courses in english
courses in english
courses in english
- TAGS
- courses
- english
- www.inf.upv.es
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ul. Mikołajczyka 5<br />
45-271 Opole, Poland<br />
Tel: +48 77 400 6153<br />
Fax.: +48 77 400 6349<br />
e-mail: iro@po.opole.pl<br />
ERASMUS Code: PL OPOLE02<br />
October 2010<br />
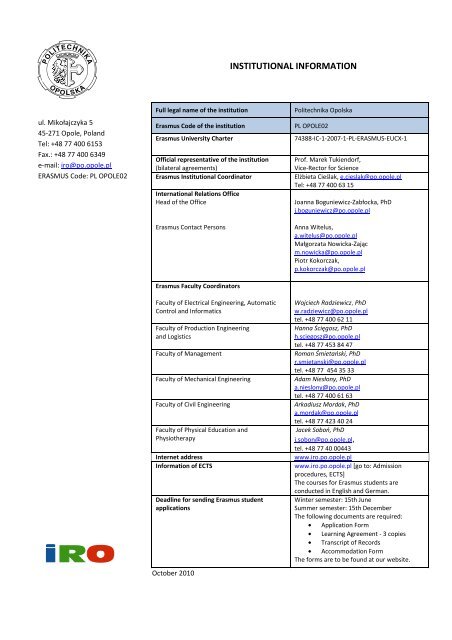
INSTITUTIONAL INFORMATION<br />
Full legal name of the <strong>in</strong>stitution Politechnika Opolska<br />
Erasmus Code of the <strong>in</strong>stitution PL OPOLE02<br />
Erasmus University Charter 74388-IC-1-2007-1-PL-ERASMUS-EUCX-1<br />
Official representative of the <strong>in</strong>stitution Prof. Marek Tukiendorf,<br />
(bilateral agreements)<br />
Vice-Rector for Science<br />
Erasmus Institutional Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Elżbieta Cieślak, e.cieslak@po.opole.pl<br />
Tel: +48 77 400 63 15<br />
International Relations Office<br />
Head of the Office<br />
Erasmus Contact Persons<br />
Erasmus Faculty Coord<strong>in</strong>ators<br />
Faculty of Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Automatic<br />
Control and Informatics<br />
Faculty of Production Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and Logistics<br />
Joanna Boguniewicz-Zabłocka, PhD<br />
j.boguniewicz@po.opole.pl<br />
Anna Witelus,<br />
a.witelus@po.opole.pl<br />
Małgorzata Nowicka-Zając<br />
m.nowicka@po.opole.pl<br />
Piotr Kokorczak,<br />
p.kokorczak@po.opole.pl<br />
Wojciech Radziewicz, PhD<br />
w.radziewicz@po.opole.pl<br />
tel. +48 77 400 62 11<br />
Hanna Ścięgosz, PhD<br />
h.sciegosz@po.opole.pl<br />
tel. +48 77 453 84 47<br />
Faculty of Management Roman Śmietański, PhD<br />
r.smietanski@po.opole.pl<br />
tel. +48 77 454 35 33<br />
Faculty of Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Adam Niesłony, PhD<br />
a.nieslony@po.opole.pl<br />
tel. +48 77 400 61 63<br />
Faculty of Civil Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Arkadiusz Mordak, PhD<br />
a.mordak@po.opole.pl<br />
tel. +48 77 423 40 24<br />
Faculty of Physical Education and<br />
Physiotherapy<br />
Jacek Soboń, PhD<br />
j.sobon@po.opole.pl,<br />
tel. +48 77 40 00443<br />
Internet address www.iro.po.opole.pl<br />
Information of ECTS www.iro.po.opole.pl [go to: Admission<br />
procedures, ECTS]<br />
The <strong>courses</strong> for Erasmus students are<br />
conducted <strong>in</strong> English and German.<br />
Deadl<strong>in</strong>e for send<strong>in</strong>g Erasmus student<br />
applications<br />
W<strong>in</strong>ter semester: 15th June<br />
Summer semester: 15th December<br />
The follow<strong>in</strong>g documents are required:<br />
• Application Form<br />
• Learn<strong>in</strong>g Agreement - 3 copies<br />
• Transcript of Records<br />
• Accommodation Form<br />
The forms are to be found at our website.
FACULTY OF CIVIL ENGINEERING<br />
48 Katowicka Street, 45-061 Opole, Poland<br />
phone (+48 77) 456 50 85 - 7, tel./fax (+48 77) 456 50 84<br />
e-mail: wbud@po.opole.pl, http://: www.wb.po.opole.pl<br />
FIELDS OF STUDY � Build<strong>in</strong>g Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; (BSc, MSc, PhD)<br />
� Architecture and Town Plann<strong>in</strong>g (BSc)<br />
FACULTY DEPARTMENTS � Civil Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Architecture<br />
� Roads and Bridges<br />
� Physics Materials<br />
� Soil and Geodesy<br />
� Build<strong>in</strong>g Materials Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Build<strong>in</strong>g and Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Structures<br />
� Structural Mechanic<br />
Faculty Erasmus Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Arkadiusz Mordak, PhD; a.mordak@po.opole.pl<br />
COURSES IN ENGLISH<br />
Course<br />
code<br />
Course Name<br />
ECTS<br />
credits<br />
B001 Build<strong>in</strong>g Materials 4<br />
B002 Concrete Bridges 6<br />
B003 Concrete Structures 5<br />
B004 Computer Science <strong>in</strong> Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 5<br />
B005 Foundation Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
B006 Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Town Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Architecture 5<br />
B007 Introduction to Seismic Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 5<br />
B008 Soil Mechanics 5<br />
B009 Strength of Materials 6<br />
B010 Structural Mechanics 6<br />
B011 Steel Bridges 5<br />
B012 Environment Protection <strong>in</strong> Transportation Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
B013 Road Communication Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 6<br />
B014 Transport Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 6<br />
B015 Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Survey<strong>in</strong>g 4
1. Course title<br />
Build<strong>in</strong>g Materials<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B001<br />
Lectures, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
I/II<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. Stefania Grzeszczyk, s.grzeszczyk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Chemistry, Physics, English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about build<strong>in</strong>g materials <strong>in</strong> an aspect of civil eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The basic technical properties of build<strong>in</strong>g materials. Natural stone materials and their application <strong>in</strong> the<br />
build<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dustry. M<strong>in</strong>eral pneumatic b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g materials: lime, gypsum. Hydraulic b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g materials: cement.<br />
Build<strong>in</strong>g ceramic wares. Architectural glass. Metals applied <strong>in</strong> the build<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Special materials<br />
used for thermal and acoustic <strong>in</strong>sulation. B<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g agents and bitum<strong>in</strong>ous materials. Plastics and plastic<br />
products used <strong>in</strong> build<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Allen, Iano: Fundamentals of Build<strong>in</strong>g Construction – Materials and Methods, J. Wiley & Sons, 4 th ed., 2003;<br />
b) Simmons, Ol<strong>in</strong>: Construction – Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, Materials and Methods, J. Wiley & Sons, 7 th ed., 2001; Lecture<br />
notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Concrete Bridges<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B002<br />
Lectures, design classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
IV/VII<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Beata Stankiewicz, PhD Eng., b.stankiewicz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
English (the first certificate/ FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about architecture and dimension<strong>in</strong>g of concrete bridges
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Historical outl<strong>in</strong>e. The classification of concrete bridges. Materials used for build<strong>in</strong>g of the bridges. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples<br />
of dimension<strong>in</strong>g of concrete bridges. Typical cross-sections of concrete bridges. Elements of fitt<strong>in</strong>gs for the<br />
bridges. Re<strong>in</strong>forced concrete slab and slab-rib bridges. Bear<strong>in</strong>gs of the bridges. Frame, arch and suspension<br />
bridges. Prestressed concrete bridges. Foundations of the bridges. Modernisation and strengthen<strong>in</strong>g of the<br />
bridges.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded projects<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Concrete Structures<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of classes<br />
B003<br />
Lectures, design and exercise classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
III/V<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of classes<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. Edward Małek, e.malek@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Strength of Materials, Structural Mechanics, Soil Mechanics and Foundation Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, English (the first<br />
certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about dimension<strong>in</strong>g of re<strong>in</strong>forced concrete structures<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of design. The properties of concrete and re<strong>in</strong>forc<strong>in</strong>g steel, Methods and structural design.<br />
Dimension<strong>in</strong>g of the cross-section of a re<strong>in</strong>forced concrete beam for bend<strong>in</strong>g and shear. Limit states<br />
(ultimate and serviceability) of re<strong>in</strong>forced concrete structures.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Oral exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded projects<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Nawy E.G.: Re<strong>in</strong>forced Concrete, 5 th ed. Prentice Hall, 2003; Macgregor J.G.: Re<strong>in</strong>forced Concrete: Mechanics<br />
and Design, Prentice Hall, 1997; Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Computer Science <strong>in</strong> Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
B004<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lectures, design classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
II/IV<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30
Lesław Tarczyński, PhD Eng., l.tarczynski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about application of computer programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program (program nauczania)<br />
Basic concepts of computer science. Formal languages. Algorithms. Forms of record<strong>in</strong>g algorithms. Block<br />
diagrams. The prototype of a high-level programm<strong>in</strong>g language with structural characteristics. Data<br />
structures. Examples of algorithms. Selected numerical algorithms. The structure and general pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of<br />
the operation of computers. Basic software and useware. Cod<strong>in</strong>g, data storage and access <strong>in</strong> computer<br />
systems. Examples of a one-access operat<strong>in</strong>g system (personal computer) and <strong>in</strong>struction <strong>in</strong>terpreter. Basic<br />
functions of a text editor Computer networks. Elements of the Internet. The fundamentals of programm<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong> a high-level language. Compilation of modules and <strong>in</strong>tegration tasks. The accuracy of number<br />
representation and the accuracy of numerical calculations. Programm<strong>in</strong>g of the selected examples of<br />
numerical methods and eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g computations with use of a graphical library.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded homework and exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Numerical Recipes <strong>in</strong> Fortran 77, book on-l<strong>in</strong>e: http:///www.library.cornell.edu/nr/cbookfpdf.html; Larry R.<br />
Nyhoff, Sanford Leestma: Introduction to Fortran 90 for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers and Scientists, Prentice Hall, 1996, ISBN:<br />
0135052157; Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Foundation Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B005<br />
Lectures, design classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
III/V<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Paweł Fedczuk, PhD Eng., p.fedczuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Physics, Mathematics, Geology, Strength of Materials, Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Mechanics, Structural Mechanics, English<br />
(the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about dimension<strong>in</strong>g of typical foundations<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The classification of foundations. Design of foundations. Spot foot<strong>in</strong>gs (k<strong>in</strong>ds and calculations of the load<br />
capacity of homogenous and stratified foundation bed, stability and calculations of settlement,<br />
dimension<strong>in</strong>g). Cont<strong>in</strong>uous foot<strong>in</strong>gs (k<strong>in</strong>ds and calculations of the load capacity of homogenous and<br />
stratified foundation bed, stability and calculations of settlement, dimension<strong>in</strong>g). Grillage foundations.<br />
Foundation plates. Foundation boxes. Strengthen<strong>in</strong>g of the foundation bed. Dra<strong>in</strong>age of the foundation bed<br />
and excavations.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded design exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Braja M.: Pr<strong>in</strong>cipals of Foundation Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Brooks/Cole, Thomson 2004; Atk<strong>in</strong>son J.H.: The Mechanics of<br />
Soils and Foundations, McGraw Hill, Comp. London, New York 1993; Lecture notes
1. Course title<br />
Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Town Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Architecture<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B006<br />
Lectures, exercise classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
I/I<br />
6. Numer of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Monika Adamska, PhD Eng. Arch., mo.adamska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of arts, descriptive eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about architecture and town plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> an aspect of civil eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Concepts and def<strong>in</strong>itions. Contemporary comprehension of architecture objectives tak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to account a<br />
historical po<strong>in</strong>t of view. The orig<strong>in</strong> of contemporary architecture, ancient Greece and Rome. Renaissance<br />
style, Baroque style, Eclecticism, Secession. The orig<strong>in</strong> of contemporary architecture with regard to<br />
structure, Early Christian period style, Gothic style, Romanticism. The outl<strong>in</strong>e of history of architecture seen<br />
through the structural context. Fields of contemporary architectural design. Build<strong>in</strong>g development sets –<br />
public sets, dwell<strong>in</strong>gs, <strong>in</strong>dustry with regard to the land development plan. Contemporary directions <strong>in</strong><br />
architecture, the school of the <strong>in</strong>ternational style, late modernism and postmodernism. Structures of unique<br />
build<strong>in</strong>gs, large span roofs, geometry, high rise build<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, short speech on the chosen subject<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Pevsner, Flem<strong>in</strong>g, Honour: The Pengu<strong>in</strong> Dictionary of Architecture, Middlesex, 1980; Thoesen Ch.:<br />
Architectural theory from the Renaissance to the present, Koln 2003; Vittorio Magnano Lampugnani,<br />
Architecture and City Plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the Twentieth Century, New York 1984; Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Introduction to Seismic Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B007<br />
Lectures, design and exercise classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
III/IV<br />
6. Numer of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. Zbigniew Zembaty, z.zembaty@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Structural Statics & Structural dynamics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Acquir<strong>in</strong>g basic knowledge of seismic effects and their model<strong>in</strong>g when act<strong>in</strong>g on civil eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g structures.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Introductory <strong>in</strong>formation about earthquakes and other seismic effects (rockbursts, traffic vibrations etc).<br />
Repetition of basic <strong>in</strong>formation about structural dynamics. Response spectrum method for s<strong>in</strong>gle degree of
freedom structures. Introductory <strong>in</strong>formation on seismic codes. Response spectrum method for multi degree<br />
of freedom structures. Information on seismic codes with particular attention on Eurocode 8.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam, graded homework and exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Clough, Penzien „Dynamics of Structures”<br />
b) A.K.Chopra „Dynamics of Structures”<br />
1. Course title<br />
Soil Mechanics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B008<br />
Lectures, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
II/IV<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Paweł Fedczuk, PhD Eng., p.fedczuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Physics, Mathematics, Geology, Strength of Materials, Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Mechanics, English (the first<br />
certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about soil properties <strong>in</strong> an aspect of civil eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The three-phase structure of soils. The orig<strong>in</strong> of soils. The classification of soils. The physical properties of<br />
soils. Ground water. The mechanical properties of soils. Stresses <strong>in</strong> the foundation bed. Ground settlement.<br />
The load capacity of the foundation bed.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Atk<strong>in</strong>son J.H., Bransby P.L.: The Mechanics of Soils, McGraw Hill, London, 1978; Atk<strong>in</strong>son J.H.: The Mechanics<br />
of Soils and Foundations, McGraw Hill, Comp. London, New York 1993; Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Strength of Materials<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B009<br />
Lectures, design and exercise classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
II/III<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Zbigniew Perkowski, PhD Eng., z.perkowski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Mechanics, Mathematics, L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra, English (the first certificate/FCE level)
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about methods and concepts of strength of materials used <strong>in</strong> dimension<strong>in</strong>g of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
structures<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the <strong>in</strong>ternal forces <strong>in</strong> the complex rod systems. Fundamentals of solid body mechanics.<br />
Description of stress and stra<strong>in</strong> state <strong>in</strong> a deformable solid. Physical equations of the l<strong>in</strong>ear elasticity. The<br />
simple cases of strength of materials: pure compression and tension, pure shear, bend<strong>in</strong>g and torsion. Basic<br />
calculations of displacements of rod structures.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded homework and exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Hibbeler R.C.: Mechanics of Materials, 4 th ed., Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 2000; Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Structural Mechanics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B010<br />
Lectures, design and exercise classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
II/IV<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. Tadeusz Chmielewski, t.chmielewski@po.opole.pl; Seweryn Kokot, PhD Eng., s.kokot@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Mechanics, Mathematics, L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra, English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about methods and concepts of structural mechanics used <strong>in</strong> calculations of <strong>in</strong>ternal forces<br />
for eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g structures<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Analysis of statically determ<strong>in</strong>ate structures: beams, three-h<strong>in</strong>ged arches and frames, trusses, space<br />
framework and <strong>in</strong>fluence l<strong>in</strong>es for them. Envelopes of <strong>in</strong>ternal forces for moveable and variable loads. The<br />
k<strong>in</strong>ematic analysis of structures. The virtual work pr<strong>in</strong>ciple under the virtual states of displacement and<br />
loads. The analysis of statically <strong>in</strong>determ<strong>in</strong>ate structures by the method of forces: cont<strong>in</strong>uous beams and<br />
their <strong>in</strong>fluence l<strong>in</strong>es, plane frames, arches, trusses, grids.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded homework and exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Meriam J.L. Kraige L.G.: Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g mechanics-statistics, J. Wiley & Sons, 2003; Hibbeler R.C.: Structural<br />
Analysis, 5 th ed., Prentice-Hall, 2002; Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Steel Bridges<br />
2. Course Code<br />
B011<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lectures, design classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
II/IV<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week 9. Number of hours per semester
2 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Przemysław Jakiel, PhD Eng., p.jakiel@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Steel Structures, Strength of Materials, Structural Mechanics, Basis about Bridge Structures, English (the first<br />
certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about rational dimension<strong>in</strong>g and design<strong>in</strong>g of modern steel bridge structures.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program (program nauczania)<br />
Basic knowledge about materials and structures concern<strong>in</strong>g steel bridges. The pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of design road and<br />
railway steel bridges: steel bridge decks, cross-sections, plate, box and composite girders, portal, truss and<br />
arch girders, brac<strong>in</strong>gs, layout of steel suspension and cable-stayed bridges, bear<strong>in</strong>gs, pretension of steel<br />
bridges. Methods and structural design. Limit states design (ultimate and serviceability) of steel bridge<br />
structures.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Oral exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded project.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a. Chatte Sukhen, The Design of Modern Steel Bridges Book. Wiley Blackwell, 2003.<br />
b. Ghosh Utpal K., New Design and Construction of Steel Bridges. Taylor & Francis, 2006.<br />
c. Lecture notes.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environment Protection <strong>in</strong> Transportation Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
B012<br />
4. Type of course<br />
Compulsory<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Damian Beben, PhD Eng. d.beben@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture<br />
5. Semester III/IV<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about environment protection <strong>in</strong> transportation eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
European program of the environmental protection (The Ecological Network Nature 2000). Noise caused by<br />
the transportation eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Air pollution nearby roads. Cross<strong>in</strong>gs for animals as the effective protection<br />
method of wild fauna. Ground and water pollutions dur<strong>in</strong>g service of the transportation routes.<br />
Environmental monitor<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the transportation <strong>in</strong>vestments.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam and oral discussion.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g
a. Salvato J.A., Nemerow N.L., Agardy F.J.: Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g (5th Edition), John Wiley & Sons,<br />
2003.<br />
b. Hester R.E., Harrison R.M. (Editors): Transport and the Environment. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2004.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Road Communication Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B013<br />
Lecture, des<strong>in</strong>g classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
IV/VII<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic/ <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Wojciech Kozłowski, PhD Eng., w.kozlowski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
English (the first certificate / FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about architecture and dimension<strong>in</strong>g of communication build<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Polish technical guidel<strong>in</strong>es projections of motor roads. The geometrical formation of motor roads (the road <strong>in</strong> the<br />
plan, <strong>in</strong> the profile, <strong>in</strong> the cross-section). Road - earthworks - the projection and the technology of the execution.<br />
The projection of road surfaces - methods and Polish catalogues. The projection of cross-roads (Polish directions).<br />
Basic eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of the road traffic (measurement and the analysis of the traffic, the model<strong>in</strong>g, the capacity of<br />
roads, streets and cross<strong>in</strong>gs). Basic knowledge about bridges (types, k<strong>in</strong>ds, the classification and the<br />
characterization of bridge objects ). Bridge constructions - the projection and the execution<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Oral or written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded projects<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Transport Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B014<br />
Lectures, design classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
IV/VII<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Beata Stankiewicz, PhD Eng., b.stankiewicz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course
Basic knowledge about dimension<strong>in</strong>g of road and bridge structures.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The basic technical properties of build<strong>in</strong>g materials us<strong>in</strong>g for road and bridge structures. The classification of<br />
roads. Typical bridge structures. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of dimension<strong>in</strong>g of road structures. Basic rules <strong>in</strong> highway<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam<strong>in</strong>ation, graded projects<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes, presentations.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Survey<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
B015<br />
Lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
II/III<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic/<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Wojciech ANIGACZ, Prof. PhD Eng. w.anigacz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
English (the first certificate/FCE level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge about eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g survey<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> civil eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Levell<strong>in</strong>g. Total stations. Survey<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments. Electronic and Electro-optical distance measurement. GPS.<br />
Exam<strong>in</strong>ation of the plumb-l<strong>in</strong>e and edge of a build<strong>in</strong>g. Control checks of hydrotechnical structures on the example of<br />
a weir. Inventory surveys of cranes and crane tracks.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written exam and oral discussion.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Uren J., Price W.F.: Survey<strong>in</strong>g for eng<strong>in</strong>eers. Fourth edition. Palgrave Macmillan. 2006<br />
Bannister A., Raymond S.: Survey<strong>in</strong>g. Frouth edition. Pitman 1977.<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>formation regard<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>courses</strong> taught at Faculty of Civil Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g should be consulted with the<br />
lecturers and/or Faculty coord<strong>in</strong>ator<br />
_____________________________________________________________
FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING,<br />
AUTOMATIC CONTROL AND INFORMATICS<br />
31 Sosnkowskiego Street, 45-272 Opole,<br />
tel. +48 077 400 62 43/ 400 62 13; tel./fax: +48 077 400 63 45, 400 63 46,<br />
http://www.we.po.opole.pl<br />
FIELDS OF STUDY • Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; (BSc, MSc, PhD)<br />
• Automatic Control Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Robotics; (BSc, MSc,<br />
PhD)<br />
• Computer Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; (BSc, MSc)<br />
• Electronics and Telecommunication; (BSc)<br />
FACULTY DEPARTMENTS • Power Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Materials and Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Electromechanical Systems and Industrial Electronics<br />
• Industrial Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Electrical Drives, Diagnostics and Industrial Electronics<br />
• Robotics and Computer Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Application<br />
Faculty Erasmus Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Wojciech Radziewicz, PhD; w.radziewicz@po.opole.pl<br />
COURSES IN ENGLISH<br />
Course<br />
code<br />
Course Name<br />
ECTS<br />
credits<br />
E001 Microprocessor Technology 4<br />
E002 Digital Signal Processors (DSP) 4<br />
E003 Electrical and Electronic Metrology 5<br />
