</strong>n Emerg Med 22:1633–1635.<br />
Fernandez-Herlihy L. (1988). Temporal arteritis: cl<strong>in</strong>ical aids to diagnosis. J Rheumatol 15:1797.<br />
Fife A, Dorrell L, Snow MH, Ong EL. (1994). Giant cell arteritis—a cause of pyrexia of unknown orig<strong>in</strong>. Scott Med J<br />
39:114–115.<br />
F<strong>in</strong>elli PF. (1997). Alternat<strong>in</strong>g amaurosis fugax and temporal arteritis. Am J Ophthalmol 123:850–851.<br />
F<strong>in</strong>eman MS, Sav<strong>in</strong>o PJ, Federman JL, Eagle RC, Jr. (1996). Branch ret<strong>in</strong>al artery occlusion as the <strong>in</strong>itial sign of<br />
giant cell arteritis. Am J Ophthalmol 122:428–430.<br />
Freddo T, Price M, Kase C, Goldste<strong>in</strong> MP. (1999). Myocardial <strong>in</strong>farction and coronary artery <strong>in</strong>volvement <strong>in</strong> giant<br />
cell arteritis. Optom Vis Sci 76:14–18.<br />
Gabriel S, Espy M, Erdman DD, et al. (1999). The role of parvovirus B19 <strong>in</strong> the pathogenesis of giant cell arteritis.<br />
A prelim<strong>in</strong>ary evaluation. Arthritis Rheum 42:1255–1258.<br />
Gabriel SE, O’Fallon WM, Achkar AA, Lie JT, Hunder GG. (1995). The use of cl<strong>in</strong>ical characteristics to predict the<br />
results of temporal artery biopsy among patients with suspected giant cell arteritis. J Rheumatol 22:93–96.<br />
Galetta SL, Balcer LJ, Lieberman AP, et al. (1997a). Refractory giant cell arteritis with sp<strong>in</strong>al cord <strong>in</strong>farction.<br />
<strong>Neuro</strong>logy 49:1720–1723.<br />
Galetta SL, Balcer LJ, Liu GT. (1997b). Giant cell arteritis with unusual flow-related neuro-ophthalmologic<br />
manifestations. <strong>Neuro</strong>logy 49:1463–1465.<br />
Galetta SL, Raps EC, Wulc AE, et al. (1990). Conjugal temporal arteritis. <strong>Neuro</strong>logy 40:1839–1842.<br />
Garcia Vazquez JM, Carreira JM, Seoane C, Vidal JJ. (1999). Superior and <strong>in</strong>ferior limb ischemia <strong>in</strong> giant cell<br />
arteritis: angiography follow-up. Cl<strong>in</strong> Rheumatol 18:61–65.<br />
Gaynes BI. (1994). Occult giant cell arteritis: a diagnosis of suspicion. J Am Optom Assoc 65:564–571.









![SISTEM SENSORY [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/20667975/1/190x245/sistem-sensory-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)