E004 Modern Informatics Technologies - ActionScript Programm<strong>in</strong>g Lng. 5<br />
E005 Specialized Programm<strong>in</strong>g Languages 5<br />
E006 Power Electronics I 3<br />
E007 Biomedical Electrical Instrumentation 5<br />
E008 Elektrotechnik 8<br />
E009 Tele<strong>in</strong>formatik 2<br />
E010 AutoCAD Technology 5<br />
E011 Electronic Circuits 5<br />
E012 Electrical mach<strong>in</strong>es 4<br />
E013 Computer and telecommunication systems 4<br />
E014 Enterprise Portals 4<br />
E015 Optical Fibre Systems 4<br />
E016 Optical Telecommunication 4
1. Course title<br />
Microprocessor Technology<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E001<br />
lecture and laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mirosław Szmajda PhD, e-mail: m.szmajda@po.opole.pl<br />
Krzysztof Górecki PhD, e-mail: k.gorecki@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basics of C language, basics of electronics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
As a result of the course student should know how to: characterize an compare peripherials of<br />
microcontrollers, use peripherals of MSP430FG4618, use programm<strong>in</strong>g environment of Texas Instruments<br />
microcontrollers, implement and program simple algorithms for measurement systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Number codes, arithmetic of b<strong>in</strong>ary codes, architecture of microcontrollers MSP430 family; central<br />
processor unit (CPU), <strong>in</strong>structions, assembler, cooperat<strong>in</strong>g CPU with memories. Peripherals of MSP430<br />
family; timers, ports, <strong>in</strong>terruptions, LCD drivers. Us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>ternal A/D, D/A converters and LCD. Project<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
implementation algorithms for low-power measurement systems based on MSP430 family.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Laboratory: three programs <strong>in</strong> C language (20 % each) and one project – (40%);<br />
Lecture: one written exam<strong>in</strong>ation – (100%).<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. www.ti.com: \L<strong>in</strong>ks\ msp430fg4618.pdf,<br />
2. John H. Davies: MSP430 Microcontroller Basics, Elsevier 2008.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Digital Signal Processors (DSP)<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E002<br />
lecture and laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mirosław Szmajda PhD, m.szmajda@po.opole.pl , Krzysztof Górecki PhD , k.gorecki@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basics of C language, basics of electronics, basics of microprocessors technology<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
As a result of the course student should know: ma<strong>in</strong> features of different families of DSPs processors,<br />
characteriz<strong>in</strong>g an compar<strong>in</strong>g peripherals of DSP architecture, us<strong>in</strong>g peripheral of TMS320C6713 <strong>in</strong> signal<br />
analysis, us<strong>in</strong>g Environment of programm<strong>in</strong>g Texas Instruments DSP’s, project<strong>in</strong>g and programm<strong>in</strong>g simple<br />
systems for signal process<strong>in</strong>g (filters, generators)<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program
DSPs processors families, architecture of DSP; central processor units, <strong>in</strong>structions, assembler, cooperat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
CPU with memories. Peripherals of DSP; timers, ports, <strong>in</strong>terruptions. Us<strong>in</strong>g external codecs - A/D and D/A<br />
converters. Project<strong>in</strong>g and implementation FIR and IIR filter on DSP (TMS320C6713). Implementation of FFT<br />
algorithms on DSP (TMS320C6713).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Laboratory: Three programs <strong>in</strong> C language (20 % each) and one project – FIR, IIR or FFT (40%).<br />
Lecture: One written exam – (100%).<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
www.ti.com: spru301c.pdf - TMS320C6000 Code Composer Studio Tutorial,<br />
www.ti.com: C6713 data sheet: tms320c6713.pdf,<br />
www.ti.com: TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide spru189f.pdf,<br />
Lyons R. G.: Understand<strong>in</strong>g Digital Signal Process<strong>in</strong>g, Prentice Hall, New Jersey 2004.<br />
DSP implementation us<strong>in</strong>g TMS320c6711, TMS320c6713 and TMS320c6416. Texas Instruments teach<strong>in</strong>g ROM<br />
1. Course title<br />
Electrical and Electronic Metrology<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E003<br />
lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
Basic or <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Maria Wrzuszczak PhD , m.wrzuszczak@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basics of electronics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>troduction to the measurement equipment and calculat<strong>in</strong>g the uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Metrology standards, International standards organizations, static and dynamic control of transducer.<br />
Accuracy of measurement, uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty. measurements of current, voltage, resistance. A/D and D/A<br />
conversion, digital multimeters and oscilloscopes<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
One written exam (50%)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Mc Ghee J., Henderson J., Korczyński A., Kulesza W.: Scientific Metrology, Lodart, Łódź Poland 1998<br />
Mc Ghee J., Kulesza W., Korczyński A., Henderson J.: Measurement data handl<strong>in</strong>g, Lodart, Łódź Poland 2001<br />
1. Course title<br />
Modern Informatics Technologies – ActionScript Programm<strong>in</strong>g Language<br />
2. Course code<br />
E004<br />
4. Type of course<br />
elective<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lecture, computer laboratory projects<br />
5. Semester<br />
VII<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Marc<strong>in</strong> Kamiński, Ph. D., m.kam<strong>in</strong>ski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introductory level course of ActionScript – the language designed for vector graphic programm<strong>in</strong>g – lead<strong>in</strong>g<br />
to practical skills of its use<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
ActionScript programm<strong>in</strong>g language: Core Language Fundamentals, Object Oriented Programm<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Properties, Methods, Events, Display List, Timel<strong>in</strong>e, Motion, Draw<strong>in</strong>g, Text, Sound, Video, XML, Programm<strong>in</strong>g<br />
with Design Patterns<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Student’s work dur<strong>in</strong>g problem solv<strong>in</strong>g computer laboratories and exam<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Joey Lott, Danny Patterson : Advanced Actionscript 3 with Design Patterns, Adobe Press, 2006<br />
1. Course title<br />
Specialized Programm<strong>in</strong>g Languages<br />
2. Course code<br />
E005<br />
4. Type of course<br />
elective<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Marc<strong>in</strong> Kamiński, Ph. D., m.kam<strong>in</strong>ski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lecture, computer laboratory projects<br />
5. Semester<br />
VII<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introductory level course of selected specialized programm<strong>in</strong>g languages lead<strong>in</strong>g to practical skills of their use<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Python programm<strong>in</strong>g language: types and operators, statements and syntax, functions, modules, text and<br />
b<strong>in</strong>ary files, databases, Python’s support for regular expressions, graphical user <strong>in</strong>terface(wxPython), Python<br />
extensions: VPython, Numerical Python, etc.<br />
LaTeX – document preparation system: <strong>in</strong>put files, layout of the document, typesett<strong>in</strong>g text, <strong>in</strong>ternational<br />
language support, environments, typesett<strong>in</strong>g mathematical formulae, <strong>in</strong>sert<strong>in</strong>g graphics, presentation tools<br />
(beamer).<br />
ImageMagick – image process<strong>in</strong>g environment: basic and advanced image transformations, us<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g<br />
commands, image conversions, batch process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Student’s work dur<strong>in</strong>g problem solv<strong>in</strong>g computer laboratories and written exam<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Mark Lutz: Learn<strong>in</strong>g Python, O’Reilly Media Inc., 2007<br />
b) Leslie Lamport: LaTeX – A Document Preparation System, Addison-Wesley, 1994.<br />
c) Michael Still: The Def<strong>in</strong>itive Guide to ImageMagick, Apress, 1005
1. Course title<br />
Power Electronics I<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E006<br />
lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
IV/V<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ryszard Beniak, PhD, r.beniak@po.opole.pl, +4877 4538447 <strong>in</strong>t. 126<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Analyse of simple electric circuits. Base knowledge about differential equations and methods of solv<strong>in</strong>g them.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
To enhance knowledge and understand<strong>in</strong>g of power electronic converters and their application <strong>in</strong> power<br />
electronic systems. To provide students with the skills and techniques necessary to analyse and synthesise<br />
power electronic circuits utilis<strong>in</strong>g modern power electronic devices.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Fundamentals of current conduction <strong>in</strong> solids, semiconductors structure.<br />
� Semiconductor components: semiconductor diodes, thyristors, field-effect transistors and <strong>in</strong>sulated gate<br />
bipolar transistors.<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>e-commutated rectifiers: system components for rectification, s<strong>in</strong>gle-pulse rectifier with resistive and<br />
<strong>in</strong>ductive loads, current and voltage value. Two-pulse rectifier, centres tap and bridge <strong>in</strong> rectifier and <strong>in</strong>verter<br />
operation. Three-pulse rectifier end six-pulse rectifier.<br />
� Operational behaviour of l<strong>in</strong>e-commutated rectifiers: operation and power chart, active power, apparent<br />
power and reactive power; power charts, harmonic analysis.<br />
� Self-controlled converter. The function of choppers end self-controlled <strong>in</strong>verters (<strong>in</strong>verter with voltage source<br />
l<strong>in</strong>k and <strong>in</strong>verter with current source l<strong>in</strong>k) are expla<strong>in</strong>ed.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lectures provide core material and guidance for further read<strong>in</strong>g. Problems solv<strong>in</strong>g is <strong>in</strong>troduced through<br />
lectures and practiced dur<strong>in</strong>g private study. Students’ grades are based on their solution of problems and<br />
subsequent discussion thereon.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Power Electronics - Converters Applications and Design<br />
Author: Mohan, T M Undeland and WP Robb<strong>in</strong>s; Notes: Wiley<br />
1. Course title<br />
Biomedical Electrical Instrumentation<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E007<br />
Lecture/laboratory or sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1-3<br />
15-45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dariusz Zmarzły, dariusz@zmarzly.com tel.+48 508423732<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic Electronics
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course will give students the fundamental knowledge of biomedical electrical measurements for human<br />
subjects. Lectures will provide theoretical knowledge on orig<strong>in</strong> and basic features of bioelectrical signals and<br />
methods of their measurements. In biomedical electronic laboratory students will measure typical bioelectric<br />
signals on the human body e.g. ECG, EMG or EEG.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to Medical <strong>in</strong>strumentation<br />
� Physiology Basics, Cell structure, control nervous system, orig<strong>in</strong> of the bioelectric events.<br />
� Bioelectric signals and their characteristics, electrodes <strong>in</strong> bio<strong>in</strong>strumentation. Sk<strong>in</strong> structure.<br />
� Measurement of bio-potential. Instrumentation amplifiers, filters, amplifiers, A/D converters, basic schematics<br />
� Electrocardiography. Heart anatomy and physiology. Electrical activity of the heart. Typical ECG schematics.<br />
� Electromiography, motoneurons, EMG signal characteristics, Electrodes <strong>in</strong> EMG, basic EMG schematics<br />
� Electroencephalography, Characteristics of EEG signals. Bra<strong>in</strong> waves. Basic EEG monitor schemes. Passive and<br />
active Electrodes<br />
� Electrooculography and Electroret<strong>in</strong>ography. Eye muscles. Eye movement record<strong>in</strong>gs. ERG electrodes, Multifocal<br />
ERG.<br />
� Non-electrical Bio-signal Instrumentation. Typical transducers (<strong>in</strong>ductive, resistive, capacitive, chemical,<br />
piezoelectric).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
oral discussion, multiple choice test, experimental work documentation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) R.S. Khandpur, Handbook of biomedical Instrumentation<br />
b) J. W. Webster, Medical Instrumentation: Application and Design<br />
c) R.S. Khandpur, Modern Electronics Equipment<br />
d) L. Cromwell, Biomedical Instrumentation and Measurements<br />
e) J. Perkste<strong>in</strong>, Introduction to Biomedical Electronics<br />
f) J. D. Bronz<strong>in</strong>o, The Biomedical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
g) B. Christe, Introduction to Biomedical Instrumentation<br />
1. Course title<br />
Elektrotechnik<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E008<br />
Vorlesungen, Rechenübungen, Laborversuche<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Pflichtfach<br />
II (zweites) Semestr<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
8<br />
fortgeschritten<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
3+2+2<br />
45+30+30<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
Deutsch<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dr. Ing. Andrzej Przytulski, a.przytulski@po.opole.pl<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
Grundkenntnisse der höheren Mathematik, die durch den<br />
parallelen Besuch der Lehrveranstaltung Mathematik erworben<br />
werden können. Grundlagen der Physik.<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
Die Studenten sollen <strong>in</strong> der Lage se<strong>in</strong>:<br />
Gleichstrom- und Wechselstromnetzwerke bei s<strong>in</strong>usförmigen Anregung für den stationären Fall mit<br />
verschiedenen Methoden und energietechnische Netzwerke und Ausgleichsvorgänge bei l<strong>in</strong>earen<br />
Netzwerken zu berechnen. Sie sollen auch <strong>in</strong> der Lage se<strong>in</strong> die Leitungstheorie sowie die Elektromagnetische<br />
Feldtheorie auf praktische Probleme anzuwenden.<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program
� Grundbegriffe der Elektrotechnik: Elektrische Stromstärke, elektrische Spannung, Ohmscher Widerstand und<br />
Leitwert, elektrische Leistung, Erzeuger- und Verbraucherbepfeilung.<br />
� Grundgesetze der elektrischen Kreise: Kirchhoffsche Sätze, Ohmsches Gesetz, Superpositionspr<strong>in</strong>zip usw.<br />
� Reihen- und Parallelschaltung, Stern- und Dreieckschaltung von Widerständen.<br />
� Aktive l<strong>in</strong>eare Zweipole: Ideale Spannungsquelle, Ersatz-Spannungsquelle, ideale Stromquelle, Ersatz-<br />
Stromquelle, Äquivalenz von Zweipolen, Leistung von Zweipolen, Leistungsanpassung.<br />
� Berechnung l<strong>in</strong>earer elektrischer Gleichstromnetzwerke: Netzwerkumformungen, Ersatzquellenverfahren,<br />
Maschenstromverfahren, Knotenspannungsverfahren.<br />
� Berechnung nichtl<strong>in</strong>earer elektrischer Netzwerke.<br />
� Grundbegriffe der Wechselstromtechnik.<br />
� Darstellung s<strong>in</strong>usförmiger Wechselgröβen: L<strong>in</strong>iendiagramm, Zeigerdiagramm, Bode-Diagramm.<br />
� Ideale l<strong>in</strong>eare passive Zweipole bei s<strong>in</strong>usförmiger Erregung.<br />
� Reale l<strong>in</strong>eare passive Zweipole und ihre Ersatzschaltungen bei s<strong>in</strong>usförmiger Zeitabhängigkeit von<br />
Spannungen und Stromstärken.<br />
� Berechnung der l<strong>in</strong>earen, passiven Wechselstromnetzwerke, Anwendung der komplexen Zahlen. Methoden<br />
wie bei dem Gleichstrom.<br />
� Vierpole und elektrische Filter.<br />
� Dreiphasensysteme (Grundlagen).<br />
� Nichts<strong>in</strong>usförmige Erregungen, Fourierreihe, Fouriertransformation , Methoden zur Berechnung, Leistung<br />
bei nichts<strong>in</strong>usförmiger Erregung.<br />
� Ausgleichsvorgänge mit sprungförmiger und s<strong>in</strong>usförmiger Anregung, Verhalten der Grundelemente.<br />
� Klassisches Analyseverfahren, Aufstellender Netzwerk-Differentialgleichung <strong>in</strong> l<strong>in</strong>earen Netzwerken.<br />
� Laplace-Transformation und ihre Anwendung zur Berechnung der Ausgleichsvorgänge.<br />
� Elementare Begriffe elektrischer und magnetischer Felder.<br />
� Feldtheorie-Gleichungen <strong>in</strong> Integral- und Differentialform.<br />
� Anwendung der Feldtheorie (Ausgewählte Probleme).<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
Leistungsnachweis:<br />
Übungen: 2 Klausuren (90 m<strong>in</strong>)<br />
Vorlesung: Schriftliche und mündliche Prüfung.<br />
Während der schriftlichen Prüfung 5 Rechenaufgaben <strong>in</strong> der Zeit von 90 m<strong>in</strong>.<br />
Laborversuche: 6 schriftliche Versuchsbeschreibungen nach vorgegebenen Form.<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Ose R.: Elektrotechnik für Ingenieure 1. Fachbuchverlag Leipzig 2001 ISBN 3-446-21658-8<br />
b) Paul R., Paul S.: Repetitorium Elektrotechnik Elektromagnetische Felder, Netzwerke, Systeme. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger<br />
Lehrbuch 1995 ISBN 3-540-57003-9<br />
c) Paul R., Paul S.: Arbeitsbuch zur Elektrotechnik 1. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Lehrbuch 1996 ISBN 3-540-59484-1<br />
d) Paul R., Paul S.: Arbeitsbuch zur Elektrotechnik 2. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Lehrbuch 1996 ISBN 3-540-59485-X<br />
e) Mattes H.: Übungskurs Elektrotechnik 1 Felder und Gleichstrom-netze. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Lehrbuch 1992 ISBN 3-540-<br />
55701-6<br />
f) Mattes H.: Übungskurs Elektrotechnik 2 Wechselstromrechnung.Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Lehrbuch 1992 ISBN 3-540-55776-8<br />
g) Georg O.: Elektromagnetische Felder und Netwerke Anwendungen <strong>in</strong> Mathcad und PSpice. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger 1999<br />
ISBN 3-540-65587-5<br />
1. Course title<br />
Tele<strong>in</strong>formatik<br />
2. Course Code<br />
E009<br />
4. Type of course<br />
Pflichtfach<br />
6. Numer of ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
1+1<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Vorlesungen, Sem<strong>in</strong>are<br />
5. Semester<br />
V Semester<br />
7. Level of class<br />
grundlegend<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
15+15
Deutsch<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dr. Ing. Andrzej Przytulski, a.przytulski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Kenntnisse der höheren Mathematik und Physik sowie der Elektrotechnik und Elektronik<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Die Studenten sollen <strong>in</strong> der Lage se<strong>in</strong>:<br />
E<strong>in</strong>e vollständige Lichtwellenleiter-Übertragungsstrecke zu berechnen. (Parameter der optischen Sender und<br />
Empfänger, des Lichtwellenleiters, optischer Verstärker, Modulation- und Demodulationsanlagen usw.)<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Grundlegende Def<strong>in</strong>itionen und Begriffe der Tele<strong>in</strong>formatik.<br />
� Analog- und Digitalübertragungskanal. Verzerrungen und Störungen der Signale.<br />
� Kodierung und Dekodierung der Information. Modulation und Demodulation und ihre Arten.<br />
� Übertragungsmedium. Aufbau der Kabel- und Funkverb<strong>in</strong>dungen.<br />
� Datenkompression, Qualität der Übertragung, Durchlässigkeit des Kanals. Mehrfache Ausnutzung des Kanals<br />
TDM, FDM, WDM usw.<br />
� Entgegenwirkungen der Übertragungsstörungen.<br />
� Kommutation der Verb<strong>in</strong>dungen und Kommutation der Informationsflusses.<br />
� Aufbau des digitalen Übertragungsnetzes (Telekommunikationsnetzes).<br />
� Beschreibung der Eigenschaften von Phonie- und Videosignalen.<br />
� Lichtwellenleiter <strong>in</strong> Kommunikationssystemen.<br />
� Eigenschaften von Lichtwellenleitern. Dispersion und ihre Arten, Dämpfung.<br />
� Optische Sender und Empfänger.<br />
� Modulation und Kodierung <strong>in</strong> den Lichtwellenleitersystemen.<br />
� Entwurf e<strong>in</strong>er Lichtwellenleiterübertragungsstrecke.<br />
� Optische DWDM und WDM Systeme.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: 1 Klausur (45 m<strong>in</strong>)<br />
Vorlesung: Schriftliche Arbeit <strong>in</strong> Projektform<br />
18. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Bladau W.: Halbleiter-Optoelektronik. Carl Hanser Verlag 1995 ISBN 3-446-17712-4<br />
b) Entsprechende Internetseiten zum Beispiel: http://www.om.tu-harburg.de/ Optische Komunikationstechnik<br />
1. Course title<br />
AutoCAD Technology<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E010<br />
Lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
II (2nd cycle)<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Łukasz Dzierżanowski l.dzierzanowski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Ability of 2D and 3D object model<strong>in</strong>g and model visualization <strong>in</strong> AutoCAD enviroment<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� User <strong>in</strong>terface<br />
� Creat<strong>in</strong>g and edit<strong>in</strong>g of basic objects<br />
� Us<strong>in</strong>g layers
� Dimensions. Techniques, edit<strong>in</strong>g, us<strong>in</strong>g styles.<br />
� Coord<strong>in</strong>ate systems<br />
� Solid modell<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Solid edit<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
� Us<strong>in</strong>g blocks<br />
� Dynamic blocks<br />
� Render<strong>in</strong>g basics<br />
� Plott<strong>in</strong>g – work<strong>in</strong>g with Paperspace<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
The students works on a model based on a traditional, paper documentation throughout the semester. The<br />
grade corresponds to the model quality.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
AutoCAD2010 HELP<br />
G. Omura „Master<strong>in</strong>g AutoCAD 2010 and AutoCAD LT 2010”, AutoDesk Press 2009<br />
1. Course title<br />
Electronic Circuits<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E011<br />
Lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Elective<br />
III/IV (2nd cycle)<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Maria Wrzuszczak, e-mail: m.wrzuszczak@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introduction to the analog and digital circuits<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Voltage transfer fuction, voltage amplifier with transistors and OA, s<strong>in</strong>us oscillators. Comparators, astable,<br />
monostable and bistable circuits, Schmitt triggers, digital electronic circuits<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
One written exam (50%)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lectures notes.<br />
Alexander Ch., Sadiku M.: Fundamentals of Electronic Circuits, Mc Graw – Hill 2004.<br />
Hayes J.: Introduction to Digital Logic Design, Addison Wesley 1993.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Electrical mach<strong>in</strong>es<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
E012<br />
4. Type of course<br />
Elective<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture/class<br />
5. Semester<br />
V (1st cycle)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mariusz Jagieła, PhD. Hab. (Eng.)<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Core mathematics, Circuit theory<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Mak<strong>in</strong>g student competent to understand basic mechanisms of energy conversion (generation of voltage,<br />
force and torque, efficiency and losses) and to be able to apply them to solve basic problems like s<strong>in</strong>glephase<br />
transformer design, predictions of performance for certa<strong>in</strong> electrical mach<strong>in</strong>es such as DC mach<strong>in</strong>es or<br />
<strong>in</strong>duction mach<strong>in</strong>es. Also, to understand the basic pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of control of electrical mach<strong>in</strong>es.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lectures:<br />
1. Physics of magnetic materials: magnetic steels, ferrites and permanent magnets, basic equations <strong>in</strong><br />
magnetics, magnetic quantities and units;<br />
2. Equivalent magnetic circuits, formulation and solution of equations us<strong>in</strong>g computers with applications;<br />
3. AC currents, eddy currents, forces and losses;<br />
4. DC mach<strong>in</strong>es: series and shunt mach<strong>in</strong>es, permanent magnet mach<strong>in</strong>es, pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of operation, basic<br />
configurations, w<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g topologies of DC mach<strong>in</strong>es, mechanical characteristics, efficiency and losses, dynamic<br />
performance of a DC motor, basic methods of control;<br />
5. Three-phase <strong>in</strong>duction motors: rotat<strong>in</strong>g field, pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of operation, wound rotors and cage rotors, basic<br />
three-phase s<strong>in</strong>usoidal w<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g configuration, characteristics, Kloss equation, start<strong>in</strong>g torque, critical torque,<br />
dynamic performance of <strong>in</strong>duction motor, basic concepts of control;<br />
6. Special <strong>in</strong>duction mach<strong>in</strong>es: solid rotor motors, s<strong>in</strong>gle-phase mach<strong>in</strong>e: pulsat<strong>in</strong>g field, capacitor start/run,<br />
shaded-pole motor<br />
7. Synchronous mach<strong>in</strong>es: configurations and pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of operation of motors and generators, applications,<br />
stability and control of synchronous motors, control of synchronous generator, V-curves, permanent magnet<br />
synchronous mach<strong>in</strong>es;<br />
8. Brushless motors: PM-BLDC motors: pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of operation and control, basic configurations, switched<br />
reluctance motor: pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of operation and control;<br />
9. Drive systems: applications of mach<strong>in</strong>es, stepper motors and servos, goals and pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of closed-loop<br />
control.<br />
Classes:<br />
1. Fundamentals of magnetic circuit analysis: nodal analysis (magnetic potential -based) and loop analysis<br />
(magnetic flux-based) of magnetic circuits, circuits conta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g gaps with l<strong>in</strong>ear materials, <strong>in</strong>troduction of<br />
nonl<strong>in</strong>earity, handl<strong>in</strong>g nonl<strong>in</strong>earity <strong>in</strong> magnetic circuit analysis, application of computers;<br />
2. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of <strong>in</strong>ductances and losses us<strong>in</strong>g magnetic equivalent magnetic circuits, application of<br />
computer analysis, self-, mutual-,magnetiz<strong>in</strong>g- and leakage <strong>in</strong>ductance;<br />
3. Transformers:calculation of equivalent circuit parameters, us<strong>in</strong>g experiments to determ<strong>in</strong>e equivalent<br />
circuit parameters,<br />
obta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g characteristics;<br />
4. DC mach<strong>in</strong>es: calculation of static characteristics of shunt-type and permanent-magnet mach<strong>in</strong>e from basic<br />
relations;<br />
5. Three-phase <strong>in</strong>duction mach<strong>in</strong>es: us<strong>in</strong>g Kloss formula to compute slip for the given load, comput<strong>in</strong>g<br />
currents and torque;<br />
6. Use of phasor diagrams <strong>in</strong> the analysis of synchronous mach<strong>in</strong>es;<br />
7. Use of equations of DC mach<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> the analysis of a PM-BLDC motor, prediction of characteristics of PM-<br />
BLDC motor, us<strong>in</strong>g computer simulation to analyze operation of PM-BLDC and Switched reluctance motor,<br />
<strong>in</strong>fluence of commutation angle.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lectures: written exam<br />
Classes: grades from home works (40%), f<strong>in</strong>al project (60%)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Fitzgerald A.E et al.: Electic mach<strong>in</strong>ery, McGraw-Hill, 2005.<br />
Sen P.C: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of electrical mach<strong>in</strong>es and power electronics, Willey, 1996.<br />
Wildi T: Electrical mach<strong>in</strong>es, drives and power systems, Prentice Hall, 2005.
1. Course title<br />
Computer and telecommunication systems<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E013<br />
Lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
I (2nd cycle)<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Janusz Dulas, e-mail: j.dulas@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge <strong>in</strong> electrical eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Student has basic knowledge about modern computer and telecommunication systems, can connect<br />
electronic circuits accord<strong>in</strong>g diagrams, know basic rules of wireless transmission, know basic elements used <strong>in</strong><br />
telecommunication and their pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of operation<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Develop of the computer and telecommunication systems, classic and wireless communication,<br />
telecommunication systems, mobile phone communication, computer systems (GPS)<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture: oral exam<br />
Laboratory: marks given after each exercise<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Electronic parts catalogues<br />
Horowitz P, Hill W.: The art of electronics<br />
Norris M.: Communications Technology Expla<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
Hayk<strong>in</strong> S.:Communication systems<br />
1. Course title<br />
Enterprise Portals<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E014<br />
Lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
III (2nd cycle)<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Michał Tomaszewski, e-mail: m.tomaszewski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Programm<strong>in</strong>g Languages (basic level), E-commerce (basic level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Knowledge of enterprise portals. Ability to us<strong>in</strong>g user experience design methods and techniques. Students<br />
work <strong>in</strong> small groups to create part of the corporate portal. Evaluated is the degree of difficulty of the task<br />
and the complexity of implementation<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� The classification of portals<br />
� The role and tasks of a corporate portal <strong>in</strong> enterprise
� Content Management Systems (CMS)<br />
� Features of user experience design<br />
� Design<strong>in</strong>g of enterprise portals<br />
� Three-Tier Architecture<br />
� Development languages and methodologies<br />
� Structure <strong>in</strong> Portal Interface<br />
� Ensur<strong>in</strong>g Portal Adoption<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Essays, projects and practical exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Sullivan D, Proven Portals: Best Practices for Plann<strong>in</strong>g, Design<strong>in</strong>g, and Develop<strong>in</strong>g Enterprise Portals, Addison<br />
Wesley Professional, 2003<br />
Davydov M., Corporate Portals and eBus<strong>in</strong>ess Integration, McGraw Hill, 2001<br />
Greenspan J. , Bulger B., MySQL/PHP Database Applications, M&T Books, 2004<br />
www.php.net (PHP Manual)<br />
1. Course title<br />
Optical Fibre Systems<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E015<br />
Lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
III (2nd cycle)<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Feliks Szczot, e-mail: f.szczot@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of optics, electronics, quantum electronics and communication systems, data transmission<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course content is knowledge of fibre-optical components and systems. Aims of the course are:<br />
fundamentals of optical fibres, optical sources and receivers, active and passive elements of networks, optical<br />
telecommunications systems and sensor systems. This course provides the student with the essential<br />
knowledge <strong>in</strong> optical fibres, optical communication and measurement sensor systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Optical fibres: glass and plastic fibres, attenuation, wavelength dispersion, polarisation, birefr<strong>in</strong>gence,<br />
polarisation ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g fibres, polarisation crosstalk, fibre couplers, isolators. Fibre Bragg Grat<strong>in</strong>gs: Bragg<br />
grat<strong>in</strong>gs, grat<strong>in</strong>g response, dispersion compensation. Integrated optical devices: Mach-Zehnder<br />
<strong>in</strong>terferometers, arrayed waveguide grat<strong>in</strong>gs, WDM filters, electrooptic modulators, photonics crystals.<br />
Optical amplifiers: semiconductor laser amplifiers, erbium doped fibre amplifiers. LED and laser diodes,<br />
s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode lasers, narrow l<strong>in</strong>e width lasers, tunable lasers. PIN diode, avalanche diode, responsively,<br />
bandwidth, noise. Systems: analogue and digital transmission, l<strong>in</strong>k power budget, dynamic range, system<br />
bandwidth, direct detection systems, dispersion limitations, attenuation limitations, additive noise, signal<br />
dependent noise, bit error rate, soliton systems, coherent systems, optical networks. Video transmission, RF<br />
Photonic Systems, system requirements, optical modulators, RF conversion ga<strong>in</strong>, l<strong>in</strong>k power budget, dynamic<br />
range. Optical communication networks and MAN, LAN and Home applications. Optical fibre sensors and<br />
sensor networks and their application. Optical computer <strong>in</strong>terconnection (short and long distance).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test exam, <strong>in</strong>dividual sem<strong>in</strong>ar/project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
G. E<strong>in</strong>arsson, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Lightwave Communications, John Wiley, 1996<br />
D.K. Mynbaev and L.L. Sche<strong>in</strong>er, Fiber-Optic Communications Technology, Prentice Hall, 2001<br />
G. Keiser, Optical Fiber Communications, (3rd ed.), McGraw Hill, 2000
J. Dak<strong>in</strong>, B. Culshaw, Optical Fiber Sensors, Artech House, Vol. I-IV, 1988-1999.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Optical Telecommunication<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
E016<br />
Lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
III/IV<br />
6. Number of ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Feliks Szczot, e-mail: f.szczot@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of optics, electronics, quantum electronics and communication systems, data transmission<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course content is knowledge of fibre-optical components and systems. Aims of the course are:<br />
fundamentals of optical fibres, optical sources and receivers, active and passive elements of networks and<br />
optical telecommunications systems. This course provides the student with the essential knowledge <strong>in</strong> optical<br />
fibres and optical communication systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Optical fibres: s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode and multi-mode fibres, glass and plastic fibres, attenuation, wavelength<br />
dispersion, polarisation, birefr<strong>in</strong>gence, polarisation ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g fibres, polarisation crosstalk, fibre couplers,<br />
isolators. Fibre Bragg Grat<strong>in</strong>gs: Bragg grat<strong>in</strong>gs, grat<strong>in</strong>g response, dispersion compensation. Integrated optical<br />
devices: Mach-Zehnder <strong>in</strong>terferometers, arrayed waveguide grat<strong>in</strong>gs, WDM filters, electrooptic modulators,<br />
photonics crystals. Optical amplifiers: semiconductor laser amplifiers, erbium doped fibre amplifiers.<br />
Advanced LED and laser diodes, s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode lasers, narrow l<strong>in</strong>ewidth lasers, tunable lasers. Detectors: PIN<br />
diode, avalanche diode, responsivity, bandwidth, noise. Systems: analogue and digital transmission (data<br />
transmission), l<strong>in</strong>k power budget, dynamic range, system bandwidth, direct detection systems, dispersion<br />
limitations, attenuation limitations, additive noise, signal dependent noise, bit error rate, soliton systems,<br />
coherent systems, optical networks. Video transmission, RF Photonic Systems, system requirements, optical<br />
modulators, RF conversion ga<strong>in</strong>, l<strong>in</strong>k power budget, dynamic range. Free space optical communication and<br />
WAN, MAN, LAN and Home applications.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test exam, <strong>in</strong>dividual sem<strong>in</strong>ar/project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
G. E<strong>in</strong>arsson, Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Lightwave Communications, John Wiley, 1996<br />
D.K. Mynbaev and L.L. Sche<strong>in</strong>er, Fiber-Optic Communications Technology, Prentice Hall, 2001<br />
G. Keiser, Optical Fiber Communications, (3rd ed.), McGraw Hill, 2000<br />
J. Hecht, Understand<strong>in</strong>g Fiber Optics, Prentice Hall, 1999<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>formation regard<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>courses</strong> taught at Faculty of Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Automatic Control and<br />
Computer Science should be consulted with the lecturers and/or Faculty coord<strong>in</strong>ator
FACULTY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING<br />
5 Mikołajczyka Street, 45-271 Opole, Poland<br />
phone (+48 77) 400 61 57, 400 62 53, tel./fax (+48 77) 400 63 42<br />
e-mail: wmech@po.opole.pl<br />
FIELDS OF STUDY � Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Build<strong>in</strong>g;<br />
(BSc,MSc,PhD)<br />
� Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; (BSc,MSc)<br />
� Agricultural and Forest Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; (BSc,MSc)<br />
� Mechatronics; (BSc)<br />
� Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g;(BSc)<br />
FACULTY DEPARTMENTS � Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Materials Science and Chipless Production Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Mechanics and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design<br />
� Thermal Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Industrial Facilities<br />
� Agricultural and Forest Technology<br />
� Road and Agricultural Vehicles<br />
� Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Automation<br />
� Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Faculty Erasmus Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Dr hab. <strong>in</strong>ż Adam Niesłony, a.nieslony@po.opole.pl<br />
COURSES IN ENGLISH<br />
Course<br />
code<br />
Course Name<br />
ECTS<br />
credits<br />
M001 Simulation In Mach<strong>in</strong>e Dynamics 6<br />
M002 Environmental Biology 3<br />
M004 Basics of Ecology 2<br />
M005 Bioprocess Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 6<br />
M006 Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of Reactors 6<br />
M007 Basics of Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Entities Economy 2<br />
M008 Heat Transfer 6<br />
M009 Fluid Mechanics 6<br />
M010 Applications of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) 4<br />
M011 Hydrology and Hydraulics 4<br />
M012 Informatics 5<br />
M013 Meteorology and Climatology 3<br />
M014 Pollution Diffusion <strong>in</strong> Atmosphere 4<br />
M015 Spatial Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Urban Design 3<br />
M016 Numerical Method <strong>in</strong> Mechanics 6<br />
M017 Build<strong>in</strong>g Structures 6<br />
M018 Mechanics 5<br />
M019 Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design 4
M020 Mach<strong>in</strong>e Life 5<br />
M021 Strength of Materials 6<br />
M022 Weld<strong>in</strong>g 3<br />
M023 Introduction to Mechatronics 5<br />
M024 Membrane Processes 8<br />
M025 Environment Protection 3<br />
M026 Organization of Agricultural Production and Services 2<br />
M027 Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 6<br />
M028 Design: Cool<strong>in</strong>g and Gas Scrubb<strong>in</strong>g Removal Installation 6<br />
M029 Processes and Technology of Production 8<br />
M030 Fuels Combustion <strong>in</strong> Industry Process 3<br />
M031 Computer Aided Design 6<br />
M033 Computational Fluid Mechanics 6<br />
M034 Gas Dynamic 4<br />
M035 Hydraulic and Hydrologic 4<br />
M036 Hydraulic Mach<strong>in</strong>es 4<br />
M037 Fundamentals of Chemical and Food Technology 2<br />
M038 Multiphase Flows 6<br />
M039 Process Flow Systems 4<br />
M040 Selected Process Techniques 5<br />
M041 Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
M042 Food Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
M043 Selected Elements of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 6<br />
M044 Water Technology 4<br />
M045 Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> MATLAB 4<br />
M046 Mathematical Statistics 4<br />
M047 Methods and Techniques of the Quality Control 6<br />
M048 Soil Science 4<br />
M050 Environmental Metrology 4<br />
M051 Heat<strong>in</strong>g Systems 2<br />
M052 Environmental Management 3<br />
M053 Environmental Protection and Monitor<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
M054 Modern Non-<strong>in</strong>vasive Measurement Techniques for Multiphase Flow Systems 2<br />
M055 Ventilation and Air-Condition<strong>in</strong>g 2<br />
M056 Energy Consumption of Industrial Processes 4<br />
M057 Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Electronics 5<br />
M058 Computer Measurement Systems 4<br />
M059 Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
M060 Design Work – Individual Report 6<br />
M061 Design Work – Installation for Solution Production 6<br />
M062 Heat and Mass Transfer Operations 4<br />
M063 Mechanical Operations 4<br />
M064 Mechanics Elements and Mach<strong>in</strong>es Design 5<br />
M065 Structural Mechanics <strong>in</strong> Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design 6<br />
M066 Build<strong>in</strong>g structures-docks and coasts 6<br />
M067 Design work – <strong>in</strong>dividual report 6<br />
M068 Mach<strong>in</strong>e life 5<br />
M069 Steel structures 6
M070 Strength of materials 6<br />
M071 Structural Design 5<br />
M072 Technology, economy and organisation of build<strong>in</strong>g site 5<br />
M073 Computer aided programm<strong>in</strong>g of the CNC mach<strong>in</strong>e tools 4<br />
1. Course title<br />
Simulation In Mach<strong>in</strong>e Dynamics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M001<br />
Lecture and laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
w<strong>in</strong>ter semester<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dr <strong>in</strong>ż. Józef Grzelak, tel. 048774006356, email: j.grzelak@po.opole.pl,<br />
Opole University of Technology, Faculty of Mechanics, Departament of Mechanics and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design, ul.<br />
Mikolajczyka 5, 45-271 Opole, Poland.<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematical analysis, analytical mechanics, theory of vibrations foundamentals<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Mathematical model<strong>in</strong>g and computer simulation of l<strong>in</strong>ear and nonl<strong>in</strong>ear mechanical systems with one and<br />
more degrees of freedom us<strong>in</strong>g Matlab-Simul<strong>in</strong>k programme<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to Matlab-Simul<strong>in</strong>k programme, numerical methods <strong>in</strong> Matlab,<br />
� Differential equations model<strong>in</strong>g methods us<strong>in</strong>g Simul<strong>in</strong>k programme,<br />
� Simulation and model<strong>in</strong>g of l<strong>in</strong>ear mechanical systems us<strong>in</strong>g general and operational methods,<br />
� Simulation and model<strong>in</strong>g of nonl<strong>in</strong>ear mechanical systems us<strong>in</strong>g general method,<br />
� Transfer function concept for l<strong>in</strong>ear mechanical systems with one and more degrees of freedom, frequency<br />
characteristics of the l<strong>in</strong>ear systems,<br />
� Application of FFT or DFT functions for frequency characteristics determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the nonl<strong>in</strong>ear mechanical<br />
systems,<br />
� Movement stability analysysis for l<strong>in</strong>ear and nonl<strong>in</strong>ear mechanical systems.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
reports written by students<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) B.Skalmierski, Mechanics, Warszawa-Amsterdam, PWN-Elsevier 1992.<br />
b) J.L.Meriam, L.G.Kraige, Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Mechanics, vol.2 Dynamics, 3 rd ed. – New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1993.<br />
c) R.Dautray, J.L.Lions, Mathematical Analysis and Numerical Methods for Science and Technology, vol.1,<br />
Physical Orig<strong>in</strong>s and Classical Methods, Berl<strong>in</strong>: Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Verlag 1990.<br />
d) Simul<strong>in</strong>k, Dynamic System Simulation for MATLAB, Us<strong>in</strong>g Simul<strong>in</strong>k, v.3, The MathWorks 1999.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environmental Biology<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M002<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture and laboratory<br />
4. Type of course 5. Semester
compulsory 3<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
Basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1 (laboratory); 2 (lecture)<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jolanta KRÓLCZYK, PhD Eng. , e-mail: j.krolczyk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
None<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Biological processes occurs <strong>in</strong> environment; processes accompany<strong>in</strong>g pollution neutralization and soil<br />
reclamation; water reclamation; landfill reclamation; biological threat assessment.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Plant and trees recognition. Ways of recognition and f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g species based on key to plant recognition.<br />
� Rules and techniques of microscop<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
� Prepar<strong>in</strong>g and observation samples to microscop<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
� Plant cell structure.<br />
� A role of plant and animals tissues <strong>in</strong> physiological processes.<br />
� Osmose <strong>in</strong> cell. Plasmolysis.<br />
� Characteristic of selected groups of microorganisms based on activated sludge<br />
� Description of Procaryota and Eucaryota.<br />
� Structure and function of cell components.<br />
� The role of plant and animal tissues <strong>in</strong> physiological processes.<br />
� Recognition of selected microorganisms: virus, bacteria, fungus, algae,<br />
� Ways of nutrition: heterotrophism, autotrophism (chemosynthesis and photosynthesis)<br />
� Metabolism – catabolism, anabolism<br />
� ATP – phosphorylation<br />
� Aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration and fermentation.<br />
� Photosynthesis as a basic anabolic process.<br />
� Material cycles and life processes – the role of microorganisms<br />
� The role of microorganism <strong>in</strong> objects destruction and devastation.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Taken after each laboratory<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Ville Eldra Pearl, Berg L<strong>in</strong>da R., Mart<strong>in</strong> Diana W., Villee Claude A., Biology, MULTICO, 2000, 2 nd edition<br />
b) Bergey's Manuał of Determ<strong>in</strong>ative Bacteriology. Baltimowe: Williams and Wilk<strong>in</strong>s Co., Ed. VII, 1974<br />
c) Brock T.D., Madigan M.T. Biology of Micro-organisms. Prentice Hall. International London<br />
d) Lengerer J.W., Drews G., Schlegel H.G. (red). Biology of prokaryotes. Blackwell Science,Thieme, Stuttgart,<br />
New York, 1999<br />
1. Course title<br />
Basics of Ecology<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M004<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture<br />
5. Semester<br />
1<br />
7. Level of class<br />
Basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. Marek Tukiendorf, e-mail: m.tukiendorf@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
None<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic terms and laws connected with environmental science and ecology, i.e. material cycles and life<br />
processes, flow of energy. Basic <strong>in</strong>formation about population dynamics. Effects of anthropopression and<br />
ways of nature protection.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Basic ecological terms – ecology, ecosystem, biotic community, ecological landscape, environmental science<br />
� A brief history of conservation and environmentalism<br />
� Modern environmentalism<br />
� Environmental dilemmas, signs to hope, North/South: a divided world<br />
� Environmental ethics and philosophy, worldviews and ethical perspectives<br />
� Matter, energy and life: from atoms to cells, energy and matter, energy for life, from species to ecosystem,<br />
material cycles and life processes<br />
� Matter, energy and life: population, biological environment, ecosystem, photosynthesis, respiration<br />
� Material cycles and life processes – the carbon cycle, the nitro gen cycle<br />
� Population dynamics<br />
� Biological communities and species <strong>in</strong>teraction<br />
� Communities <strong>in</strong> transition<br />
� Ecological succession<br />
� Air, climate and wheatear – air pollution<br />
� Water use and management, water pollution,<br />
� 15. Soils pollution<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Exam (test)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Cunn<strong>in</strong>gham Wiliam P., Woodworth Saido B., Environmental Science, McGraw-Hill, 4 th edition<br />
b) Ville Eldra Pearl, Berg L<strong>in</strong>da R., Mart<strong>in</strong> Diana W., Villee Claude A., Biology, MULTICO, 2000, 2 nd edition<br />
1. Course title<br />
Bioprocess Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M005<br />
exercise, sem<strong>in</strong>ar, project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
exercise (1h)<br />
exercise (15h)<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar (1h)<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar (15h)<br />
project (1h)<br />
project (15h)<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. Małgorzata Płaczek, Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics, chemistry, biology<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this study is to provide <strong>in</strong>formation on biochemistry of cell, build<strong>in</strong>g and physiology of<br />
microorganisms, their proprieties, activity, and use <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustrial processes. Moreover, the aim of this course<br />
is to <strong>in</strong>troduction to basic problems of performance of typical biotechnology processes on a large scale, as<br />
well as <strong>in</strong>troduction to construction and the utilization of different bioreactors types. The course is designed
to be a study of all aspects of practical application of microorganisms. Some part of the course is deal<strong>in</strong>g<br />
with production of different substances <strong>in</strong> a biotechnological way (alcohols, organic acid, fermented foods<br />
and feeds, enzymes and its immobilization, antibiotics, vitam<strong>in</strong>s and plant hormones, plant, microbial<br />
pesticides, vacc<strong>in</strong>es and biological fuels). Additionally ,some <strong>in</strong>formation about waste water treatment and<br />
bioremediation will be also provided.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to bioprocess eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Comparison of chemical and biochemical ways of production<br />
� Bioreactors as ma<strong>in</strong> unit of bioprocess apparatus (construction of different bioreactors types)<br />
� Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of bioprocess conduct<br />
� The choice of optimum configuration of bioreactors system to typical bioprocess<br />
� Elements of genetics and genetic eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Comparizon of biochemical transformations<br />
� K<strong>in</strong>etics of biomass growth<br />
� Classification of models of biomass growth<br />
� Culture and conditions of growth of <strong>in</strong>dustrial microorganisms<br />
� Production technology of selected products<br />
� Bioprocess eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and environment protection<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (10 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
consultations<br />
project: study of biochemical reactor project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Bioprocess Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g: Basic Concepts (2nd Edition) (Hardcover) by Michael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi (Prentice<br />
Hall)<br />
b) Biology of Industrial Microorganisms, Brock T.D., Madigan M.T. Prient<strong>in</strong>ce Hall, 2005<br />
c) Biotechnology: An Introduction (with InfoTrac), Susan R. Barnum, Brooks Cole, 2000<br />
1. Course title<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of Reactors<br />
2. Course Code (kod przedmiotu)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M006<br />
exercise, sem<strong>in</strong>ar, project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
exercise (1h)<br />
exercise (15h)<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar (1h)<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar (15h)<br />
project (1h)<br />
project (15h)<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. Małgorzata Płaczek, email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics,<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give <strong>in</strong>formation about k<strong>in</strong>etics of reaction <strong>in</strong> different type of chemical reactors<br />
as well as knowledge about design eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of different type of reactors. This course will provide handson<br />
experience <strong>in</strong> upstream process<strong>in</strong>g and will focus on the selection, preparation, and operation of<br />
chemical reactors and <strong>in</strong>strumentation.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of chemical reactors<br />
� Classification of chemical reaction
� Basics of k<strong>in</strong>etics of chemical reaction<br />
� Basic types of chemical reactors<br />
� Mass balance for different types of chemical reactors<br />
� Energetic balance of ideal reactors<br />
� Stationary and nonstationary state of chemical reactor<br />
� Models of heterogeneous catalytic reactors<br />
� Chemical reactor design, optimization, and scaleup<br />
15. Assessment methods (<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (10 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
consultations<br />
project: study of chemical reactor project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Bioprocess Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g: Basic Concepts (2nd Edition) (Hardcover) by Michael L. Shuler, Fikret Kargi (Prentice<br />
Hall)<br />
b) The Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of Chemical Reactions, Schmidt, Lanny D., New York, Oxford University Press, 1998<br />
c) Chemical Reactor Design, Optimization, and Scaleup, Nauman, E. Bruce, 2002 McGraw-Hill<br />
d) Inżynieria reaktorów chemicznych, Burghart, Andrzej, T.1. Reaktory dla układów homogenicznych / Andrzej<br />
Burghart, Grażyna Bartelmus. - Warszawa : Wydaw. Naukowe PWN, 2001. - 367 s<br />
e) Inżynieria reaktorów chemicznych, Burghart, Andrzej T.2. Reaktory dla układów heterogenicznych / Andrzej<br />
Burghart, Grażyna Bartelmus. - Warszawa : Wydaw. Naukowe PWN, 2001. - 353 s.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Basics of Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Entities Economy<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M007<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
dr Anna Kuczuk, a.kuczuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
None<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
30<br />
Introduction to basics and consolidation of fundamental notions and rights <strong>in</strong> scope of micro-and<br />
macroeconomics and fundamentals of <strong>in</strong>vestments’ economic account us<strong>in</strong>g chosen idustry examples.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
���� Fundamentals of economics notions – rarity effect, problem of management, goods and services, resources;<br />
���� Market, price, demand, supply – market structure, market mechanism, merket balance;<br />
���� Conumer’s decisions – rules of consumer decisions, usability theory;<br />
���� Producer’s decisions - production’s function, costs;<br />
���� Market structures – perfect rivalship, full monopoly, non-perfect rivalship;<br />
���� Chosen aspects of economic account – Investments’ efficiency, cash-flow, dicount, NPV, IRR;<br />
���� Job market, capital market, ground market;<br />
���� Macroeconomics <strong>in</strong>troduction;<br />
���� Circulation of product and <strong>in</strong>come , ways of Groos National Income measurment;<br />
���� Aggregated supply and demand, macroeconomics balance;<br />
���� Unemployment, k<strong>in</strong>ds of unemployment;<br />
���� Inflation – k<strong>in</strong>ds, reasons, measures;<br />
���� Economy cycle, cycles of economic situation;
���� Fiscal policy;<br />
���� Money <strong>in</strong> econymy.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Economics (a student's guide) - John Beardshaw, David. Brewster<br />
b) Economics - David Begg, Stanley Fisher<br />
1. Course title<br />
Heat Transfer<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M008<br />
lecture, exercise, laboratory, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
lecture (2h),exercise (1h)<br />
lecture (30h),exercise (15h)<br />
laboratory,(1h) sem<strong>in</strong>ar (1h)<br />
laboratory,(15h), sem<strong>in</strong>ar (15h)<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. Małgorzata Płaczek; Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics,<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
This course exam<strong>in</strong>es the three heat transfer mechanisms - conduction, convection and electromagnetic<br />
radiation. Solutions are obta<strong>in</strong>ed for one dimensional steady heat conduction through composite, pla<strong>in</strong> and<br />
tubular walls, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g with <strong>in</strong>ternal heat generation. The Reynolds' analogy is <strong>in</strong>troduced to l<strong>in</strong>k forced<br />
convective heat transfer with momentum transfer <strong>in</strong> lam<strong>in</strong>ar and turbulent boundary layers. Free<br />
convection, <strong>in</strong> which heat transfer itself <strong>in</strong>duces its own buoyant flow is then considered. The radiative<br />
emission characteristics of black and grey bodies are exam<strong>in</strong>ed and radiative heat transfer between such<br />
bodies is analysed. The objective of this course is to <strong>in</strong>troduce, through a comb<strong>in</strong>ation of theory, exercise<br />
and laboratory practice, the basic heat transfer processes. Acquire knowledge about basics of heat transfer<br />
<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and calculations of heat transfer processes constitut<strong>in</strong>g background for analysis of heat<br />
exchangers, thermal equipment and systems. A theoretical discussion of selected processes of heat transfer<br />
will be followed by laboratory experiments.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Fundamentals of heat transfer processes<br />
� Introduction to conduction (one - and two - dimensional, steady state conduction, transient conduction)<br />
� Fluid dynamics and convection<br />
� Forced convection (external flow, <strong>in</strong>ternal flow)<br />
� Free convection<br />
� Radiation (processes and properties, exchange between surfaces)<br />
� Construction and work of heat exchangers<br />
� Examples of heat transfer processes studied <strong>in</strong> the laboratory <strong>in</strong>clude: convective heat transfer, heat transfer<br />
<strong>in</strong> pipes with ribs, heat transfer <strong>in</strong> boiled mixtures and heat transfer <strong>in</strong> pipes with metal foam<br />
� Heat transfer—general applications (fluidized beds, food process<strong>in</strong>g, nuclear reactors, manufactur<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
process<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
lecture: exam-test, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (10 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
consultations
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Elements of heat transfer, Bayazitoğlu Y., Özişik M. N., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.<br />
b) Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, Frank P. Incropera [et all]. - 6th ed. - Hoboken, NJ, John Wiley &<br />
Sons, cop. 2007. - XXV, [1], 997 s.<br />
c) Interfacial Transport Phenomena, Slattery J. C., Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Verlag, New York Inc., 1990<br />
d) Materials prepared by lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Fluid Mechanics<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M009<br />
Lecture/laboratory/practice ex.<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
5<br />
75<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
Grzegorz Borsuk, g.borsuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra and Differential Equations; Multivariable Calculus; Dynamics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Ma<strong>in</strong> objective of the course is to give the students a strong background <strong>in</strong> fundamental laws of physics<br />
applicable <strong>in</strong> fluid mechanics, applications of fluid mechanics and current measurement techniques.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lectures/practice<br />
� Introduction<br />
� Fluid Statics<br />
� Conservation of mass and momentum<br />
� Bernoulli equation<br />
� Equations of motion <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tegral form<br />
� Equations of motion <strong>in</strong> differential form<br />
� K<strong>in</strong>ematics, vorticity, potential flow<br />
� Potential flow<br />
� Dimensional analysis<br />
� Viscous flows, exact solutions, pipe flow<br />
� Lam<strong>in</strong>ar boundary layers<br />
� Boundary layer solution methods<br />
� Turbulence<br />
� Turbulent <strong>in</strong>ternal and external flows<br />
Laboratory<br />
� Flow Measurements and Calibration of Flow Meters<br />
� Reynolds Experiment and Estimation of the Critical Reynolds Number<br />
� Unsteady Flow Through an Orifice<br />
� Potential Flow<br />
� Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of Energy & Hydraulic Grade L<strong>in</strong>es<br />
� Flow Over Weirs<br />
� Pumps<br />
� Compressible Flow Through Pipe<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Pass all laboratories and tests.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g
a) All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the texts below.<br />
b) Daugherty R.L. “Fluid Mechanics with Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Applications”, McGrew-Hill, Inc., New York 1977<br />
c) Gerhart P.M. „Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics”, Addison-Wesley Publish<strong>in</strong>g Company, New York 1992<br />
d) Nakayama Y. “Introduction to Fluid Mechanics”, Butterworth-He<strong>in</strong>emann, Oxford 1999<br />
1. Course title<br />
Applications of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M010<br />
Lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
There are no prerequisites but some background <strong>in</strong> computer science or geography is helpful.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
By the end of the course, students will be able to:<br />
� Identify, locate, and acquire spatial data pert<strong>in</strong>ent to projects <strong>in</strong> their field of <strong>in</strong>terest, as well as p<strong>in</strong>po<strong>in</strong>t<br />
significant gaps <strong>in</strong> or problems with exist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation.<br />
� Evaluate the appropriateness of the exist<strong>in</strong>g data sources for use <strong>in</strong> a project.<br />
� Understand the data creation process and create simple data sets and/or add to exist<strong>in</strong>g data<br />
� Create spatial data from tabular <strong>in</strong>formation that <strong>in</strong>cludes a spatial reference<br />
� Perform basic spatial analyses (attribute and spatial queries, buffer<strong>in</strong>g, overlays) as well as l<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g these<br />
methods together <strong>in</strong> a more complex analytical model.<br />
� Create high-quality maps and associated graphics and text that clearly communicate spatial <strong>in</strong>formation and<br />
analyses<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction<br />
� GIS Data and Spatial Models<br />
� Topology and Spatial Operations<br />
� Projections, Scale and Coord<strong>in</strong>ate Systems<br />
� Thematic Mapp<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� GIS Analysis<br />
� Cartography<br />
� Network Model<strong>in</strong>g & Surface Model<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Remote Sens<strong>in</strong>g and Raster Model<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� The Environmental Case for GIS<br />
� Data Storage Strategies<br />
� Enterprise GIS<br />
� GIS Application Development<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
There will be three homework assignments, a group project and two <strong>in</strong>dividual f<strong>in</strong>al projects.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the text below.<br />
Longley P.A. „GIS teoria i praktyka”; eng. „Geographic Information Systems and Science”, PWN, Warszawa
2008<br />
1. Course title<br />
Hydrology and Hydraulics<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M011<br />
Lecture/laboratory/practice ex.<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Advanced knowledge of mathematics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The primary objective is the demonstration and understand<strong>in</strong>g of the fundamental concepts and processes<br />
associated with the hydraulic and water quality design, operation and performance aspects of agriculture<br />
and urban dra<strong>in</strong>age systems. Modell<strong>in</strong>g tools will be used to support the design of urban dra<strong>in</strong>age systems<br />
(<strong>in</strong>cl. pump<strong>in</strong>g stations, overflows, and other flow regulat<strong>in</strong>g structures). The tools will also be used to<br />
develop understand<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> current pollution problems, and to identify mitigation/rehabilitation measures. In<br />
this way, the students will ga<strong>in</strong> a sound understand<strong>in</strong>g of the modell<strong>in</strong>g tools, which can be used to aid<br />
decision-mak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> pollution management, and will get experience <strong>in</strong> the use of modell<strong>in</strong>g tools through<br />
applications with<strong>in</strong> the Integrated Project case studies.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lectures/practice:<br />
� Introduction<br />
� Hydrologic cycle, water balance, precipitation<br />
� Evaporation, transpiration, and <strong>in</strong>filtration<br />
� Direct Surface Runoff Stream flow Measurement Hydrographs<br />
� Unit hydrographs and design Hydrographs<br />
� Flood Frequency Analysis<br />
� Flood Rout<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� Open Channel Flow Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples Uniform Flow and Design of channels<br />
� Critical flow and Gradually varied Flow<br />
� Roadway Dra<strong>in</strong>age System – Culverts Computer model: CulvertMaster<br />
� Urban Hydrology and Urban Dra<strong>in</strong>age Systems<br />
� Computation of Storm water<br />
� Storm Sewers Design, Detention Pond<br />
� Groundwater Flow<br />
� Pressure Flows: Pipe System<br />
� Pumps and Turb<strong>in</strong>es<br />
� Storage and Control Structures<br />
Laboratory:<br />
� Closed-Conduit Flow: Pipe Systems; Frictional Resistance and M<strong>in</strong>or Losses; Pipe Networks; Pumps; Water<br />
Distribution Networks<br />
� Open Channel Flow: Steady Uniform Flow; Flow Through Transitions; Gradually Varied Flow; Rapidly Varied<br />
Flow; Discharge Measurements<br />
� Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Hydrology: Dra<strong>in</strong>age Design; Ra<strong>in</strong>fall-Runoff Predictions; Unit Hydrographs; Design Flood<br />
Frequency Estimation<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
6 quantitative problem sets solved us<strong>in</strong>g Excel or similar program, literature review of relevant technical<br />
journals. 6 quantitative and qualitative lab reports that build toward the design project and follow
ecommended writ<strong>in</strong>g style and format<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the texts below.<br />
a) Philip B. Bedient, Wayne C. Huber: Hydrology and Floodpla<strong>in</strong> Analysis, Prentice Hall, 2002.<br />
b) Mays L.W. „Hydraulic Design Handbook”, McGrew-Hill, Inc., New York 1999<br />
c) Potter T.D. “Handbook of Weather, Climate and Water – Atmospheric Chemistry, Hydrology and Social<br />
Impacts”, Wiley-Interscience 2003<br />
1. Course title<br />
Informatics<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M012<br />
Lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
2<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
4<br />
60<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
None<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Upon complet<strong>in</strong>g the course, the students will be able to deal with real-life programm<strong>in</strong>g problems. The<br />
course will <strong>in</strong>troduce programm<strong>in</strong>g concepts with use MS Visual C++ 2008. This course uses many examples<br />
to expla<strong>in</strong> the theoretical material, and <strong>in</strong>cludes many suggestions for practical use of the C++.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction<br />
� Hardware<br />
� Operat<strong>in</strong>g systems<br />
� W<strong>in</strong>dows applications<br />
� Algorithms applied to eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
� C++ language with use MS Visual C++ 2008<br />
� History, Characteristics of the language, A simple program, Stages of program development.<br />
� Variables<br />
� Units of memory, Representation of numbers <strong>in</strong> memory, Variable types <strong>in</strong> C++, Variables – Declaration and<br />
Usage, Assign<strong>in</strong>g values to variables, I/O - pr<strong>in</strong>tf(), scanf(), Type modifiers, Type conversion, Overflow.<br />
� Expressions and Operators<br />
� Expressions, Operators , Some standard library functions: getchar(), putchar(), Random<br />
numbers.<br />
� Flow Control – Conditions<br />
� if statement, Conditional operator, Nested if, switch statement, break – cont<strong>in</strong>ue.<br />
� More Flow Control – Loops<br />
� Arrays and Str<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
� Arrays, Multidimensional arrays, Str<strong>in</strong>gs – arrays of characters, Library functions for manipulat<strong>in</strong>g str<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
� Functions<br />
� Functions , Pass<strong>in</strong>g<br />
parameters , Scope and visibility, Lifetime of variables.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Assignments are of two types: labs and homework. Labs are to be completed <strong>in</strong> the lab section itself, with<br />
some write-up afterward. Homework is to be done follow<strong>in</strong>g the lab section, where practice problems will<br />
be discussed.
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the texts below.<br />
a) S. Walton, 1997, Computer Fundamentals,<br />
b) D.S.Malik, 2002, C++ Programm<strong>in</strong>g: From Problem Analysis to Program design<br />
c) Horton, Beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g Visual C++ 2008, Wiley Publish<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong>c.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Meteorology and Climatology<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M013<br />
Lecture/practice/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
3<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra and Differential Equations; Multivariable Calculus; Dynamics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
This course aims at develop<strong>in</strong>g a sound understand<strong>in</strong>g of the physical processes that <strong>in</strong>fluence weather and<br />
climate. Students will be able to acquire the basic skills used <strong>in</strong> meteorology and climatology.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction; Meteorology and climatology as sciences<br />
� The Earth System; Atmosphere and its features<br />
� Basic meteorological elements and their climatological characteristics<br />
� Atmospheric Thermodynamics, Radiative Transfer; Atmospheric Chemistry<br />
� Cloud Microphysics, Atmospheric Dynamics; General atmospheric circulation<br />
� Weather Systems; Atmospheric Boundary Layer<br />
� Climate Dynamics; Basic climate-form<strong>in</strong>g factors<br />
� Climate change; Impacts of climate change<br />
� Paleoclimate; Different sources of meteorological data and <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
� Weather forecast; Climate models; Climate scenarios<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Formal assessment <strong>in</strong>cludes a Mid-Term Test and a F<strong>in</strong>al Test. Both these tests are comprehensive and cover<br />
the entire course material up to that date, from lectures, exercises and read<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the texts below.<br />
Potter T.D. “Handbook of Weather, Climate and Water – Atmospheric Chemistry, Hydrology and Social<br />
Impacts”, Wiley-Interscience 2003<br />
1. Course title<br />
Pollution Diffusion <strong>in</strong> Atmosphere<br />
2. Course code<br />
M014<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week 9. Number of hours per semester
3 45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Elementary knowledge on flow and diffusion <strong>in</strong> boundary layer of atmosphere.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Basic knowledge on the ma<strong>in</strong> problems of air pollution, air pollution spread<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> atmosphere, dry and wet<br />
deposition, chemical reactions and possibilities of air pollution modell<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Sources of air-pollution, air-pollution spread<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the earth atmosphere,<br />
� Dry and wet deposition, types of anthropogeneous compounds,<br />
� Bases of their chemistry,<br />
� Space scal<strong>in</strong>g of air-pollution transport,<br />
� Lagrangian and Eulerian models, plume models,<br />
� Puff models, dispersion model<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
� Practical application of Gaussian models,<br />
� Types of meteorological conditions for air-pollution spread<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
� Effects of air-pollution on meteorological processes.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Formal assessment <strong>in</strong>cludes a Mid-Term Test and a F<strong>in</strong>al Test. Both these tests are comprehensive and cover<br />
the entire course material up to that date, from lectures, exercises and read<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the texts below.<br />
a) Lyons T.J., Scott W.D.: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Air Pollution Meteorology, Belhaven Press, London 1990<br />
He<strong>in</strong>sohn R.J., Kabel R.L.: Soures and Control of Air Pollution, Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River , New Jersey<br />
1996.<br />
b) Potter T.D. “Handbook of Weather, Climate and Water – Atmospheric Chemistry, Hydrology and Social<br />
Impacts”, Wiley-Interscience 2003<br />
c) Ramaswami A. „Integrated environmental model<strong>in</strong>g – Pollutant Transport, Fate and Risk <strong>in</strong> the<br />
Environment”, Wiley 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Spatial Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Urban Design<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M015<br />
Lecture<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jacek Wydrych; j.wydrych@po.opole.pl; +48-77-4006313; +48606240087<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
None<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The subject extends knowledge from fields of study of land-use plann<strong>in</strong>g and urbanismus and is optional <strong>in</strong><br />
terms of academic specialization <strong>in</strong> regional economy and public adm<strong>in</strong>istration. The purpose of the course<br />
is to develop a deeper understand<strong>in</strong>g of the processes and actors which determ<strong>in</strong>e urban and regional<br />
development, and how these affect plann<strong>in</strong>g practice. After complet<strong>in</strong>g the course, the student shall be able<br />
to evaluate and critically analyse plann<strong>in</strong>g practice <strong>in</strong> Poland, Europe and elsewhere.
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Spatial conjunctions of society development (space and time like essential entities and progress parameters<br />
of human society; historical development, current situation and evolutional tendency <strong>in</strong> global, national and<br />
regional criteria, especially <strong>in</strong> central Europe, spatial consequences of globalization)<br />
� Settlement of Poland (structure of residential system, mutual relations of seats; town-plann<strong>in</strong>g and build<strong>in</strong>g<br />
structure of seats, use of territory; <strong>in</strong>ternational confrontation, especially with neighbour<strong>in</strong>g states;<br />
settlement changes <strong>in</strong> conditions)<br />
� Settlement system and towns theory (urbanization, suburbanization, des-urbanization, re-urbanization)<br />
� Typology of town agglomerations and towns <strong>in</strong> Europe and <strong>in</strong> Poland (factor affect<strong>in</strong>g settlement and town<br />
development; tools for purposeful <strong>in</strong>teraction development of municipal system and towns; resident axis<br />
and centre seats,"network of towns"; relation between towns and its background)<br />
� Function of towns, functional, town-plann<strong>in</strong>g and build<strong>in</strong>g structure of towns (town like grown organism;<br />
urban analysis of towns; zon<strong>in</strong>g and draft "towns of short routes"; town-plann<strong>in</strong>g structure of contemporary<br />
big towns <strong>in</strong> Poland and parameters of their parts, morphology of towns)<br />
� Characteristic of the ma<strong>in</strong> functional components of towns and their mutual connections (a town like place<br />
of residence and workplace, rest<strong>in</strong>g-place and recreation, centre of adm<strong>in</strong>istration, culture and education<br />
and their operational and town-plann<strong>in</strong>g connections) 7) Characterization of "technical" components of<br />
towns" (technical <strong>in</strong>frastructure, traffic roads and arrangements, telecommunication)<br />
� Rural space and rural seats and landscape (typology of rural space and rural seats and their functional,<br />
town-plann<strong>in</strong>g and build<strong>in</strong>g characteristics, structure of land and changes <strong>in</strong> its arrangements and use)<br />
� Land-use plann<strong>in</strong>g like <strong>in</strong>strument of regulation development, arrang<strong>in</strong>g seats and land and relation to other<br />
territorial relevant k<strong>in</strong>ds of plann<strong>in</strong>g (relation to territorial plann<strong>in</strong>g and develop<strong>in</strong>g programs on level of<br />
regions and municipalities; territorial connections develop<strong>in</strong>g plan corporations and <strong>in</strong>stitutions; land-use<br />
plann<strong>in</strong>g and landed modifications; land-use plann<strong>in</strong>g and branch plann<strong>in</strong>g - <strong>in</strong> sector of agriculture and<br />
wood economy, transport and technical <strong>in</strong>frastructure, liv<strong>in</strong>g and civic equipments and services)<br />
� Systematics spatially relevant plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> European union - divergences of spatial plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Germany and<br />
France and land-use plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Poland, territorial basic <strong>in</strong>formations for cross-border cooperation;<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation system and land-use plann<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Formal assessment <strong>in</strong>cludes a Mid-Term Test and a F<strong>in</strong>al Test. Both these tests are comprehensive and cover<br />
the entire course material up to that date, from lectures and read<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
All read<strong>in</strong>gs will be scanned <strong>in</strong>to the course. If students are unhappy with the quality of scans then they are<br />
advised to purchase the texts below.<br />
a) G<strong>in</strong>droz R. “The Urban Design Handbook: Techniques and Work<strong>in</strong>g Methods”, Norton & Company, New York<br />
2003<br />
b) Miller D. “Urban Environmental Plann<strong>in</strong>g: Policies, Instruments, and Methods <strong>in</strong> an International<br />
Perspective”, Ashgate Publish<strong>in</strong>g, Ltd., 2005<br />
c) Adams N. “Regional Development and Spatial Plann<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> an Enlarged European Union”, Ashgate Publish<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Ltd., 2006<br />
1. Course title<br />
Numerical Method <strong>in</strong> Mechanics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M016<br />
Laboratory<br />
4. Type of course 5. Semester<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
Prealim<strong>in</strong>ary (basic and Intermediate)<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Cyprian T. Lachowicz, e-mail: c.lachowicz.@po.opole.pl
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematics, Mechanics, Strength of Materials<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ite Element Method is part of Numerical Method <strong>in</strong> Mechanics.<br />
In range of the laboratory, students learn about software programme Femap NX Nastran or Patran/ Nastran<br />
while perform<strong>in</strong>g projects concern<strong>in</strong>g the analysis of stress and deformation state <strong>in</strong> different structures and<br />
structural members.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introductory meet<strong>in</strong>g. Presentation of the software programme Femap NX/Nastran Stress and stra<strong>in</strong> analysis<br />
with the application of Nastran programme<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>ear static analysis of a simply supported truss.<br />
� Analysis of a Beam Model .<br />
� Analyz<strong>in</strong>g Buckl<strong>in</strong>g for a Bracket<br />
� Creat<strong>in</strong>g and Mesh<strong>in</strong>g a Solid Model<br />
� Analyz<strong>in</strong>g an Axisymmetric Model<br />
� Plastic Deformation of Rod -Nonl<strong>in</strong>ear Material<br />
� Gap Contact - Cantilever Beam<br />
� Large Deformation – Cantilever Beam<br />
� Surface to Surface Contact - Advanced Nonl<strong>in</strong>ear<br />
� Analysis of a Simple Assembly<br />
� Thermal Stress Analysis -Mount<strong>in</strong>g Plate<br />
� Direct Transient and Modal Analysis – H<strong>in</strong>ge Model<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Form of Assessment Laboratory: Cont<strong>in</strong>uous assessment of reports (LR)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
English manuals for all exercises shall be provided<br />
1. Course title<br />
Build<strong>in</strong>g Structures<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M017<br />
Lecture+exercise+labolatory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2+2+1<br />
75<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda, t.lagoda@po.opole.pl ; Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat, k.walat@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge on mechanics, strength of materials<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Some materials applied <strong>in</strong> build<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dustry. General rules of build<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Elements of build<strong>in</strong>gs,<br />
basic terms, k<strong>in</strong>ds and aims: foundation trenches and foundations, walls and floors, roofs and dra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g of<br />
water, water, sewage and gas <strong>in</strong>stallations, stairs and communication systems. Load<strong>in</strong>g of build<strong>in</strong>g<br />
structures. Connections of build<strong>in</strong>g structures. Constructional system and stiffness of the build<strong>in</strong>g. Build<strong>in</strong>g<br />
baffles and their requirements. Ventilation and combustion ducts. Constructions made of bricks, re<strong>in</strong>forced<br />
concrete, steel and wood. Technical specifications of build<strong>in</strong>g utilization<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test, presentations, labolatory<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer
1. Course title<br />
Mechanics<br />
2. Course code<br />
M018<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2+2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda, t.lagoda@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture+exercise<br />
5. Semester<br />
2<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Statics, k<strong>in</strong>ematics and dynamics of the particle and particle system. Equilibrium of plane and spatial<br />
systems (determ<strong>in</strong>ation of unknown support quantities). Static analysis of beams, pillars, frames and<br />
frameworks. K<strong>in</strong>ematics and foundations of rigid body dynamics. Resultant motion. Coriolis acceleration.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test, calculations<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M019<br />
Lecture, project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
4<br />
60<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda, t.lagoda@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mechacs, strength of materials, graphisc<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Theory of mach<strong>in</strong>es – some chosen problems. Fundamentals of structure theory. Fundamentals of fatigue<br />
strength and fatigue calculations. Elements of tribology. Jo<strong>in</strong>ts. Pipel<strong>in</strong>es and valves. Flexible elements.<br />
Shafts and axles. Coupl<strong>in</strong>gs. Brakes. Mechanical transmissions. Operation and reliability of mach<strong>in</strong>e and<br />
devices. Algorithms of design<strong>in</strong>g. Fundamentals of optimization. Simulation of mechanical systems <strong>in</strong><br />
mach<strong>in</strong>e build<strong>in</strong>g – digital simulation. Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g data bases. Advanced methods of computer-aided<br />
design<strong>in</strong>g (CAD).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mach<strong>in</strong>e Life<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M020<br />
Lecture+labolatory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2+2<br />
60<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda, t.lagoda@po.opole.pl; Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat, k.walat@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge of mechanics, strength of materials<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of standard fatigue characteristics. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the cyclic stra<strong>in</strong> curve and its modell<strong>in</strong>g<br />
with the Ramberg-Osgood equation. Investigations of notch <strong>in</strong>fluence on fatigue life of elements under<br />
simple load<strong>in</strong>gs. Schematization of random histories of service load<strong>in</strong>gs, damage accumulation and fatigue<br />
life calculations. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of fatigue life of welded jo<strong>in</strong>ts under simple load<strong>in</strong>gs. Simulation of service<br />
load<strong>in</strong>gs with the computer generator of random signals. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of fatigue life under constantamplitude<br />
and random load<strong>in</strong>gs with mean stresses. Fatigue life of materials under constant-amplitude<br />
bend<strong>in</strong>g and torsion with phase displacement. Investigations of notch <strong>in</strong>fluence on fatigue life under<br />
complex load<strong>in</strong>gs. Investigations of <strong>in</strong>fluence of correlation between stress state components on fatigue life.<br />
Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of fatigue life of welded jo<strong>in</strong>ts tak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to account the fictitious notch radius. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
of the expected position of the fatigue fracture plane with the damage accumulation method. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
of fatigue life with the spectral method. Fatigue tests under polyharmonic load<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Strength of Materials<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M021<br />
Lecture, exercise, labolatory<br />
4. Type of course 5. Semester<br />
3<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2+2+1<br />
75<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda, t.lagoda@po.opole.pl, Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat, k.walat@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge of mechanics<br />
13. Objectives of the course
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
State of stresses and shifts of beams and bars. K<strong>in</strong>ematics and foundations of rigid body dynamics.<br />
Permissible stresses. Limit<strong>in</strong>g load capacity and relations between the stress and stra<strong>in</strong> states. Strength<br />
hypotheses. Analysis of strength of mach<strong>in</strong>e elements. L<strong>in</strong>ear-elastic systems. Loss of stability of bar<br />
systems. Strength analysis of th<strong>in</strong>-walled plates and shells.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test, calculations and experiment<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Weld<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course code<br />
M022<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda, t.lagoda@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lecture<br />
5. Semester<br />
3 or 4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Characteristic of weld<strong>in</strong>g processes. Gas and electrical weld<strong>in</strong>g. K<strong>in</strong>ds of electrical weld<strong>in</strong>g. Preparation of<br />
jo<strong>in</strong>ts for weld<strong>in</strong>g. Weld<strong>in</strong>g positions and production schedule. Nam<strong>in</strong>g conventions and classification of<br />
weld<strong>in</strong>g processes. Requirements and qualifications (procedures, welders, operations). Quality control.<br />
Thermal phenomena and strength of materials. Weld<strong>in</strong>g. Functional quality and control, weld<strong>in</strong>g mach<strong>in</strong>e<br />
and plant; Laboratory diagnostic. Weld<strong>in</strong>g jo<strong>in</strong>ts as dual stress concentrators – geometrical and structural.<br />
Variation of the structure and residual stresses.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
test<br />
1. Course title<br />
Introduction to Mechatronics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M023<br />
lecture, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
2<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English, Polish<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Roland Pawliczek, D.Sc , e-mail: r.pawliczek@po.opole.pl; Mikolajczyka 5, 45-271 Opole, Poland<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic of: mechanics, mathematics, electrical and electronic eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Integration of electrical and electronic eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, computer technology and control eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g with<br />
mechanical eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the design, manufacture and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of a range of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g products and<br />
processes. Electro-mechanical devices, computer <strong>in</strong>terfac<strong>in</strong>g, real-time operat<strong>in</strong>g systems and control<br />
systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture: Basic structure of mechatronics systems, Mechatronics concept of design process. Mechatronics<br />
systems simulation. Electromechanical, hydraulic and piezoelectric actuators; <strong>in</strong>tegrated drives. Sensors.<br />
Signals: characteristics, measurement and analysis. System response. Basic of digital control: P, PI, PID<br />
controllers. Stability of the system.<br />
Laboratory: Functional description of mechanics system and their modernization to the mechatronical one.<br />
Control system of the step motor. DC motor speed model<strong>in</strong>g. Measurement and analysis of the signals.<br />
Characteristics of the first and second order systems. Step and dynamic response of the system. Digital<br />
control systems: P, PI, PID controls.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Laboratory report, project, presentation.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Membrane Processes<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M024<br />
lecture, exercise, laboratory, sem<strong>in</strong>ar, design work<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
8<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
lecture (2h),<br />
lecture (30h),<br />
exercise (1h)<br />
exercise (15h)<br />
laboratory,(1h)<br />
laboratory,(15h)<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar (1h)<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar (15h)<br />
design work (1h)<br />
design work (15h)<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Małgorzata Płaczek PhD Eng., email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl; Department of Chemical and Process<br />
Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give the students a deeper <strong>in</strong>troduction to the theory of membrane processes, to<br />
acquire advanced separation processes knowledge. Student capture of skill of appo<strong>in</strong>ted the fundamental<br />
quantities described the separation processes. Recognition of construction and methods of design and<br />
build<strong>in</strong>g membrane modulus<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Fundamentals of membrane processes: def<strong>in</strong>ition, separation mechanism<br />
� Classification and proprieties of membranes<br />
� Mechanism of mass transport<br />
� Disadvantageous phenomena <strong>in</strong> membrane processes (foul<strong>in</strong>g, scal<strong>in</strong>g, Donnan effect, concentration<br />
polarization)<br />
� Classification and characteristics of pressure-driven membrane processes: (micro-, ultra, nanofiltration and<br />
reversed osmosis)<br />
� Classification and characteristics of concentration driven membrane processes (dialysis, electrodialysis,<br />
permeation, pervaporation)<br />
� Membranes <strong>in</strong> bioreactors and hybrid processes
� Characterization of membrane processes with the eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and economic aspects of device performance,<br />
device and module design<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
lecture: <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations, exam- test<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (10 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
consultations<br />
design work: study of membrane modulus project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g (zalecane lektury i materiały pomocnicze)<br />
a) Membrane process, Rautenbach R., WNT, Warsaw, 1996<br />
b) Handbook of <strong>in</strong>dustrial membrane technology m. Porter , William Andrew publish<strong>in</strong>g, 2008<br />
c) Microfiltration and ultrafiltration: pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and applications. Zydney, Andrew L.; Zeman, Leos J., New York,<br />
1996<br />
d) Basic pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of membrane technology (2 ed.), Mulder, Marcel, Kluwer Academic, Spr<strong>in</strong>ger, 1996<br />
e) Membrane Science and Technology, Osada Y., Nakagawa T., New York, Marcel Dekker, Inc,1992<br />
f) Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and Applications, Zeaman, Leos J., Zydney, Andrew L., New York,<br />
Marcel Dekker, Inc,1996<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environment Protection<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M025<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture/other<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1 hour of lecture/2 hours of other form of class<br />
15 + 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Anna Kuczuk PhD, a.kuczuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basic knowledge of ecology, connections between environment and human activity<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Assimilation and consolidation of chosen <strong>in</strong>formation <strong>in</strong> scope of environment menaces, and possibilities of<br />
environmental protection <strong>in</strong> many areas of human activity. Ability to f<strong>in</strong>d out and estimate some<br />
environment menaces.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program (program nauczania)<br />
Lecture<br />
���� Law basis of environmental protection.<br />
���� Strategy of susta<strong>in</strong>able development <strong>in</strong> global and local area.<br />
���� Characteristic of environmental components.<br />
���� Air protection – ma<strong>in</strong> reasons of air pollution (<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g noise) and ways of protection.<br />
���� Soil proptection – ma<strong>in</strong> reasons of soil pollution and ways of protection.<br />
���� Waste management – k<strong>in</strong>ds of watses, and ways of use and neutralize.<br />
���� Water protection – ma<strong>in</strong> reasons of water pollution and ways of protection.<br />
���� Environment monitor<strong>in</strong>g – aims and scope.<br />
���� Methods of environmental-tests tak<strong>in</strong>g for analysis purposes.<br />
���� Cost-benefit analysis, methods of environmental valorization;<br />
���� Environment protection <strong>in</strong> agricultural area.<br />
���� Nature 2000 areas.<br />
Other class<br />
���� Trip to organic farm – ecological education <strong>in</strong> farm, environmental protection <strong>in</strong> farm;<br />
���� Model of ecological activity – waste management company analysis.
���� Model of ecological activity –“Green-schools” activity analysis.<br />
���� Model of ecological activity – sewage treatment plant.<br />
���� Model of ecological activity – delivery of eco-food.<br />
���� Didactic films (x2) and discussion.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test <strong>in</strong> writ<strong>in</strong>g (lecture), mak<strong>in</strong>g correct exercise (other k<strong>in</strong>ds of class).<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Swanson T., Johnson S. Global environmental problems and <strong>in</strong>ternational agreements. The economics<br />
<strong>in</strong>stitution build<strong>in</strong>g, Edward Elgar, 1999<br />
b) New tools for environmental protection: education, <strong>in</strong>formation and voluntary measures (onl<strong>in</strong>e free -<br />
http://www.nap.edu/catalog);<br />
c) http://www.ecosystemvaluation.org/<br />
1. Course title<br />
Organization of Agricultural Production and Services<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M026<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture/other<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
7<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1 hour of lecture/1 hour of another k<strong>in</strong>d of class<br />
15 + 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Anna Kuczuk PhD, a.kuczuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basic knowledge of economy, management, plant and animal production<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Assimilation and consolidation of fundamental notions and rights <strong>in</strong> scope of agricultural organization,<br />
economic accountand services connected with agriculture. The ability to count a f<strong>in</strong>ancial results and<br />
plann<strong>in</strong>g of production processes <strong>in</strong> agriculture.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture<br />
���� Fundamental notions used <strong>in</strong> organization and economics’ agriculture. Characterization of production<br />
factors and farm<strong>in</strong>g resources, rationality of management <strong>in</strong> agribus<strong>in</strong>ess;<br />
���� Production process In agriculture – basis categories of production, divisions and production’s branches,<br />
production’s activity <strong>in</strong> farm, specification ofagricultural production <strong>in</strong>tensity, specialization of production,<br />
simplification of production, concentration of production;<br />
���� Fundamental organization-economics notions of plant production – mean<strong>in</strong>g and specifiti of crop<br />
production, structure of agricultural lands and sow<strong>in</strong>g, harvest and yields, crop-rotation, fertilization ;<br />
���� Fundamental organization-economics notions of animal production – livestock population, rotation of herd,<br />
prelim<strong>in</strong>ary and balance of manure, prelim<strong>in</strong>ary and balance of fodder, <strong>in</strong>tensity of of animal production;<br />
���� Economics and organization of work <strong>in</strong> agriculture – k<strong>in</strong>ds of work, rules of rational work’s organization,<br />
rules of work statnarization, plann<strong>in</strong>g of live and non-live work, work gratification a<strong>in</strong> agriculture;<br />
���� Mechanization <strong>in</strong> agriculture – level of work mechanization <strong>in</strong> agriculture, <strong>in</strong>dex of mechanization, rules of<br />
equipment of farms <strong>in</strong> agricultural mach<strong>in</strong>es;<br />
���� Agribus<strong>in</strong>ess – sett<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong>terstructure, production and trade <strong>in</strong>tegration <strong>in</strong> agribus<strong>in</strong>ess. Agricultural<br />
services – agricultural services organization, agricultural market ;<br />
���� Analysis of production processes with special attention f<strong>in</strong>ancial analysis - farm f<strong>in</strong>alncial balance, account<br />
results, <strong>in</strong>dex analysiss of account balance, cash-flow.<br />
Other lass<br />
���� Farm territory – calculation of factors of fields shape. Organization of agricultural land. Count<strong>in</strong>g of<br />
agriculturaal lands structure and sstructure of total area, measure of soil quality;<br />
���� Count<strong>in</strong>g and analysis of sow<strong>in</strong>g structure, share of plants mak<strong>in</strong>g the soil more fertile, count<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>tesity of
crop production;<br />
���� Study of crop-rotation, qualification of fertilization level;<br />
���� Count<strong>in</strong>g of example of livestock rotation, prelim<strong>in</strong>ary of fodder and manure balance;<br />
���� Count<strong>in</strong> of work resource <strong>in</strong> farm;<br />
1. Amortization;<br />
2. Farm economic account - count<strong>in</strong>g of profits and direct surplus.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test <strong>in</strong> writ<strong>in</strong>g (lecture), mak<strong>in</strong>g correct exercise (other k<strong>in</strong>d of class).<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Agriculture and the economy(http://economics.about.com/od/americanagriculture/a/agriculture.htm)<br />
b) http://aphg.jhsph.edu/<strong>in</strong>dex.cfm;<br />
c) Karl A. Fox (1987), Agricultural Economics, The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics, v. 1, pp. 55-62.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M027<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lecture, exercise, laboratory, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
lecture (2h),exercise (1h)<br />
lecture (30h), exercise (15h)<br />
10. laboratory,(1h), sem<strong>in</strong>ar (1h)<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
laboratory,(15h), sem<strong>in</strong>ar (15h)<br />
Małgorzata Płaczek PhD Eng., email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give the students a deeper <strong>in</strong>troduction to the theory of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, to<br />
acquire advanced process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g knowledge and expose students to general laboratorial techniques<br />
related to mixture distillation process, dry<strong>in</strong>g of solids, mix<strong>in</strong>g process and many other unit operations.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g equipment<br />
� Selected unit operations<br />
-filtration process<br />
-mix<strong>in</strong>g process<br />
-fluidization process<br />
-dry<strong>in</strong>g process<br />
-separation processes<br />
-heat and mass transfer processes<br />
-adsorption and absorption<br />
� Projections view of fluid flow (flow patterns, pressure drop)<br />
� Materials treatment<br />
� Special processes of gas removal (dry and wet dust clean<strong>in</strong>g, absorption process <strong>in</strong> fluidization column,<br />
bubbles column, scrubbers with packed beds, elements of apparatuses construction)<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
lecture: exam-test, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (10 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
consultations<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g
a) Elements of heat transfer, Bayazitoğlu Y., Özişik M. N., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.<br />
b) Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, Frank P., Incropera [iet all.]. - 6th ed. - Hoboken, NJ, John Wiley &<br />
Sons, cop. 2007. - XXV, [1], 997 s.<br />
c) Interfacial Transport Phenomena, Slattery J. C., Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Verlag, New York Inc., 1990<br />
d) Unit Operations and Processes <strong>in</strong> Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Reynolds and Richards, 1996, PWS Publish<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Second Edition.<br />
e) Handbook of Multiphase Systems / Schriftl. Gad Hetsroni. - New York, McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1982. - XX,<br />
1503 s.<br />
f) Unit Operations of Chemical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g / Warren Lee McCabe, Julian Cleveland Smith [et all.], International<br />
Student Edition. - 3 ed. – Tokyo, McGraw-Hill Kogakusha 1976. - VIII, [1], 1028 s<br />
g) Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g L. Pawlowski, Taylor & Francis, 2008<br />
1. Course title<br />
Design: Cool<strong>in</strong>g and gas scrubb<strong>in</strong>g removal <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M028<br />
project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
V and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
project (1h)<br />
project (15h),<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Małgorzata Płaczek PhD Eng., email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The goal of this course is to give the students <strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong>to the methodology that is used <strong>in</strong> process plant<br />
design and the various phases the work goes through. The aim of this course is to expose students to general<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g design work of special k<strong>in</strong>ds of <strong>in</strong>dustrial <strong>in</strong>stallation related to calculation of heat and mass<br />
transfer, fluid flows, the selection of different elements of apparatuses equipment (pip<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
<strong>in</strong>strumentation) and f<strong>in</strong>ally preparation of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g of designed <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the medium proprieties (water, steam, condenser)<br />
� Calculation of heat exchanger (heat transfer area, heat exchangers type selection)<br />
� Calculation of scrubber (diameter and high of scrubber, check on holdup, maximum gas velocity)<br />
� Calculation and selection of pipes diameter as <strong>in</strong>stallation elements.<br />
� Selection of scrubber device (selection of type of liquid collector and redistributors, bed limiter, droplet<br />
separator)<br />
� Selection of equipment to the <strong>in</strong>stallation (flange to pipes, bottoms to scrubber and heat exchanger, support<br />
to <strong>in</strong>stallation elements)<br />
� Calculation of volume of liquid tank, selection of geometry and material<br />
� Calculation of total pressure drop, power and selection of pump<br />
� Realization of draw<strong>in</strong>g of designed <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
project: <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations, active participation under the project, written report <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g process<br />
calculation, eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g of designed <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Materials and tables prepared by lecturer<br />
b) Elements of heat transfer, Bayazitoğlu Y., Özişik M. N., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.<br />
c) Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, Frank P. Incropera - 6th ed. - Hoboken, NJ, John Wiley & Sons, cop.<br />
2007. - XXV, [1], 997 s.<br />
d) Interfacial Transport Phenomena, Slattery J. C., Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Verlag, New York Inc., 1990
e) Handbook of Multiphase Systems / Schriftl. Gad Hetsroni. - New York : McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1982. - XX,<br />
1503 s.<br />
f) Unit Operations of Chemical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Warren Lee McCabe, Julian Cleveland Smith, International Student<br />
Edition. - 3 ed. – Tokyo, McGraw-Hill Kogakusha, 1976. - VIII, [1], 1028 s<br />
1. Course title<br />
Processes and Technology of Production<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M029<br />
Laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
8<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Malgorzata Wzorek PhD Eng.; m.wzorek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Unit operation, chemical and processes technology<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give the students a practical knowledge on Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, and expose<br />
students to general laboratorial techniques as dry<strong>in</strong>g of solids, mix<strong>in</strong>g process and many other eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
processes.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Practical application of production technology<br />
� Material distribution for level replacement, relations demonstrate, formula of preparation to development,<br />
method and techniques <strong>in</strong> process operations.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Active perception under laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Fuels Combustion <strong>in</strong> Industry Process<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M030<br />
Laboratory and Exercises<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
laboratory – 1h; class – 1h<br />
laboratory – 15h; class – 15h<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Malgorzata Wzorek PhD Eng.,e-mail: m.wzorek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics and thermodynamics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give the students a theoretical and practical knowledge of fuels combustion <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>dustry processes, additional expose students to general laboratorial techniques of tak<strong>in</strong>g measurements of
properties of fuels and emissions<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Exersies<br />
� Calculations of high heat value and low heat value of solid, liquid and gases fuels.<br />
� Calculations of dry and humidity combustion gas contents, emission levels.<br />
� Complete combustion and <strong>in</strong>complete combustion<br />
� Energy balance of different boilers<br />
� Efficiency of combustion process<br />
Laboratory<br />
� Def<strong>in</strong>itions of energetic properties of solid fuels: measurement of heat value, measurements of moisture,<br />
ash and voltaire matter contents<br />
� Combustion process and emissions measurements of different k<strong>in</strong>d of solid fuels,<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Exercises: Exam-test<br />
Laboratory: Active perception under laboratory, laboratory report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Warnatz, Jürgen, Combustion: Physical and Chemical Fundamentals- Berl<strong>in</strong>, Spr<strong>in</strong>ger - Verlag, 1999.<br />
b) Niessen, Walter R: Combustion and Inc<strong>in</strong>eration processes: Applications <strong>in</strong> Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, New<br />
York; Basel; Hong Kong, 1995.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Computer Aided Design<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M031<br />
laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
laboratory,(1h)<br />
laboratory,(15h)<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Małgorzata Płaczek PhD Eng., email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics,<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The objective of the course is to make students familiar with professional program systems concern<strong>in</strong>g<br />
design<strong>in</strong>g, construction and operation of mach<strong>in</strong>es elements.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to Fast Track to Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire 3.0<br />
� Edition of constructional models<br />
� Creat<strong>in</strong>g direct attributes<br />
� Sketch<strong>in</strong>g the basic attributes of geometry<br />
� Creat<strong>in</strong>g assembly use constra<strong>in</strong>ts<br />
� Models management<br />
� Creat<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
� Multiply<strong>in</strong>g the sights of constructional models<br />
� Analysis of constructional models<br />
1. Assessment methods<br />
laboratory: have all the <strong>in</strong>dividual projects accepted<br />
2. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Inside Pro/Eng<strong>in</strong>eer Wildfire, Graham Gary, Steffen Dennis, Steffen Dennis, 2003<br />
b) Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Design with Pro/ENGINEER, Mark Archibald SDC, Release 2001<br />
c) Materials prepared by lecturer
1. Course title<br />
Computational Fluid Mechanics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M033<br />
Lecture/exercise/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
II – II sem.<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Grzegorz Borsuk PhD Eng. ; g.borsuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematics, Fluid Mechanic<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Describe flows <strong>in</strong> computational method, <strong>in</strong>troduce the basic techniques used to dicretize l<strong>in</strong>ear partial<br />
differential equations and to analyse convergence and precision of f<strong>in</strong>ite difference schemes for <strong>in</strong>itial value<br />
problems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to numerical calculations. Introduction to computational fluid dynamics.<br />
� Navier-Stokes equation. F<strong>in</strong>ite-difference method. F<strong>in</strong>ite-volume method. F<strong>in</strong>ite-element method.<br />
� Application of CFD.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
F<strong>in</strong>al mark consists of sum of components: tutorials, laboratory, theory for the task and solv<strong>in</strong>g exercises.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Selected topics from Fluid Mechanics and CFD Programs - prepared at the library of Opole University of<br />
Technology.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Gas Dynamic<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M034<br />
Lecture/exercise/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
III - II sem.<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
5<br />
75<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Grzegorz Borsuk PhD Eng. ; g.borsuk@po.opole.pl<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematics, Measurement and Instrumentation<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
Tra<strong>in</strong> students to acquire the knowledge and skill of analyz<strong>in</strong>g different ideal and real gas <strong>in</strong> isentropic flow.<br />
Provide the students with the necessary knowledge and skill to design of compressors, turb<strong>in</strong>e and fan.<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Basic concept thermodynamic and first low of thermodynamic. Second low of thermodynamic. Ideal gas<br />
mixtures, isentropic state equilibrium , special state and Maxwell equilibriums. Real gas mixtures , state
equilibrium , compressibility, specific heats.<br />
Mass Action Low, dissociation, condensations. One dimensional gas dynamics, steady state flow dynamic<br />
equations. Steady state flow energy equations. Euler equation. Sonic velocity and mach number. Energy<br />
equations results.<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
F<strong>in</strong>al mark consists of sum of components: tutorials, laboratory, theory for the task and solv<strong>in</strong>g exercises.<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Selected topics from Gas Dynamic and Fluid Mechanics - prepared at the library of Opole University of<br />
Technology.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Hydraulic and Hydrologic<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M035<br />
Lecture/exercise/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
V<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Grzegorz Borsuk PhD Eng. ; g.borsuk@po.opole.pl<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematics, Measurement and Instrumentation<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the subject is to teach the student the basics of fluid mechanics and the fundamental analysis of<br />
fluid motion, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g the calculus of pressure pipes and free nappe. The students will also be taught the<br />
basic concepts of quantitative hydrology.<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Hydrostatics: Basic equations and calculus of equilibrium and thrust. Fundamental equation of movement of<br />
fluids <strong>in</strong> pipes. Theory of the boundary layer. Study of constant and non-constant movement <strong>in</strong> pipes. Study<br />
of movement <strong>in</strong> free-nappe. Constant motion <strong>in</strong> channels. Fast varied motion (transitions, outlet works, and<br />
spillways).<br />
� Hydrology: Precipitation, evaporation, transpiration and <strong>in</strong>terception. Infiltration and soil humidity. Surface<br />
run-off. Hydrographs. Flood rout<strong>in</strong>g. Basic concepts of underground hydrology. Equations and methods<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
F<strong>in</strong>al mark consists of sum of components: tutorials, laboratory, theory for the task and solv<strong>in</strong>g exercises<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Selected topics from Fluid Mechanics and Hydrology - prepared at the library of Opole University of<br />
Technology.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Hydraulic Mach<strong>in</strong>es<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M036<br />
4. Type of course<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
5<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture/exercise/laboratory<br />
5. Semester<br />
III - II st.<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
75
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Grzegorz Borsuk PhD Eng. ; g.borsuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematics, Measurement and Instrumentation<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
This course <strong>in</strong>troduces the work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of fluid mach<strong>in</strong>es such as pumps and turb<strong>in</strong>es. It’s aimed at<br />
develop<strong>in</strong>g an understand<strong>in</strong>g, from a fluid-mechanics and thermodynamics po<strong>in</strong>t of view, how these devices<br />
work, performs and can be regulated.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Introduction to the hydraulic mach<strong>in</strong>es. Hydraulic mach<strong>in</strong>es types: Turb<strong>in</strong>es and pumps. Fundamentals of<br />
turbomach<strong>in</strong>e theory: momentum pr<strong>in</strong>ciple applied to flow through a rotor; thrust on the rotor; torque<br />
exerted on the rotor; Euler equation for turbomach<strong>in</strong>es; velocity triangles. Axial reaction turb<strong>in</strong>es.<br />
Centrifugal pumps: impeller vanes design; diffuser design. Dimensionless parameters and similarity laws<br />
applied to the design and selection of turbomach<strong>in</strong>es. Volumetric pumps: selection and dynamic<br />
characteristics.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
F<strong>in</strong>al mark consists of sum of components: tutorials, laboratory, theory for the task and solv<strong>in</strong>g exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Selected topics from Hydraulic and Fluid Mechanic - prepared at the library of Opole University of<br />
Technology.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Fundamentals of Chemical and Food Technology<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class:<br />
M037<br />
lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar/exercises<br />
4. Type of course:<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
basic/ <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Barbara Dybek PhD Eng., email: b.dybek@po.opole.pl, Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, tel.: 774006328<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics and physics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introduc<strong>in</strong>g students to specification of large-scale chemical processes. Transferr<strong>in</strong>g, obta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g conditions<br />
allow<strong>in</strong>g chemical reaction to occur from laboratory conditions/scale to <strong>in</strong>dustrial scale.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Process<strong>in</strong>g of natural materials<br />
� The technological diagrams<br />
� The process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of nitrogen<br />
� The process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g of sulfur<br />
� The artificial fertilizers<br />
� The chemical process<strong>in</strong>g of stone coal<br />
� The chemical process<strong>in</strong>g of oil<br />
� The dangerous of wastes materials<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
lectures: <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: essay (8 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g
a) The Chemistry and Technology of Coal; James Speight; CRC Press; 1999<br />
b) Environmental Technology Handbook; Sunggyu Lee; James Speight; CRC Press; 2000<br />
c) J.R.Couper, W.R.Penney; Chemical Process equipment, Elsevier 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Multiphase Flows<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class:<br />
M038<br />
lecture/laboratory/sem<strong>in</strong>ar/exercises<br />
4. Type of course:<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic/ <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2/1/1<br />
30/15/15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Barbara Dybek PhD Eng.; email: b.dybek@po.opole.pl, Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; tel.: +48<br />
774006328<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Unit operations<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introduc<strong>in</strong>g students to basic multiphase flow mechanisms and acquir<strong>in</strong>g skills for calculat<strong>in</strong>g flows<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Two-/ Three - phase flow for gas-liquid and solid flow – map and flow patterns, pressure drop, volume<br />
fraction. Flow <strong>in</strong> microchannel. The thickness of the layer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
lectures: exam-test, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (8 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual<br />
consultations,<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Multiphase Flow Handbook red. Clayton T. Crowe. - Boca Raton : Taylor & Francis : CRC Press, 2006<br />
b) Multiphase Flow Dynamice Vol. 1, 2 Kolev, Nikolay, Berl<strong>in</strong> : Spr<strong>in</strong>ger – Verlag, 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Process Flow Systems<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class:<br />
M039<br />
lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar/exercises<br />
4. Type of course:<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic/ <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1/2/1<br />
15/30/15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. B.Dybek; email: b.dybek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g; tel.: +48774006328<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics and physics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Master<strong>in</strong>g and consolidat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>formation and knowledge related to pump<strong>in</strong>g issues and practical skills for
calculat<strong>in</strong>g pressure drop <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g select<strong>in</strong>g drop pump<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>stallations<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� The systematic of liquids <strong>in</strong> rheology<br />
� The viscosity of newton and non-newton liquids<br />
� The theory of border layer<br />
� The pressure drop of flow liquids <strong>in</strong> pipel<strong>in</strong>es<br />
� The selection of the pumps and ventilators<br />
� The characteristic of pump work<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
lectures: <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: essay (10 pages) or oral presentation of set task, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations,<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Fluid Mechanics, 2 nd ed., White F. M., McGraw-Hill1986<br />
b) Multiphase Flow Dynamice Vol. 1, 2 Kolev, Nikolay, Berl<strong>in</strong> : Spr<strong>in</strong>ger – Verlag, 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Selected Process Techniques<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class:<br />
M040<br />
laboratory/exercises<br />
4. Type of course:<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
V<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic/ <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1/1<br />
15/15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. B.Dybek, email: b.dybek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g , tel.: 774006328<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamentals of mathematics and physics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introduc<strong>in</strong>g students to basic/chosen isolated processes operations applied while <strong>in</strong>dustrial production and<br />
to elementary types of <strong>in</strong>stallations used to realize them.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Fluid flow and heat transfer processes. Cool<strong>in</strong>g and gas scrubb<strong>in</strong>g removal – <strong>in</strong>stallation project. Phase<br />
equilibrium; liquid vapour graphical presentation, distillation of b<strong>in</strong>ary mixtures. Membrane separation.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
exercise: active participation under the exercise, <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Multiphase Flow Handbook red. Clayton T. Crowe. - Boca Raton : Taylor & Francis : CRC Press, 2006<br />
b) Multiphase Flow Dynamic Vol. 1, 2 Kolev Nikolay, Berl<strong>in</strong> : Spr<strong>in</strong>ger – Verlag, 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course code<br />
M041<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
3. Form of class<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
5. Semester<br />
5<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Anna Król , e-mail: a.krol@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of waste, basic knowledge of cement <strong>in</strong>dustry<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course presents technologies, <strong>in</strong>stallations and equipment for waste treatment. This course gives an<br />
<strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong>to the different technologies of us<strong>in</strong>g waste <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustry<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Introduction to waste treatment. Current status. New directions. Waste treatment objectives and methods.<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g of waste <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustry. Waste as m<strong>in</strong>eral addition <strong>in</strong> cement <strong>in</strong>dustry. Waste as alternative fuels <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>dustry. Susta<strong>in</strong>able development. Equipment used <strong>in</strong> waste treatment. Physical processes used <strong>in</strong> waste<br />
treatment. Chemical processes used <strong>in</strong> waste treatment.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Internet resources, and books <strong>in</strong> English about waste treatment recommended by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Food Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Couse Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M042<br />
lecture, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
lecture: 1h<br />
lecture: 15h<br />
laboratory: 1h<br />
laboratory: 15h<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name of lecturer<br />
PhD Eng Dom<strong>in</strong>ika Matuszek, e-mail: d.matuszek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Agricultural and Forest Technology, room: E309a<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge of the bases of chemistry and botany<br />
13. Objective of the course<br />
Basic problems of the food technology. Def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and characteristics of raw materials of the plant and animal<br />
orig<strong>in</strong>. Basic properties of food products<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture:<br />
� Basic def<strong>in</strong>itions of the food technology<br />
� Characteristics of raw materials of the plant orig<strong>in</strong><br />
� Characteristics of raw materials of the animal orig<strong>in</strong><br />
� The food technology as the unit of the activity and basic processes<br />
� The pollution and contam<strong>in</strong>ation of the food<br />
Laboratory:<br />
� Morphology of the air mycelium of chosen mould<br />
� Morphology of yeast<br />
� Comparative analysis the traditional and genetically modified products of the plant<br />
� Analysis of pollut<strong>in</strong>g plant products with computer analysis of the image<br />
15. Assessment methods
Lecture: the oral answer at the end of semester<br />
Laboratory: the grade from the reports after the exercises<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) R. Paul S<strong>in</strong>gh, Dennis R. Heldman Introduction to Food Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
b) S.E. Charm. The fundamentals of food eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. 1964<br />
c) J. E. Lozano, C. Arion, E. Parada-Arias, G. V. Barbosa-Canowas. Trends <strong>in</strong> Food Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Selected Elements of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M043<br />
Lecture and sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
4th or above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture – 2<br />
Lecture – 30<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 1<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. Gabriel Filipczak, prof. OUTech, g.filipczak@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g or Environmental and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g programme<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Profile of this lecture comes to know the some chosen elements of process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g connected with<br />
multiphase fluids flow processes and equipments.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Two-phase flow (8 hours): nature and general application of multiphase flow (2), gas-liquid flow – flow<br />
patterns and pressure drop (2), liquid-liquid flow – flow patterns and pressure drop (1), liquid-liquid-gas flow<br />
– flow patterns and pressure drop (1), multiphase fluids flow – transport <strong>in</strong> pipes (2);<br />
� Two-phase flow processes (14 hours): pool and convective boil<strong>in</strong>g – heat transfer mechanism (4), flow<br />
boil<strong>in</strong>g and evaporation – water and others liquids (4), heat transfer coefficient – the basic method for<br />
calculation (4), project and design exercises (2);<br />
� Modell<strong>in</strong>g of multiphase heat transfer processes (4 hours): basic equations of two-phase flow (2), the<br />
homogenous and separated models (2),<br />
� Practice and applications (4 hours): boilers (2), evaporators (2);<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written and oral assessment, <strong>in</strong>dividual elaborate<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Hestroni G.: Handbook of multiphase systems, Hemisphere Publ. Corp. 1986<br />
b) Brennen C. E.: Fundamentals of multiphase flows, Cambridge Univ. Press 2005<br />
c) Carrad<strong>in</strong>i M. L.: Fundamentals of multiphase flows, University of Wiscons<strong>in</strong> 1997<br />
d) Wolver<strong>in</strong>e Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g Data Book, Research and Development Team 2001<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: power-po<strong>in</strong>t presentation, elaborate and discussion,<br />
1. Course title<br />
Water Technology<br />
2. Course code<br />
M044<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture/labolatory<br />
5. Semester<br />
V<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2/1<br />
30/15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Kłosok-Bazan mail: i.klosok-bazan@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Course of chemistry<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course presents technologies, <strong>in</strong>stallations and equipment for physical, biological and chemical water<br />
treatment. This course gives an <strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong>to the different technologies of municipal and <strong>in</strong>dustrial water<br />
treatment.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Water quality, water analyses, water treatment process: percolation, sedimentation, coagulation, filtration, ion<br />
exchange, aeration, iron and manganese removal, water technology application forms<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test, oral assessment<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Nicholas P. Cheremis<strong>in</strong>off, Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies; The Nalco Water<br />
Handbook - accessible <strong>in</strong> electronic version <strong>in</strong> our library.<br />
17. Lecture: powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion ; laboratory: test of water mak<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> MATLAB<br />
2. Couse Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M045<br />
Laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
I<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name of lecturer<br />
Karolczuk Aleksander, a.karolczuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basis of mathematics<br />
13. Objective of the course<br />
Introduction to high level of programm<strong>in</strong>g, familiarize with professional tools <strong>in</strong> data analysis<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction to Matlab<br />
� Array and matrix operations<br />
� Variables, numbers<br />
� Basic plott<strong>in</strong>g functions<br />
� Programm<strong>in</strong>g with MATLAB<br />
� More advance programm<strong>in</strong>g with MATLAB<br />
� Images, animation and applications<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Gett<strong>in</strong>g Started with MATLAB, version 6, The MathWorks<br />
b) Graeme Chandler, Introduction to Matlab, Mathematics Department, The University of Queensland, February<br />
2000, http://www.eeng.nuim.ie/~semcloone/Teach<strong>in</strong>g/Matlab/mlb.pdf)<br />
c) David F. Griffiths, An Introduction to Matlab, Department of Mathematics, The University Dundee, 2005,
(http://www.maths.dundee.ac.uk/~ftp/na-reports/MatlabNotes.pdf)<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mathematical Statistics<br />
2. Couse Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M046<br />
Lecture, project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture -1h<br />
Lecture – 15h<br />
Project – 1h<br />
Project – 15h<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name of lecturer<br />
Dom<strong>in</strong>ika Matuszek, e-mail: d.matuszek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Agricultural and Forest Technology, room: E309a<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge of mathematics<br />
13. Objective of the course<br />
Acqua<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g the students with the basic problems of agricultural statistics for eng<strong>in</strong>eers, with methodology of<br />
tak<strong>in</strong>g samples, studd<strong>in</strong>g the results, conclud<strong>in</strong>g and statistical model<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture:<br />
� Basic statistical concepts<br />
� Normal schedule<br />
� Probability<br />
� Tak<strong>in</strong>g samples<br />
� Test<strong>in</strong>g hypotheses<br />
� Analysis of the variance<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>ear and non-l<strong>in</strong>ear regression<br />
Project:<br />
� Normal distribution<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>ear regression<br />
15. Assessment methods (metody i formy oceny pracy studenta)<br />
Lecture: oral exam at the end of semester<br />
Project: grade on the basis of design work and written report.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g (zalecane lektury i materiały pomocnicze)<br />
� Delwiche, Lora D. The Little SAS [Statistical Analisis System] Book : a Primer / Lora D. Delwiche, Susan J.<br />
Slaughter. - 4th pr<strong>in</strong>t. - Cary : SAS Institute, 1998.<br />
� Aczel Amir D. Complete Buss<strong>in</strong>es Statistics. 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Methods and Techniques of the Quality Control<br />
2. Couse Code<br />
M047<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours<br />
lecture: 1h,<br />
laboratory:1h<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lecture, laboratory<br />
5. Semester<br />
V and above<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture: 15h<br />
laboratory: 15h
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name of lecturer<br />
Phd Eng Dom<strong>in</strong>ika Matuszek, e-mail: d.matuszek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Agricultural and Forest Technology, room: E309a<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objective of the course<br />
Acqua<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g the students with problems of manag<strong>in</strong>g the quality with agricultural and food products and<br />
methods of their control.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture:<br />
� Basic <strong>in</strong>formation about the quality of the food<br />
� Manag<strong>in</strong>g the quality<br />
� Improv<strong>in</strong>g the quality<br />
� Assur<strong>in</strong>g the quality HACCP, ISO<br />
Laboratory:<br />
� Analysis of errors of the measurement<br />
� Sieve analysis ofgr<strong>in</strong>ded materials gr<strong>in</strong>ded<br />
� Study<strong>in</strong>g the physical properties of the cereal crops gra<strong>in</strong><br />
� Assessment of agricultural and food products qualities with the method of computer analysis of the image<br />
� Analysis of mark<strong>in</strong>g wrapp<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture: written test at the end of the semester<br />
Laboratory: grade from the reports after the classes<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Encyklopedia of Ford Science and Technology. Vol. 1- 4. A-D/ed. Y.H. Hui–New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1992<br />
b) Food Technology and Quality Evaluation: R. Dris, A. Sharma (Eds.); Science Publishers, Inc., Enfield, NH, USA,<br />
2003<br />
1. Course title<br />
Soil Science<br />
2. Couse Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M048<br />
lecture, laboratory, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
lecture: 1h<br />
Lecture: 15h<br />
laboratory: 1h<br />
laboratory: 15h<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: 1h<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: 15h<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name of lecturer<br />
PhD Eng Dom<strong>in</strong>ika Matuszek, e-mail: d.matuszek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Agricultural and Forest Technology, room: E309a<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge from the range of basic issue of ecology.<br />
13. Objective of the course<br />
Acqua<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g the students with bases of pedology, the create soil processes, physical and chemical properties<br />
of soils, the agricultural usefulness of soils. Ability of def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the property of soils on the basis of analysis <strong>in</strong><br />
field and laboratory conditions<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture: basic <strong>in</strong>formation about the soil; rock-form<strong>in</strong>g m<strong>in</strong>erals; mechanical composition of soils; physical<br />
and chemical properties of soils; soil as the biological environment; protection of soils;<br />
Laboratory: mechanical analysis of soils; def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the basic properties of soils; the samples of soil
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: rehabilitation and protection of soils; fertiliz<strong>in</strong>g soils<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture: oral answer at the end of the semester<br />
Laboratory: grade from reports after the exercise<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: grade <strong>in</strong> prepar<strong>in</strong>g on a presentation the paper to given topics (the PowerPo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and<br />
the paper version)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Rattan Lal ed. Encyklopedia of Soil Science. 2005<br />
b) Kim H. Tan. Environmental Soil Science. 2000<br />
c) Kim H. Tan. Soil Sampl<strong>in</strong>g, Preparation, and Analysis. 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environmental Metrology<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M050<br />
lecture/laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Daniel Zając, e-mail: d.zajac@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Physisc for eng<strong>in</strong>eers<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Provide students the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of preparation and implementation of measurement, with particular<br />
emphasis on measurement techniques and <strong>in</strong>struments used <strong>in</strong> eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and environmental protection.<br />
Discussion of specific cases of the measurements.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Introduction to environmental metrology, pressure measurements, temperature measurements, air<br />
humidity measurements, fluid flow and velocity measurements, density measurements, viscosity<br />
measurements, noise measurements<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Fraden J: Handbook of modern sensors: physics, designs and applications, Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Verlag 2004<br />
Webster J.G.: Measurement Instrumentation and Sensors, CRC Press LCC 1999<br />
Liptak B.G: Process measurement and analysis – Instrument eng<strong>in</strong>eers’ handbook, CRC 2003<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Lecture: powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion<br />
Experiments <strong>in</strong> laboratory<br />
1. Course title<br />
Heat<strong>in</strong>g Systems<br />
2. Course code<br />
M051<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lecture/exercises<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week 9. Number of hours per semester
2 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Daniel Zając, e-mail: d.zajac@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Thermodynamic course<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Provide students the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of basic heat<strong>in</strong>g systems, equipment and sensors used <strong>in</strong> heat<strong>in</strong>g systems.<br />
Also student will receive <strong>in</strong>formation about design of such systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture: Introduction: fuels, combustion. Energy balance <strong>in</strong> heat<strong>in</strong>g objects. Heat<strong>in</strong>g systems: boilers, heat<br />
exchangers, <strong>in</strong>stallations, heat<strong>in</strong>g nodes. Heat<strong>in</strong>g pipe network. Preparation of hot water. Water treatment<br />
for heat<strong>in</strong>g systems.<br />
Exercises: heat transfer, combustion, heat exchangers, Wet gases, Gas and steam flow<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
A. Day, M. Ratcliffe, K. Shepherd: Heat<strong>in</strong>g systems, plant and control , Willey-Blackwell 2003<br />
2008 ASHRAE Handbook – Heat<strong>in</strong>g, Ventilat<strong>in</strong>g, and Air-Condition<strong>in</strong>g systems<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Lecture: powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion<br />
1. Course title<br />
Ventilation and Air-Condition<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M055<br />
lecture/exercises<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Daniel Zając, e-mail: d.zajac@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Thermodynamic course<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Provide students the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of basic HVAC systems, their design, standards and most popular technical<br />
solutions for such systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture: Energy conservation and air quality, construction and design of HVAC, ventilation and air<br />
condition<strong>in</strong>g for build<strong>in</strong>gs – methods and requirements, thermal comfort, heat recovery systems, Air<br />
condition<strong>in</strong>g systems - pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of operation, the calculation<br />
Exercises: Basics of air flow <strong>in</strong> channels, Calculations of the ventilation and acoustic silencer selection,<br />
coolers and heat<strong>in</strong>g pumps, dimension<strong>in</strong>g of the HVAC systems<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Wang, S. Handbook of Air Condition<strong>in</strong>g and Refrigeration, McGraw-Hill 2001<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Lecture: powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion
1. Course title<br />
Energy Consumption of Industrial Processes<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M056<br />
lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
4<br />
60<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Daniel Zając, e-mail: d.zajac@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Thermodynamic course, heat transfer, Renewable energy sources, environmental protection<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
To present pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of rational use of energy <strong>in</strong> various sectors of <strong>in</strong>dustry and the possibilities to improve<br />
the current state of energy consumption.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture: Energy production opportunities <strong>in</strong>dustrial purposes, Analysis of the energy management system of<br />
an <strong>in</strong>dustrial plant, energy consumption <strong>in</strong> heavy <strong>in</strong>dustry – selected sectors, Rationalization of steam and<br />
water boilers, and heat transport <strong>in</strong> pipel<strong>in</strong>es, Rationalization of heat exchange systems and cool<strong>in</strong>g, CHP<br />
units, Recovery of waste energy <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>dustry, Environmental effects of changes <strong>in</strong> the energy consumption <strong>in</strong><br />
<strong>in</strong>dustry<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ars: Analysis of energy consumption <strong>in</strong> various <strong>in</strong>dustry sectors, Low-energy technologies, Assessment<br />
of environmental impact of selected <strong>in</strong>dustry sectors<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written test, oral presentation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
G. Salvendy: Handbook of Industrial Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g – Technology and Operations Management, Willey and Sons<br />
2001<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar: powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion<br />
1. Course title<br />
Modern Non-<strong>in</strong>vasive Measurement Techniques for Multiphase Flow Systems<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M054<br />
lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
18. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
19. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
20. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Daniel Zając, e-mail: d.zajac@po.opole.pl<br />
21. Prerequisites<br />
Fluid mechanic, physics<br />
22. Objectives of the course<br />
To present pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of rational use of energy <strong>in</strong> various sectors of <strong>in</strong>dustry and the possibilities to improve<br />
the current state of energy consumption.
23. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Lecture/Sem<strong>in</strong>ars: Multiphase flow systems, parameters to measure, <strong>in</strong>vasive vs. non<strong>in</strong>vasive techniques,<br />
classic visualization techniques, major technical milestones of equipment, classification of techniques,<br />
selected non<strong>in</strong>vasive measurement methods: DPIV, PTV, LDA, PDA, tomography, gamma densimometry,<br />
correlation techniques.<br />
24. Assessment methods<br />
Written test, oral presentation<br />
25. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Chaouki, Larachi, Duduković: Non-<strong>in</strong>vasive monitor<strong>in</strong>g of multiphase flows, Elsevier 1997<br />
26. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar: powerpo<strong>in</strong>t presentation and discussion<br />
1. Course title<br />
Heat and Mass Transfer Operations<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M062<br />
laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
6 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. M.Płaczek ; PhD Eng. B.Dybek<br />
Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
tel.: 774006358, tel.: 774006328,<br />
email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl; b.dybek@po.opole.pl;<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
measurement and <strong>in</strong>strumentation<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give the students a deeper <strong>in</strong>troduction to the theory of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, to<br />
acquire basic process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g knowledge and expose students to general laboratorial techniques related<br />
to heat and mass transfer operations<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
• heat transfer coefficient<br />
• mass transfer coefficient<br />
• distillation process<br />
• membrane separation<br />
• radiant heat dry<strong>in</strong>g<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Elements of heat transfer, Bayazitoğlu Y., Özişik M. N., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1988.<br />
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, Frank P., Incropera [iet all.]. - 6th ed. - Hoboken, NJ, John Wiley & Sons,<br />
cop. 2007. - XXV, [1], 997 s.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mechanical Operations<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M063<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
3. Form of class<br />
laboratory<br />
5. Semester<br />
5 and above
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. M.Płaczek ; PhD Eng. B.Dybek, Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
tel.: 774006358, tel.: 774006328, email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl; b.dybek@po.opole.pl;<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
measurement and <strong>in</strong>strumentation<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to give the students a deeper <strong>in</strong>troduction to the theory of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, to<br />
acquire basic process eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g knowledge and expose students to general laboratorial techniques related<br />
to mechanical operations<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
• phisical properities of liqiud<br />
• separation processes<br />
• pressure drop<br />
• fluidization process<br />
• hydraulic of packed columns<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
laboratory: active participation under the laboratory, written laboratory report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
h) Unit Operations and Processes <strong>in</strong> Environmental Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Reynolds and Richards, 1996, PWS Publish<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
Second Edition.<br />
i) Unit Operations of Chemical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g / Warren Lee McCabe, Julian Cleveland Smith [et all.], International<br />
Student Edition. - 3 ed. – Tokyo, McGraw-Hill Kogakusha 1976. - VIII, [1], 1028<br />
11. 1<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environmental Management<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M052<br />
4. Type of course<br />
optional<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3. Form of class<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
5. Semester<br />
5 and above<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. B.Dybek, Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
tel.: 774006328, email: b.dybek@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basic knowledge of ecology, connections between environment and human activity<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Environmental management means the management, use and environmental renewal. Occurs <strong>in</strong> economic<br />
organizations and <strong>in</strong> the territorial arrangements (regions, districts, municipalities,). There is full <strong>in</strong>tegration<br />
of environmental management with the overall management system <strong>in</strong> the organization. Such <strong>in</strong>tegration<br />
can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed from the implementation of environmental management formal systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
• Quality standards specified for <strong>in</strong>dividual elements of the environment.<br />
• environmental management system<br />
• Emissions standards.
• Standards of product and process<br />
• Technological standards.<br />
• Safety regulations<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (8 pages) or oral presentation of set task,<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Internet resources<br />
1. Course title<br />
Environmental Protection and Monitor<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M053<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
5 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. B.Dybek, Department of Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
tel.: 774006328, email: b.dybek@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basic knowledge of ecology, connections between environment and human activity<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Assimilation of chosen <strong>in</strong>formation <strong>in</strong> scope of environment threats, and possibilities of environmental<br />
protection <strong>in</strong> many areas of human activity.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� environment monitor<strong>in</strong>g – aims and scope<br />
� Technologies of <strong>in</strong>dustry without pollutions<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar: active participation under the sem<strong>in</strong>ar, essay (8 pages) or oral presentation of set task,<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Swanson T., Johnson S. Global environmental problems and <strong>in</strong>ternational agreements. The economics <strong>in</strong>stitution<br />
build<strong>in</strong>g, Edward Elgar, 1999<br />
New tools for environmental protection: education, <strong>in</strong>formation and voluntary measures (onl<strong>in</strong>e free -<br />
http://www.nap.edu/catalog);<br />
1. Course title<br />
Design Work – Installation for Solution Production<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M061<br />
project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
V and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecture<br />
Małgorzata Płaczek PhD Eng., email: m.placzek@po.opole.pl<br />
Department of Chemical and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
12. Prerequisites
Fundamentals of mathematics and Process Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The goal of this course is to give the students <strong>in</strong>sight <strong>in</strong>to the methodology that is used <strong>in</strong> process plant<br />
design and the various phases the work goes through. The aim of this course is to expose students to general<br />
eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g design work of special k<strong>in</strong>ds of <strong>in</strong>dustrial <strong>in</strong>stallation related to calculation of fluid flows, the<br />
selection of different elements of apparatuses equipment (pip<strong>in</strong>g and <strong>in</strong>strumentation) and f<strong>in</strong>ally<br />
preparation of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g of designed <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the medium proprieties (liquids, mixtures)<br />
� Calculation and selection of pipes diameter as <strong>in</strong>stallation elements,<br />
� Selection of mixer (selection of geometry and material, calculation of power demand for mix<strong>in</strong>g)<br />
� Selection of equipment to the <strong>in</strong>stallation (flange to pipes, bottoms to the tank, support to <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
elements)<br />
� Calculation of volume of liquid tanks,<br />
� Calculation of frictional, local, hydrostatic and f<strong>in</strong>ally total pressure drop, power and selection of pump<br />
� Realization of draw<strong>in</strong>g of designed <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
project: <strong>in</strong>dividual consultations, active participation under the project, written report <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g process<br />
calculation, eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g of designed <strong>in</strong>stallation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Materials and tables prepared by lecturer<br />
Handbook of Multiphase Systems / Schriftl. Gad Hetsroni. - New York : McGraw-Hill Book Co., 1982. - XX, 1503 s.<br />
Unit Operations of Chemical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Warren Lee McCabe, Julian Cleveland Smith, International Student<br />
Edition. - 3 ed. – Tokyo, McGraw-Hill Kogakusha, 1976. - VIII, [1], 1028 s<br />
1. Course title<br />
Electrical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Electronics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M057<br />
4. Type of course (typ przedmiotu:<br />
compulsory/elective/ optional)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
laboratory/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
5. Semester (semestr)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English, German<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mariusz Rząsa m.rzasa@po.opole.pl +48-77-4006370; +48602345162<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Elementary knowledge on electrical eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and electronics<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Presentation of basic notions, elements and systems applied <strong>in</strong> electrical eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and electronics, skill <strong>in</strong> recognition<br />
of typical connection systems, mak<strong>in</strong>g simple electric systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Measurements of basic electric quantities and determ<strong>in</strong>ation of measurement uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty. Students learn<br />
pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of operation and service of basic devices for electric measurements. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of frequency<br />
characteristics of typical circuits for alternat<strong>in</strong>g currents <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g RC LC and RL, determ<strong>in</strong>ation of resonance<br />
frequency of LC. Start of simple control systems <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g relays. Students learn how to read simple electric<br />
schemes and how to connect electric circuits. Investigations on rectifier systems – connection of typical<br />
rectifier systems and tests of their action and measurements <strong>in</strong> characteristic po<strong>in</strong>ts of electronic circuits.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Active work of the students on the topics of the classes. Po<strong>in</strong>ts for the students activity dur<strong>in</strong>g the classes.<br />
Laboratory classes for small groups of people allow to obta<strong>in</strong> better results of teach<strong>in</strong>g.
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
To be provided by the teacher<br />
1. Course title<br />
Computer Measurement Systems<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M058<br />
4. Type of course (typ przedmiotu:<br />
compulsory/elective/ optional)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
laboratory/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
5. Semester (semestr)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English, German<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mariusz Rząsa m.rzasa@po.opole.pl +48-77-4006370; +48602345162<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Elementary knowledge on measurements and use of computer devices<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Presentation of the basic notions and elements of the computer measur<strong>in</strong>g systems. Typical DAQ and SCDA systems.<br />
Typical programm<strong>in</strong>g environments of computer measur<strong>in</strong>g systems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Acquir<strong>in</strong>g and acquisition of data us<strong>in</strong>g measur<strong>in</strong>g cards DAQ. Simple handl<strong>in</strong>g of data, spectral analysis FFT,<br />
program calibration of sensors. Design<strong>in</strong>g and programm<strong>in</strong>g of virtual measur<strong>in</strong>g devices. Programm<strong>in</strong>g of<br />
simple-programmable devices PLC and configuration of cooperation of these devices with the system of<br />
visualization and measurement. Computer algorithms of data process<strong>in</strong>g and their application <strong>in</strong> measur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
systems.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Po<strong>in</strong>ts for the students’ activity dur<strong>in</strong>g classes. The laboratory classes for small groups of people should help<br />
the students <strong>in</strong> be<strong>in</strong>g experienced <strong>in</strong> proper application of the devices for electric measurements. Active<br />
work of the students dur<strong>in</strong>g the classes.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
To be provided by the teacher<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M059<br />
4. Type of course (typ przedmiotu:<br />
compulsory/elective/ optional)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
laboratory<br />
5. Semester (semestr)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English, German<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mariusz Rząsa m.rzasa@po.opole.pl +48-77-4006370; +48602345162<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Elementary knowledge on measurements and eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g experiments<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Presentation of the basic subject of experimentation. Typical error analysis. Use the typical <strong>in</strong>strument and
system design.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Acquir<strong>in</strong>g and acquisition of data us<strong>in</strong>g measur<strong>in</strong>g cards DAQ. The nature of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g experiments.<br />
Errors of measurement. Typical <strong>in</strong>strument and system design. Test data check<strong>in</strong>g and rejection and<br />
Statistical data analysis. Graphical presentation of data results.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Po<strong>in</strong>ts for the students’ activity dur<strong>in</strong>g classes. The laboratory classes for small groups of people should help<br />
the students <strong>in</strong> be<strong>in</strong>g experienced <strong>in</strong> proper application of the devices for electric measurements. Active<br />
work of the students dur<strong>in</strong>g the classes.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
To be provided by the teacher<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mechanics Elements and Mach<strong>in</strong>es Design<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M064<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
3/4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class (poziom przedmiotu: basic/<br />
5<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate/advanced)<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda t.lagoda@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Mechanics of elements. Theory of mach<strong>in</strong>es – some chosen problems. Mach<strong>in</strong>es’ design. Fundamentals of<br />
structure theory. Fundamentals of fatigue strength and fatigue calculations. Elements of tribology. Jo<strong>in</strong>ts.<br />
Pipel<strong>in</strong>es and valves. Flexible elements. Shafts and axles. Coupl<strong>in</strong>gs. Brakes. Mechanical transmissions.<br />
Operation and reliability of mach<strong>in</strong>e and devices. Algorithms of design<strong>in</strong>g. Fundamentals of optimization.<br />
Simulation of mechanical systems <strong>in</strong> mach<strong>in</strong>e build<strong>in</strong>g – digital simulation. Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g data bases.<br />
Advanced methods of computer-aided design<strong>in</strong>g (CAD).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Design Work – Individual Report<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M060<br />
4. Type of course<br />
optional<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
3. Form of class<br />
project<br />
5. Semester<br />
5/6<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Tadeusz Łagoda t.lagoda@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Strength of material, Basic of design/Build<strong>in</strong>g structure<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Project of same eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g constructions<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Project of same eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g constructions. It will be mechanical or build<strong>in</strong>g construction.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Structural Mechanics <strong>in</strong> Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M065<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture and des<strong>in</strong>g classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
Initial and <strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Assoc. Prof. Adam Niesłony, PhD Eng.<br />
Department of Mechanics and Mach<strong>in</strong>e Design, Faculty of Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
ul. Mikołajczyka 5, 45-271 Opole, POLAND<br />
tel: +48 (0) 774 006 163, fax: +48 (0) 774 006 343<br />
e-mail: a.nieslony@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic of mathematics (high school level)<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
This course focuses on the fundamentals of structure and design<strong>in</strong>g and bond<strong>in</strong>g that underp<strong>in</strong> materials<br />
science. It is the <strong>in</strong>troductory lecture class for students <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Materials Science and Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Topics <strong>in</strong>clude: models of materials; materials phenomena, such as creep, relaxation, and fatigue; geometry<br />
of the motion and/or deformation of the structure, and conditions of geometric fit, forces on and with<strong>in</strong><br />
structures and assemblages; physical aspects of the structural system (<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g material properties) which<br />
quantify relations between the forces and motions/deformation. Typical case studies: loaded beams, bars,<br />
sections, plates and systems. Real-world applications <strong>in</strong>clude eng<strong>in</strong>eered alloys will be discussed.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
• materials used <strong>in</strong> modern design<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• typical structures and load<strong>in</strong>g conditions<br />
• typical mach<strong>in</strong>e parts, strength of components<br />
• other themes prepared by lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Writen work, active participation <strong>in</strong> laboratory classes<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Hjelmstad K.D.: Fundamentals of Structural Mechanics, Spr<strong>in</strong>ger Science 2005<br />
Lecture notes,<br />
1. Course title
Build<strong>in</strong>g structures-docks and coasts<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M066<br />
Lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
4/5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. Kont. 774006357 B315<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mechanics, <strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Build<strong>in</strong>g eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, civil eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g with special regard of modern technologies and economic conditions.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Design work – <strong>in</strong>dividual report<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M067<br />
project<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
-<br />
6. ECTS credits (liczba punków ECTS )<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
4<br />
60<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion (język nauczania)<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer (nazwisko i kontakt do wykładowcy)<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. Kont. 774006357<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
Strength of material, Basic of design/Build<strong>in</strong>g structure<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
Project of same eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g constructions<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Project of same eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g constructions. It will be mechanical or build<strong>in</strong>g construction.<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mach<strong>in</strong>e life<br />
2. Course Code 3. Form of class )
M068 Lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester (semestr)<br />
optional<br />
3/4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. kont. 774006357<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Design of mach<strong>in</strong>e elements and their life assessment<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Steel structures<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M069<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
4/5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. Kont. 774006357 B315<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
Mechanics, <strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Project on the use of steel structures <strong>in</strong> different work<strong>in</strong>g environment<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Strength of materials<br />
2. Course Code<br />
M070<br />
4. Type of course<br />
optional<br />
3. Form of class<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
5. Semester<br />
3/4
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. Kont. 774006357 B315<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
arithmetical calculations on strength of materials<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
Individual tasks to be calculated by the students<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Structural Design<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M071<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
4/5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
-<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
10. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. + 774006357 B315<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Project on the use of different structural materials<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Technology, economy and organisation of build<strong>in</strong>g site<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
M072<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
4/5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
-<br />
8. Number of hours per week 10. Number of hours per semester
2 30<br />
11. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
12. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Karol<strong>in</strong>a Walat k.walat@po.opole.pl tel. Kont. 774006357 B315<br />
13. Prerequisites<br />
Mechanics, <strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Regulations on health and safety on a build<strong>in</strong>g site, technological requirements and economic conditions<br />
<strong>in</strong> construction process<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
project<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation to be provided by the lecturer<br />
1. Course title<br />
Computer aided programm<strong>in</strong>g of the CNC mach<strong>in</strong>e tools<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Forma of class<br />
M073<br />
lecture/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English or German<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Piotr Niesłony, e-mail: p.nieslony@po.opole.pl<br />
Marian Bartoszuk, e-mail: m.bartoszuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Production and mach<strong>in</strong>e eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g. Information to be provided by the lecturer<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Preparation of NC program for CNC mach<strong>in</strong>e tools basic on the CAM software’s (Mastercam, GTJ)<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Theory of CNC mach<strong>in</strong>e tools. Type of mach<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g centres. Type of control systems. CAM software’s.<br />
Postprocessors. Methods of CNC programm<strong>in</strong>g by us<strong>in</strong>g simulation software’s. Programm<strong>in</strong>g by us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Mastercam software.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Information to be provided by the lecturer<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>formation regard<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>courses</strong> taught at Faculty of Mechanical Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g should be consulted with the<br />
lecturers and/or Faculty coord<strong>in</strong>ator<br />
_____________________________________________________________
FACULTY OF MANAGEMENT<br />
4 Waryńskiego Street 45-047 Opole, Poland<br />
phone: (+48 77) 454 35 33, 453 04 72, phone/fax (+48 77) 453 04 71<br />
e-mail: wz@po.opole.pl, http: www.zarzadzanie.opole.pl<br />
FIELDS OF STUDY � Management (BSc, MSc)<br />
� European Studies (BSc, MSc)<br />
� Adm<strong>in</strong>istration (BSc)<br />
FACULTY DEPARTMENTS � Processes and Products Innovation<br />
� F<strong>in</strong>ance and Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Management<br />
� Market<strong>in</strong>g and Logistics<br />
� Labour Market and Human Capital<br />
� Life-long Learn<strong>in</strong>g and International Studies<br />
� Economics and Regional Research<br />
� Operations Research <strong>in</strong> Management<br />
� Law on Public and Private Economic Activities<br />
� Intellectual Property, Adm<strong>in</strong>istrative and European Law<br />
Regional Policy<br />
� Development Economics and Economic Policy<br />
Faculty Erasmus Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Roman Śmietański, PhD; r.smietanski@po.opole.pl<br />
Course<br />
code<br />
Course Name ECTS credits<br />
ZAL035 Account<strong>in</strong>g and F<strong>in</strong>ance Enterprise 2<br />
ZZL019 Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g 7
ZEL053 Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g and Market Research 3<br />
ZZM042 Clusters and cluster <strong>in</strong>itiatives 3<br />
ZZM001 Concepts of Management 5<br />
ZZL022 Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance 7<br />
ZZM015 Cost Account 4<br />
ZEM002 Culture identities <strong>in</strong> Europe 5<br />
ZAL012 Diritto costituzionale 5<br />
ZEL029 Demographic processes <strong>in</strong> Europe 3<br />
ZPH001 Ecological Reflection 2<br />
ZZL031 Economic Analysis 2<br />
ZZL021 F<strong>in</strong>ancial Accountancy 6<br />
ZEM012 F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statement Standards 3<br />
ZZM019 Forecasts and Simulations 5<br />
ZEL008a Economy I 8<br />
ZEL008b Economy II 8<br />
ZZL007 Fundamentals of Management 8<br />
ZZL016 Human Resources Management (<strong>in</strong> English) 6<br />
ZZL016 Human Resources Management (<strong>in</strong> German) 6<br />
ZEL013 Institutions européennes et le processus de décision 5<br />
ZZM009 Managerial Accountancy 5<br />
ZAL40 Manag<strong>in</strong>g and Adm<strong>in</strong>istration of Local Authority Projects 4<br />
ZAL046 Market<strong>in</strong>g and Market Research 4<br />
ZZL020 Market<strong>in</strong>g Research 7<br />
ZZL012 Mathematics <strong>in</strong> Economics and Management 8<br />
ZZL009a Microeconomics I 5<br />
ZEL040 Organization and Operation of Public Adm<strong>in</strong>istration 4<br />
ZZL014 Organizational Behavior 5<br />
ZZL045 Organizational Culture 3<br />
ZZL045 Organizational Culture 3<br />
ZZM036 Regional Policy 5<br />
ZEL007a Society and Culture of Europe I 6<br />
ZEL007b Society and Culture of Europe II 6<br />
ZZL040 Sociology and Psychology of Management 3<br />
ZZM006 Strategic Management 6<br />
ZEM004 EU`s Common Foreign and Security Policy 5<br />
ZZL017 Quality Management 7<br />
ZZM034 Value-Based Management 3<br />
1. Course title<br />
Account<strong>in</strong>g and F<strong>in</strong>ance Enterprise<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZAL035<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture<br />
5. Semester<br />
4 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD, a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl ; Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Usage basics rules <strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ancial and accountancy scope to manage enterprises and their f<strong>in</strong>ance<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
National f<strong>in</strong>ancial system <strong>in</strong> market economy. Streams and f<strong>in</strong>ancial resources <strong>in</strong> economy. Connections<br />
between enterprise’s f<strong>in</strong>ancial system and national f<strong>in</strong>ancial system. F<strong>in</strong>ance and <strong>in</strong>vestment pr<strong>in</strong>ciples -<br />
outside capital and its acquisition. Cost of equity and outside capital. Investment, methods of account<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>vestment projects. Account<strong>in</strong>g as an enterprise <strong>in</strong>formational system. Accountancy essentials and<br />
pr<strong>in</strong>ciples. Assets and capitals of enterprises - balance. Account<strong>in</strong>g transactions. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of accounts<br />
function<strong>in</strong>g, accounts scheme. Incomes and costs <strong>in</strong> enterprise accountancy. F<strong>in</strong>ancial statement as a<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation source of f<strong>in</strong>ancial stand<strong>in</strong>g (balance read<strong>in</strong>g, analysis of profit and loss account). F<strong>in</strong>ancial result<br />
– sett<strong>in</strong>g and sett<strong>in</strong>g of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial stand<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Curran, Account<strong>in</strong>g Fundamentals, Mcgraw-Hill 2005.<br />
C. Gowthrope, Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Account<strong>in</strong>g And F<strong>in</strong>ance: For Non Specialists, TL 2003.<br />
C. Warren, J. Reeve, P. Fess, Account<strong>in</strong>g And F<strong>in</strong>ance. A Firm Foundation, TL 2001.<br />
A. Damodaran, Applied Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance, WILEY 2006.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL019<br />
Lecture, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
7<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc. Zofia Wieszczeczyńska, z.wieszczeczynska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basics of management<br />
requirements: basic knowledge about organization; structure, functions and environment of organization.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The most important goal of the subject is for students to understand the importance of a Market<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the<br />
organization, its general concept and<br />
presence <strong>in</strong> life<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
- Basic concepts of market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- Market<strong>in</strong>g environment<br />
- Consumers and their behavior on the Market<br />
- Market segmentation<br />
- Product
- Price<br />
- Promotion<br />
- Advertisement, Public relations<br />
- Distribution<br />
- Market<strong>in</strong>g Information System<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test and grade from work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> groups<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Gary Armstrong,Michael Harker,Philip Kotler,Ross Brennan: Market<strong>in</strong>g: An Introduction<br />
Jerzy Altkorn, Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g and Market Research<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEL053<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
6 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc. Zofia Wieszczeczyńska, z.wieszczeczynska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge about organization; structure, functions and environment of organization. methods of research<br />
used <strong>in</strong> Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The most important goal of the subject is for students to understand the importance of a Market<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the<br />
organization, its general concept and<br />
presence <strong>in</strong> life, methods of Market research used to improve function<strong>in</strong>g of organization<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
- Basic concepts of market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- Market<strong>in</strong>g environment<br />
- Consumers and their behavior on the Market<br />
- Market segmentation<br />
- Product<br />
- Price<br />
- Promotion<br />
- Advertisement, Public relations<br />
- Distribution<br />
- Market<strong>in</strong>g Information System<br />
- Market research methods<br />
- Examples and case studies<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test and grade from work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> groups<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Gary Armstrong,Michael Harker,Philip Kotler,Ross Brennan: Market<strong>in</strong>g: An Introduction<br />
Jerzy Altkorn, Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Clusters and cluster <strong>in</strong>itiatives
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZM042<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
3 (master – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1, 1<br />
15, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
<strong>english</strong><br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc eng<strong>in</strong>eer, Brygida Klemens, b.klemens@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Theoretical preparation from other <strong>courses</strong>, i.e. Microeconomic, Macroeconomics, Low, Local and Regional<br />
Policy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students learn about clusters and cluster-based policy<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Def<strong>in</strong>itions of clusters and cluster <strong>in</strong>itiatives,<br />
SME’s,<br />
Role of SME’s <strong>in</strong> cluster development,<br />
Live circle of clusters,<br />
Typology of clusters.<br />
Role of clusters <strong>in</strong> regional development,<br />
Competitiveness <strong>in</strong> clusters,<br />
Cooperation, competition and coo petition,<br />
Case studies of clusters <strong>in</strong> Poland and EU,<br />
Cluster-based Policy (e.g. European Commission documents).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
- credit based on students participation <strong>in</strong> classes,<br />
- project,<br />
- activity.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
O. Sölvell, Clusters. Balanc<strong>in</strong>g Evolutionary and Constructive Forces (Redbook), Ivory Tower Publishers, Stockholm<br />
2008<br />
O. Sölvell, G. L<strong>in</strong>dqvist, Ch. Ketels, The Cluster Initiative Greenbook, Ivory Tower, Stockholm 2003<br />
1. Course title<br />
Concepts of Management<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZM001<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1 (master – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
<strong>english</strong><br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Liliana Hawrysz PhD Eng., l.hawrysz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g classical and modern concepts of management, us<strong>in</strong>g modern method <strong>in</strong> describ<strong>in</strong>g and
expla<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g situation from management area<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Contemporary orientation and conception of management (for example TQM; Lean management, Benchmark<strong>in</strong>g<br />
,BPR), Learn<strong>in</strong>g organization, <strong>in</strong>telligent organization, virtual, network organization<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
On the basis of participation <strong>in</strong> discussions<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
M. Armstrong, A Handbook of Management Techniques: The Best Sell<strong>in</strong>g Guide to Modern Management<br />
Method<br />
M.T., Czarnecki, Manag<strong>in</strong>g by Measur<strong>in</strong>g: How to Improve Your Organization's Performance Through<br />
Effective Benchmark<strong>in</strong>g (Hardcover)<br />
M. Zairi, Benchmark<strong>in</strong>g for Best Practice<br />
S. A. Mohrman, J. R. Galbraith, E. E., III Lawler, Tomorrow's Organization: Craft<strong>in</strong>g W<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Capabilities <strong>in</strong> a Dynamic World<br />
1. Course title<br />
Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL022<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
7<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD, a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl ; Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The usage of f<strong>in</strong>ancial rules and methods to manage enterprises and their f<strong>in</strong>ance<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Corporate f<strong>in</strong>ance issues and problems. F<strong>in</strong>ance and <strong>in</strong>vestment pr<strong>in</strong>ciples – debt capital and its ga<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
process. Shares and bonds issues. Cost of capital. Methods of <strong>in</strong>vestment evaluation. Short-term corporate<br />
f<strong>in</strong>ance management - current receivables and current liabilities management. Functional analysis of a<br />
corporate (f<strong>in</strong>ancial and branch <strong>in</strong>dicators). Corporate tax strategies<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) J. Van Horne, J. Wachowicz, Fundamentals of F<strong>in</strong>ancial Management, 2004, 12th edition<br />
b) A. Damodaran, Applied Corporate F<strong>in</strong>ance, WILEY 2006<br />
c) J. E. Edw<strong>in</strong>, Modern Portfolio Theory and Investment Analysis, Wiley 2004<br />
d) D. Dayananda, R. Irons, S. Harrison, J. Herbohn, P. Rowland, Capital Budget<strong>in</strong>g. F<strong>in</strong>ancial Apprisal Of<br />
Investment Projects, CAMBRIDGE 2002<br />
1. Course title<br />
Cost Account<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZZM015<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
3 (master – degree studies)
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1, 1<br />
15, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD, a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl , Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Knowledge development about costs from different dimensions and their importance for enterprise<br />
strategic and operat<strong>in</strong>g decisions.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The essence and the functions of cost account. The cost classification. The methods of cost calculation. The<br />
pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of cost accountability. Cost budget<strong>in</strong>g. Cost analysis. The cost account <strong>in</strong>fluence on company<br />
f<strong>in</strong>ancial results. Cost account <strong>in</strong> company – activity costs, products costs, clients cost.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
D. Russell, A. Patel, Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g An Essential Guide, FT/PH 2002.<br />
Horngren, Datar, Foster, Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g A Managerial Emphasis, PH, 2005<br />
S. Bragg, Cost Account<strong>in</strong>g, WILEY, 2001<br />
1. Course title<br />
Culture identities <strong>in</strong> Europe<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZEM002<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 1<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
1 (master – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dorota Schreiber – Kurpiers, PhD,<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
The education effects – skills and abilities: understand<strong>in</strong>g of national identity cultivation and<br />
deconstruction processes; understand<strong>in</strong>g of European <strong>in</strong>tegration processes seen as culture and<br />
identity categories; analysis of identity models (with prejudices) as dynamic cultural phenomenon.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Cultivation of culture-territorial identities on subsequent levels: local, reg<strong>in</strong>al, national,<br />
<strong>in</strong>ternational, European. Identity cultivation of m<strong>in</strong>ority groups accord<strong>in</strong>g to ethnicity, religion, life<br />
style, sexual orientation and other socially crucial and culturally significant criteria. Prejudices and<br />
their alterations. Intercultural dialogue. Alterations of collective cultural identities. Common<br />
European identity and its relations to European democratic civil society.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURE:<br />
1. „Construction of a nation”, protonationality, sense of the French Revolution, theories about orig<strong>in</strong> of<br />
national identity sense: primal, modernistic, symbolistic<br />
2. Emblematics. Symbolism. Theory
3. Symbolism of the authority and state symbolizm.<br />
4. Identity cultivated by elite groups and charismatic leaders<br />
5. Prejudices and their alterations.<br />
6. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation and dynamics of national prejudices. Alterations of the conception of a Pole <strong>in</strong> German’s view<br />
and the conception of a German <strong>in</strong> Pole’s view.<br />
7. „Broken identity” – social stigmatism. Example of destigmatization process: red hairs of St. Agatha.<br />
8. Religious and ecclesiastic identity.<br />
9. Gender;<br />
10. Identity cultivation of m<strong>in</strong>ority groups accord<strong>in</strong>g to ethnicity, religion, life style, sexual orientation<br />
11. Heterosexual matrix.<br />
12. Between pornography and erotism – <strong>in</strong> the historical grasp: Europe aga<strong>in</strong>st other cont<strong>in</strong>ents – the lecture<br />
only for volunteers.<br />
13. Foucault, Michel. (1998). The History of Sexuality. London: Pengu<strong>in</strong>.<br />
14. Butler, Judith (1990) : Gender Trouble. Fem<strong>in</strong>ism and the Subversion of Identity<br />
15. Identity <strong>in</strong> postmodernism<br />
16. Strategies of identity cultivation <strong>in</strong> suburban culture and hip-hop-culture / polemics with Eva Kimmnich<br />
17. Intercultural dialogue<br />
18. Cultivation of common European identity / Common European identity and its relations to European<br />
democratic civil society<br />
CLASSES:<br />
1. The students have to read set texts and be prepared to discussion. The f<strong>in</strong>al grade <strong>in</strong> 90% depends on the<br />
grade obta<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> research work.<br />
2. Information meet<strong>in</strong>g. How to write a research report.<br />
3. Collective identity<br />
4. Identity aga<strong>in</strong>st nationalism<br />
5. Africans – creation of national identity sense and ideology of apartheid<br />
6. Card<strong>in</strong>al symbols<br />
7. Between xenophobia and xenophilia. The Strangers.<br />
8. The groups present their research<strong>in</strong>g tool<br />
9. The myth of Serbian warrior before outbreak of war <strong>in</strong> former Yugoslavia<br />
10. The groups preset their research reports<br />
11. The operation on the nation – creation of a new citizen. On the example of West (so called Recovered)<br />
Territories of Poland.<br />
12. Silesian identity<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture<br />
General conditions of pass<strong>in</strong>g the subject<br />
Exam<strong>in</strong>ations: pre-first exam and the first exam – writ<strong>in</strong>g test<br />
second exam – writ<strong>in</strong>g test<br />
Attention! To pass the exam<strong>in</strong>ation, it is needed to obta<strong>in</strong> at least 75 % po<strong>in</strong>ts.<br />
The exam<strong>in</strong>ation will comprise the material realized dur<strong>in</strong>g the lectures and sem<strong>in</strong>ars.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Kimm<strong>in</strong>ich E. (2003), Kulturelle Identität. Konstruktionen und Krisen, Frankfurt/M<br />
Delamont S. (1995), Appetities and Identities. An. Introduction of the Social Anthropology of<br />
Western Europe. London<br />
Butler, Judith (2008) Gender Trouble: Fem<strong>in</strong>ism and the Subversion of Identity<br />
1. Course title<br />
Diritto costituzionale<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZAL012<br />
4. Type of course<br />
Elementare (basilare)<br />
3. Form of class<br />
lezione, esercizio<br />
5. Semester<br />
2 (Laurea)
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 1<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
Italian<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dr Monika Haczkowska, m.haczkowska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
7. Level of class<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 15<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Il trasmettere a studenti una scienza riguardante i pr<strong>in</strong>cipi del regime economico e sociale <strong>in</strong> Repubblica<br />
Polacca, dei fonti di diritti vigenti <strong>in</strong> Polonia e del sistema degli organi del potere pubblico secondo la<br />
Costituzione RP del 1997.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LEZIONE : Sistema governativo e giuridico <strong>in</strong> Polonia, i pr<strong>in</strong>cipi fondamentali, i fonti dei diritti, Il separazione<br />
(divisione) dei poteri, il Parlamento, il Presidente della Repubblica Polacca, il Consiglio dei M<strong>in</strong>istri,<br />
l'Amm<strong>in</strong>istrazione della giustizia, Corte Costituzionale, Corte dello Stato, gli organi del controllo statale, il<br />
Referendum nazionale, regionale e costituzionale, il sistema di dei diritti e liberte' fondamentali degli<br />
Dom<strong>in</strong>i.<br />
ESERCIZIO : Sistema governativo e giuridico <strong>in</strong> Polonia, i pr<strong>in</strong>cipi fondamentali, i fonti dei diritti, Il<br />
separazione (divisione) dei poteri, il Parlamento, il Presidente della Repubblica Polacca, il Consiglio dei<br />
M<strong>in</strong>istri, l'Amm<strong>in</strong>istrazione della giustizia, Corte Costituzionale, Corte dello Stato, gli organi del controllo<br />
statale, il Referendum nazionale, regionale e costituzionale, il sistema di dei diritti e liberte' fondamentali<br />
degli Uom<strong>in</strong>i.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Relazione con presentazione multimedialne. Firma di esercitazioni – colloquio.<br />
Firma di lezioni – esame orale.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
L. Garlicki, Polskie prawo konstytucyjne. Zarys wykładu, wyd. Liber, wyd. 13, Warszawa 2008<br />
M. Bartoszewicz, M. Haczkowska, System organów państwowych według Konstytucji Rzeczypospolitej<br />
Polskiej. Podręcznik akademicki Opole 2010<br />
B. Banaszak, Prawo konstytucyjne, wyd. C.H.Beck, Warszawa 2008<br />
Konstytucja RP z 2 kwietnia 1997 r. (Dz. U. z 1997 r. Nr 78, poz. 483)<br />
Polish Constitutional Law. The Constitution and selected statutory materials, Chancellery of the Sejm,<br />
Warszawa 2009<br />
1. Course title<br />
Demographic processes <strong>in</strong> Europe<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEL029<br />
lectures<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Kornelia Polek-Duraj, PhD k.polek-duraj@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Introduction of students with basic problems of the demography.
Presentation and the analysis of population-problems of Poland and the world.<br />
Presentation and the analysis of spr<strong>in</strong>g-texts and statistical sources of <strong>in</strong>formation.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
History of demography<br />
Data sources of population<br />
Methods and manners of the data presentation about the population<br />
Condition of population<br />
The structure of population and the process of senescence<br />
Elements of natural movement of population<br />
Population pyramid<br />
Infant mortality, <strong>in</strong>ternal and foreign migrations<br />
The tramp movement<br />
The potential demography<br />
Demographic prognoses<br />
The theory of demographic passage<br />
The optimum of population<br />
The population-policy<br />
The history of the development of demographic world<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Essay, oral exam and presentation <strong>in</strong> Power Po<strong>in</strong>t<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
J. Z. Holzer, Demografia, PWE, Warszawa (najnowsze wydanie).<br />
M. Mitręga, Demografia społeczna, Wyd. Śląsk, Katowice 1995.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Ecological Reflection<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZPH001<br />
4. Type of course<br />
elective<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture<br />
5. Semester<br />
2 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
17. Number of hours per semester<br />
30<br />
18. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
19. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Alicja Kolasa –Więcek, PhD, a.kolasa-wiecek@po.opole.pl<br />
20. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
21. Objectives of the course<br />
Develop<strong>in</strong>g a full awareness and awaken<strong>in</strong>g public <strong>in</strong>terest of <strong>in</strong>terrelated economic, social, political and<br />
environmental issues.<br />
Allow<strong>in</strong>g everyone to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for environmental improvement.<br />
Creat<strong>in</strong>g new patterns of behavior, shap<strong>in</strong>g attitudes, values and beliefs of <strong>in</strong>dividuals, groups and societies,<br />
tak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to account the concern for environmental quality.<br />
22. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Expla<strong>in</strong> the basic concepts of ecology, ecological education and environmental protection,<br />
Ethical and sociological aspects of ecology and environmental protection:<br />
- Environmental education,<br />
- Methods of social psychology <strong>in</strong> shap<strong>in</strong>g the ecology of human attitudes,<br />
- Environmental awareness,<br />
- Shallow and deep ecology,<br />
Environmental education as an <strong>in</strong>ternational obligation,<br />
Organization of environmental education <strong>in</strong> Poland
Basis for environmental protection (<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g the basic threats and challenges of the modern world, the<br />
evolution of approaches to issues of ecology and environmental management model)<br />
Cleaner Production as a philosophy and strategy of environmental protection<br />
Models and def<strong>in</strong>itions found <strong>in</strong> the conservation and environmental management,<br />
Renewable and non-renewable resources of the environment and the rational exploitation<br />
23. Assessment methods<br />
The basic form of communication - a giv<strong>in</strong>g method -<strong>in</strong> the form of lectures, talks and discussions and a<br />
problem method - <strong>in</strong> the form of a lecture problem, bra<strong>in</strong>storm<strong>in</strong>g. F<strong>in</strong>al test, attendance.<br />
24. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Harrison Paul, The Third Rewolution. Environment, Population and a Susta<strong>in</strong>able World, I.B. Tauris/Pengu<strong>in</strong><br />
Books, London-New York, 1992,<br />
Martell, Luke, Ecology and Society: An Introduction, Polity Press, 1994,<br />
Michael Tobias ed, Deep Ecology, Avant Books, ISBN 0-932238-13-0, 1988,<br />
Palmer, J.A., Environmental Education <strong>in</strong> the 21st Century: Theory, Practice, Progress, and Promise,<br />
Routledge, 1998,<br />
Saw<strong>in</strong> Janet, Chart<strong>in</strong>g a New Energy Future, State of the World 2003, By Lester R. Brown. Boston: W. W.<br />
Norton & Company, Incorporated, 2003.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Economic Analysis<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL031<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
5 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD, a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl ; Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g and usage of methods and analytical techniques <strong>in</strong> enterprises activities. Interrelationship<br />
results of economic analyses with decision system <strong>in</strong> enterprise.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Methodical basics of economic analyses. Conditions and bases of <strong>in</strong>terpretation and presentation results of<br />
economic analyses. Information sources <strong>in</strong> economic analyses scope. Economic analysis enterprises –<br />
balance sheet and cash flow, rates analyses. Analysis: production, costs, employment, sale, prices. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess<br />
plan and enterprise’s strategy. Economic projects estimation. Estimation of <strong>in</strong>vestment efficiency.<br />
Account<strong>in</strong>g techniques of measurement <strong>in</strong>vestment projects. Discount rate. Quantitative and qualitative<br />
methods <strong>in</strong> branches and markets analyses. Prices deformities and calculation prices of commercial and non<br />
commercial goods<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
G. Friedlob, Essentials Of F<strong>in</strong>ancial Analysis, WILEY 2003.<br />
L. Bernste<strong>in</strong>, J. Wild, Analysis Of F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statements, Mcgraw-Hill 2000.<br />
K. Palepu, Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Analysis And Valuation, SOUTH WESTERN 2004.
1. Course title<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Accountancy<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL021<br />
Lecture, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
2 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD, a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl ; Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g the essence, rules and f<strong>in</strong>ancial accountancy <strong>in</strong>struments; usage f<strong>in</strong>ancial accountancy<br />
<strong>in</strong>struments <strong>in</strong> management’s problems solv<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Accountancy essentials and pr<strong>in</strong>ciples. Enterprises’ assets and funds. Balance sheet. Balance and profit and<br />
loss accounts. Economic events. Bases of accounts function<strong>in</strong>g. Accounts scheme. Record<strong>in</strong>g of liquid assets,<br />
stocks, receivables and liabilities, stockpiles, capital assets. Costs. Income statement. Methods of f<strong>in</strong>ancial<br />
result calculation. Profit and loss account. F<strong>in</strong>ancial statements report<strong>in</strong>g<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) P. Weetman, F<strong>in</strong>ancial Account<strong>in</strong>g, Pearson, 2006, 4th edition.<br />
b) B. Elliot, J. Elliott, F<strong>in</strong>ancial Report<strong>in</strong>g, Person, 2005, 10th edition.<br />
c) R. Lewis, D. Pendrill, Advanced F<strong>in</strong>ancial Account<strong>in</strong>g, Pearson, 2003<br />
Course title<br />
F<strong>in</strong>ancial Statement Standards<br />
Course code<br />
Form of class<br />
ZEM012<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
Type of course<br />
Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 (master – degree studies)<br />
ECTS credits<br />
Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1, 1<br />
15, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD , a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl ; Justyna Zygmunt, PhD , j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
To ga<strong>in</strong> practical knowledge about the f<strong>in</strong>ancial statement standards, their contents and accomplishment<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Conceptual assumptions of f<strong>in</strong>ancial statements preparation and presentation. Fixed and immaterial assets<br />
<strong>in</strong> f<strong>in</strong>ancial statements and their depreciation. F<strong>in</strong>ancial <strong>in</strong>strument pric<strong>in</strong>g. Equity and <strong>in</strong>debtedness <strong>in</strong><br />
f<strong>in</strong>ancial statements. Statement of changes <strong>in</strong> equity. Deferred tax assets and liabilities<br />
15. Assessment methods
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
K. Alfredson, Apply<strong>in</strong>g International Account<strong>in</strong>g Standards, Wiley 2005.<br />
G. Gregoriou, M. Geber, International Account<strong>in</strong>g Standards Regulations And F<strong>in</strong>ancial Report<strong>in</strong>g, ELSEVIER<br />
2007.<br />
IAS Committee, International Account<strong>in</strong>g Standards Expla<strong>in</strong>ed, WILEY 2000.<br />
D. Chorafes, International F<strong>in</strong>ancial Report<strong>in</strong>g Standards, BUTTERWORTH, 2006.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Forecasts and Simulations<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZM019<br />
Lecture, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 (master – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD. Eng. Łukasz Mach, l.mach@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Econometric, Statistics.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the subject is to give students the ability to prepare forecasts and simulations regard<strong>in</strong>g microand<br />
macroeconomics affairs.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURES:<br />
General Introduction, Identify<strong>in</strong>g Patterns <strong>in</strong> Time Series Data (Trend Analysis, Analysis of Seasonalit),<br />
Exponential Smooth<strong>in</strong>g (Brown and Holt models), Seasonal Decomposition (W<strong>in</strong>ters model ARIMA<br />
Methodology,), quantity forecast models (logit, probit, discrim<strong>in</strong>ations analysis use <strong>in</strong> economic and<br />
mamagenet phenomens).<br />
LABORATORY:<br />
General Introduction, Identify<strong>in</strong>g Patterns <strong>in</strong> Time Series Data (Trend Analysis, Analysis of Seasonalit),<br />
Exponential Smooth<strong>in</strong>g (Brown and Holt models), Seasonal Decomposition (W<strong>in</strong>ters model ARIMA<br />
Methodology,), quantity forecast models (logit, probit, discrim<strong>in</strong>ations analysis use <strong>in</strong> economic and<br />
mamagenet phenomens).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Presentations, work <strong>in</strong> Statistica 9.0 from Statsoft and Gretl. Project and exam.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Maria Cieślak – Prognozowanie gospodarcze<br />
Józef Biolik, Andrzej Stanisław Barczak – Podstawy ekonometrii<br />
Aleksander Zeliaś – Teoria prognozy<br />
Maddala G.S. Ekonometria<br />
Dziechciarz Józef – Ekonometria. Metody, Przykłady, Zadania<br />
Radzikowska Barbara – Metody prognozowania<br />
Gruszczyński Marek – Ekonometria i badania operacyjne<br />
Dittmann Paweł – Prognozowanie w przedsiębiorstwie<br />
1. Course title<br />
Economy I
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEL008a<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
8<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Kornelia Polek-Duraj, PhD, k.polek-duraj@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Knowledge <strong>in</strong> the range of basic economic problems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The genesis of economy, the doctr<strong>in</strong>e and economic schools.<br />
The creation and development economics.<br />
The plane of the economic analysis<br />
The model of market economy; the market and its elements.<br />
Market, types of markets, market operators and market objectives<br />
Demand and factors determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g it.<br />
Supply and factors determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g it.<br />
Market equilibrium and its changes. Market mechanism.<br />
The elasticity of demand and the supply.<br />
The theory of the consumer.<br />
Economic decisions of the producer.<br />
The theory of production - manufactur<strong>in</strong>g costs.<br />
Types of competition on the market (monopoly, oligopoly etc.)<br />
The labor market. The land market. Capital market.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Multiple choice test and oral exam<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
D. Begg, S. Fischer, R. Dornbusch, Ekonomia t.1 i t.3, PWE, 2003.<br />
D. Kamerschen, R. MacKenzi, N. Clark, Ekonomia, 1993<br />
B. Klimczak, Mikroekonomia, AE Wrocław, 1993<br />
R. Milewski, Podstawy ekonomii, PWN, 2002.<br />
M. Rekowski, Wprowadzenie do mikroekonomii, AE Poznań, 2006.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Economy II<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZEL008a<br />
ZEL008b<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
8<br />
8<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 2<br />
2, 2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
1 (first – degree studies)<br />
2 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 30<br />
30, 30
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Kornelia Polek-Duraj, PhD, k.polek-duraj@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Knowledge <strong>in</strong> the range of basic economic problems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Introduction to the economy and economics.<br />
Determ<strong>in</strong>ants of <strong>in</strong>come and national <strong>in</strong>come. Meters of <strong>in</strong>come.<br />
Global product and national <strong>in</strong>come as <strong>in</strong>struments of economic activity.<br />
Growth - the concept and meters.<br />
Basic macroeconomic relationships: consumption, <strong>in</strong>vestment sav<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
Macroeconomic stability.<br />
The central bank, commercial banks.<br />
Functions of money, types of money, the role of money.<br />
Demand for money. money supply - balance of the money market.<br />
Unemployment – reasons, results, k<strong>in</strong>ds.<br />
Inflation –def<strong>in</strong>ition, k<strong>in</strong>ds, reasons, results.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>ternational commerce.<br />
The state budget.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>ternational economics<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Multiple choice test and oral exam<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
D. Begg, S. Fischer, R. Dornbusch, Ekonomia t.1 i t.3, PWE, 2003.<br />
D. Kamerschen, R. MacKenzi, N. Clark, Ekonomia, 1993<br />
B. Klimczak, Mikroekonomia, AE Wrocław, 1993<br />
R. Milewski, Podstawy ekonomii, PWN, 2002.<br />
M. Rekowski, Wprowadzenie do mikroekonomii, AE Poznań, 2006.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Fundamentals of Management<br />
2. Course Code<br />
ZZL007<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
8<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Liliana Hawrysz PhD Eng., l.hawrysz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
1 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 30<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g essence and the mechanism of organization function, understand<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, correctness<br />
of the management <strong>in</strong>struments, description and analyz<strong>in</strong>g management problems<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Theory of organization management , Organization (def<strong>in</strong>itions, features, types, models , Organization<br />
structure (environment, organization liv<strong>in</strong>g cycle, mechanistic and organic organization, types of<br />
structure), leadership styles.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
On the basis of participation <strong>in</strong> discussions
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
J.Schermerhorn, Management<br />
P.J.Montana, B.H.Charnov, Management<br />
R.W. Griff<strong>in</strong>, Management<br />
1. Course title<br />
Human Resources Management (<strong>in</strong> English)<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL016<br />
Lecture, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Kornelia Polek – Duraj, e-mail: k.polek-duraj@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The ma<strong>in</strong> aim is <strong>in</strong>troduc<strong>in</strong>g the students with human resources management <strong>in</strong> an enterprise.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Aims and assignments of personnel management.<br />
� The plann<strong>in</strong>g of human resources<br />
� The selection and labour recruitment.<br />
� The adaption of employees.<br />
� Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g of employees.<br />
� Apprais<strong>in</strong>g of employees.<br />
� Stress at work.<br />
� Motivation for work.<br />
� The <strong>in</strong>terpersonal communication.<br />
� The satisfaction of workers.<br />
� Work<strong>in</strong>g conditions.<br />
� The professional burnup.<br />
� Self-assurance.<br />
� Conflicts at work.<br />
� Functions of money, types of the money, the role of money.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written essay, oral exam<strong>in</strong>ation and presentation <strong>in</strong> Power Po<strong>in</strong>t<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Armstrong M., Zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi, ABC, Kraków 2003.<br />
Bańka W., Zarządzanie personelem w przedsiębiorstwie, Wydawnictwo „Adam Marszałek”, Toruń 1999.<br />
Drucker P. F., Zarządzanie w XXI wieku, Muza SA, Warszawa 2000.<br />
Gableta M., Człowiek i praca w zmieniającym się przedsiębiorstwie, Wydawnictwo AE, Wrocław 2003.<br />
Griff<strong>in</strong> R.W., Podstawy zarządzania organizacjami, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, Warszawa 2006.<br />
Kostera M., Zarządzanie personelem, PWE, Warszawa 2000.<br />
Lundy O., Cowl<strong>in</strong>g A., Strategiczne zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi, Dom Wydawniczy ABC, Kraków 2000.<br />
McKenna E., Beech N., Zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi, Felberg SJA, Warszawa 1999.<br />
Zając cz., Zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi, Wyższa Szkoła Bankowa, Wrocław 2007.<br />
Zieniewicz K., Współczesne koncepcje i metody zarządzania, PWE, Warszawa 2003<br />
1. Course title<br />
Human Resources Management (<strong>in</strong> German)
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL016<br />
Lecture, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
German<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ms. C. Katarzyna Mazur-Kajta, k.mazur@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
In this class you will get a basic knowledge <strong>in</strong> theory and <strong>in</strong> practice for human resources management i.e.<br />
topics on the most important organization’s resources – its workers. You will learn about human relations at<br />
work start<strong>in</strong>g at recruitment and end<strong>in</strong>g at outplacement.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Dur<strong>in</strong>g the class we will discuss issues concern<strong>in</strong>g:<br />
- stages of human resources development, - management models for human resources<br />
- workforce recruitment, - workforce selection, - workforce <strong>in</strong>tegration, - motivation,<br />
- tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and development, - coach<strong>in</strong>g, - workforce evaluation,<br />
- compensation, rewards and benefits, - social <strong>in</strong>teractions and its role<br />
- safe work management, - <strong>in</strong>tercultural management, - professional burn out<br />
- outplacement<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
In this class we will do case studies and problem solv<strong>in</strong>g exercises. To receive a credit for the class you will<br />
have to be present at 93% of classes, actively participate and pass the f<strong>in</strong>al test or write a paper.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
German literature:<br />
- Hohlbaum A., Olesch G., Human Resources - Modernes Personalwesen, Merkur Verlag, August 2010.<br />
- Weeraratne M., Personalmanagement. Personalentwicklung als Instrument zur Steigerung des Human<br />
Capital Wertes, VDM Verlag, August 2010.<br />
- Buehner R., Personalmanagement, Oldenbourg Wissenschaftliche Verlag, November 2004.<br />
- Oechsler W. A., Personal und Arbeit. Grundlagen des Human Resource Management und der Arbeitgeber-<br />
Arbeitnehmer-Beziehungen., Oldenbourg Wissenschaftliche Verlag, Januar 2006.<br />
Polish literature:<br />
- Armstrong M., Zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi, ABC, Kraków 2003.<br />
- Griff<strong>in</strong> R.W., Podstawy zarządzania organizacjami, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, Warszawa 2006.<br />
- Kostera M., Zarządzanie personelem, PWE, Warszawa 2000.<br />
- Borkowska S., Zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi : teraźniejszość i przyszłość, IPiSS, Warszawa 2006.<br />
- Pocztowski A., Zarządzanie zasobami ludzkimi w procesach fuzji i przejęć, Oficyna Ekonomiczna, Kraków<br />
2004.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Institutions européennes et le processus de décision<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEL013<br />
Conférence, les classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
obligatoire<br />
3 (Diplôme de premier cycle)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
7. Level of class<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
Française (French)<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
dr Małgorzata Bielecka; m.bielecka@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Faire la connaissance d`Institutions européennes, le fonctionnement de ces <strong>in</strong>stitutions. L`explication le<br />
processus de décision.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
L`histoire et l`évolution de L`Union européenne :<br />
La Communauté européenne du charbon et du l`acier (CECA), 1951, Europe des six.<br />
La Communauté européenne de defense (CED), il est signe à Paris, le 27 mai 1952.<br />
La Communauté économique européenne (1957 – 1993) et Communauté européennes d`énergie atomique.<br />
Le traité de fusion en 1965 et fusionne les executives (par la creation de la Commission européennes et du<br />
Conseil européen) des trios Communautés européennes, alors que ce Communautés disposent déjà<br />
d`<strong>in</strong>stitutions communes en matière de justice.<br />
Basculement, vers l`Union européennes et grands élargissements (1993 – 2004). Le traité de Maastricht – il<br />
marquee une nouvelle étape dans le prpcessus d`union sans cesse plus étroite entre les peoples d`Europe. La<br />
politique européennes repose alors sur trios pilliers.<br />
Ḗtats members de l`Union européennes.<br />
Fonctionement <strong>in</strong>stitutionnel. Compétences propres et partagées :<br />
Institutions - pouvoir l`égislatif: le Conseil de l` Union européennes et le Parlement européen.<br />
Institutions – pouvoir exécutive: le Conseil européen, la Commission européenne.<br />
Institutions – pouvoir judiciaire: la Cour de justice.<br />
Institutions économique: la Cour des comptes, la Banque centrale européenne.<br />
A côté de ces sept <strong>in</strong>stitutions, on trouve quatre autres organes importants: le Comité économique et<br />
sociale, le Comité des Régions, le Médiateur européen, la Banque européenne d`<strong>in</strong>vestissement.<br />
Processus de decision:<br />
Le procedure l`égislative européennes – présidée par ces deux pr<strong>in</strong>ciples: Dans les doma<strong>in</strong>s où l`Union a des<br />
competences propres (doma<strong>in</strong>e de l`ex – premier pillier).<br />
Le procedure l`égislative européennes – présidée par ces deux pr<strong>in</strong>ciples: Dans les doma<strong>in</strong>s où l`Union a des<br />
competences partagées.(doma<strong>in</strong>s des ex – deuxième et troisième pilliers.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
La présence et l`activité pendant les emplois.<br />
Le test – révision de materiaux.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Didier Blanc, L`Union européenne, Paris, Ellipses, 2006.<br />
Jean Louis Quemonne, Le système politique de l` Union européenne, Paris, Montchrestien, 1998.<br />
Andy Smith, Le gouvernement de l` Union européenne, Paris, LGDJ, 2004.<br />
L`Internet dans Union européennes.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Managerial Accountancy<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZZM009<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
1, 1<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
2 (master – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
15, 15
Aleksandra Zygmunt, PhD, a.zygmunt@po.opole.pl , Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and microeconomy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g and treatment of the conception and <strong>in</strong>struments of managerial accountancy <strong>in</strong> a field of<br />
management enterprises’ costs<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The essence and the functions of managerial accountancy. The cost <strong>in</strong>formation significance <strong>in</strong> short and<br />
long-term decisions. Managerial accountancy of centers responsibility and its place <strong>in</strong> managerial<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation system. Balanced scorecard<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Atk<strong>in</strong>son, R. Kaplan, S. Young, Management Account<strong>in</strong>g, PRENTICE HALL, 2004, 4th edition.<br />
M. Young, Read<strong>in</strong>g Management Account<strong>in</strong>g, PRENTICE HALL, 2004, 3th edition.<br />
J. Zimmerman, Account<strong>in</strong>g for decision mak<strong>in</strong>g and control, McGraw-Hill, 2003, 4th edition<br />
W. Allan, Fundamentals Of Management Account<strong>in</strong>g, Elsevier 2008.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g and Adm<strong>in</strong>istration of Local Authority Projects<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZAL040<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
5 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1, 2<br />
15, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
<strong>english</strong><br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc eng<strong>in</strong>eer, Brygida Klemens, b.klemens@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Theoretical preparation from other <strong>courses</strong>, i.e. Management<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students learn how to put projects <strong>in</strong>to practise.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
- Types of projects.<br />
- Basic parameters of projects.<br />
- Organisation structures <strong>in</strong> projects execution.<br />
- Team selection and work division.<br />
- Methods of projects management.<br />
- Network technology.<br />
- Projects schedule.<br />
- Gantt’s graph.<br />
- Costs management.<br />
- Risk <strong>in</strong> project.<br />
- Cases<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
- students participation <strong>in</strong> classes,<br />
- project,<br />
- practical tasks,<br />
- activity.
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, PMI 2000<br />
1. Course title<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g and Market Research<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZAL046<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
5 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week 9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1, 2<br />
15, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc. Zofia Wieszczeczyńska, z.wieszczeczynska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge about organization; structure, functions and environment of organization. methods of research<br />
used <strong>in</strong> Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The most important goal of the subject is for students to understand the importance of a Market<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the<br />
organization, its general concept and<br />
presence <strong>in</strong> life, methods of Market research used to improve function<strong>in</strong>g of organization<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
- Basic concepts of market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- Market<strong>in</strong>g environment<br />
- Consumers and their behavior on the Market<br />
- Market segmentation<br />
- Product<br />
- Price<br />
- Promotion<br />
- Advertisement, Public relations<br />
- Distribution<br />
- Market<strong>in</strong>g Information System<br />
- Market research methods<br />
- Examples and case studies<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test and grade from work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> groups<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Gary Armstrong,Michael Harker,Philip Kotler,Ross Brennan: Market<strong>in</strong>g: An Introduction<br />
Jerzy Altkorn, Basics of Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g Research<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZZL020<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
5 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 30
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc Magdalena Ciesielska, m.ciesielska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g Basic<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course aims to study the process of market<strong>in</strong>g research. Students Student has to ga<strong>in</strong> the knowledge<br />
about the problem def<strong>in</strong>ition, exploratory and descriptive research, data collection methods, design<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
sample, data analysis and <strong>in</strong>terpretation.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Role of Market<strong>in</strong>g Research. Research Process. Problem Formulation. Research Design. Sampl<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
Nonsampl<strong>in</strong>g Errors. Measurement In Market<strong>in</strong>g Research. Primary and Secondary Data Collection. Sampl<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Procedure. Questionnaire Design. Data Analysis. Data Interpretation. The Research Report.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Tasks, practice tests, discussion, <strong>in</strong>dividual and group projects. Case analysis.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Gilbert A. Churchill, Jr; Dawn Iacobucci, Market<strong>in</strong>g Research. Methodological Foundation, South Western<br />
Thomson Corporation, 2005<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mathematics <strong>in</strong> Economics and Management<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZZL012<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
8<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 2<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
1 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mirosława Szewczyk Ph D, Eng , m.szewczyk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
This course is <strong>in</strong>tended for students who have a limited background <strong>in</strong> mathematics.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
This course <strong>in</strong>troduces students to the mathematical language, skills and techniques necessary for success <strong>in</strong><br />
many of today's fields. Emphasis is placed on applications <strong>in</strong> bus<strong>in</strong>ess. Develop<strong>in</strong>g skills of view expression on<br />
the basis of mathematical conceptions, symbols and terms.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURE:<br />
Review of Fundamental<br />
Relations and Functions. Operations on Sets.<br />
- Operations on Sets. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and Examples. Union, <strong>in</strong>tersection, empty set; identities, Venn diagrams.<br />
- Quantifiers. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and Examples.<br />
- Functions. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and Examples. Notation. Cartesian products.<br />
Sequences, Series and Limits<br />
- Limits: basic notion, def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples left and right limits; f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g some limits<br />
Differential and Integral Calculus<br />
- Differential calculus. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples.<br />
- Def<strong>in</strong>ite and <strong>in</strong>def<strong>in</strong>ite <strong>in</strong>tegrals; fundamental theorem of calculus; proper and improper <strong>in</strong>tegrals;<br />
def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples techniques for <strong>in</strong>tegration: l<strong>in</strong>earity, <strong>in</strong>tegration by parts.<br />
The Derivative and Differential for Functions of One Variable<br />
- Maximum, m<strong>in</strong>imum, saddle-po<strong>in</strong>ts. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples.<br />
- Economic examples.
The Derivative and Differential for Functions of More than One Variable.<br />
Vectors and Matrices<br />
- Vectors. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples.<br />
- Elementary matrices. Operations on matrices.<br />
Systems of L<strong>in</strong>ear Equations<br />
Systems of L<strong>in</strong>ear Inequalities.<br />
CLASSES:<br />
Review of Fundamental<br />
Relations and Functions. Operations on Sets.<br />
- Operations on Sets. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and Examples. Union, <strong>in</strong>tersection, empty set; identities, Venn diagrams.<br />
- Quantifiers. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and Examples.<br />
- Functions. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and Examples. Notation. Cartesian products.<br />
Sequences, Series and Limits<br />
- Limits: basic notion, def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples left and right limits; f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g some limits<br />
Differential and Integral Calculus<br />
- Differential calculus. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples.<br />
- Def<strong>in</strong>ite and <strong>in</strong>def<strong>in</strong>ite <strong>in</strong>tegrals; fundamental theorem of calculus; proper and improper <strong>in</strong>tegrals;<br />
def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples techniques for <strong>in</strong>tegration: l<strong>in</strong>earity, <strong>in</strong>tegration by parts.<br />
The Derivative and Differential for Functions of One Variable<br />
- Maximum, m<strong>in</strong>imum, saddle-po<strong>in</strong>ts. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples.<br />
- Economic examples.<br />
The Derivative and Differential for Functions of More than One Variable.<br />
Vectors and Matrices<br />
- Vectors. Def<strong>in</strong>itions and examples.<br />
- Elementary matrices. Operations on matrices.<br />
Systems of L<strong>in</strong>ear Equations<br />
Systems of L<strong>in</strong>ear Inequalities.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Classes - assessment is based on homework assignments and <strong>in</strong>-class exams. Lectures - a f<strong>in</strong>al exam.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
L. Rade, Mathematics Handbook for Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, Spr<strong>in</strong>ger - Verlag, Berl<strong>in</strong> 1999.<br />
M. Timbrell, Mathematics for economists: an <strong>in</strong>troduction, Blackwell, Oxford 1990.<br />
W. Krysicki, L. Włodarski, Analiza matematyczna w zadaniach, PWN, Warszawa 1993.<br />
J. Abtowa, K. Piasecki, T. Różański, Z. Świtalski, Matematyka wspomagająca zarządzanie, Wydawnictwo<br />
Akademia, Poznań 1997.<br />
G.N. Berman, Zbiór zadań z analizy matematycznej, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, Warszawa 1965.<br />
J.Gilewicz, Matematyka z zastosowaniami w naukach ekonomicznych, Wydawnictwo „Epsilon”, Koszal<strong>in</strong><br />
1999.<br />
A. Ostoja-Ostaszewski, Matematyka w ekonomii. Modele i metody, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN, Warszawa<br />
1996.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Microeconomics I<br />
2. Course Code<br />
ZZL009a<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
1, 2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Liliana Hawrysz PhD Eng., l.hawrysz@po.opole.pl<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
5. Semester<br />
1 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
15, 30
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g the basic microeconomics category, understand<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of function the ma<strong>in</strong> subjects<br />
<strong>in</strong> the economy of public system , understat<strong>in</strong>g to <strong>in</strong>fluence of economy system on management area<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Nature of microeconomics, consumer behavior and <strong>in</strong>dividual demand, market demand, optimal <strong>in</strong>put<br />
comb<strong>in</strong>ations and cost functions, market structure, price and output ( perfect competition, monopoly,<br />
monopolistic competition, oligopoly)<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
On the basis of participation <strong>in</strong> discussions<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
N.G. Mankiw , Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Microeconomics,<br />
O'Sullivan, S. Sheffr<strong>in</strong>, St. Perez, Microeconomics: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, Applications, and Tools<br />
C. R. McConnell Microeconomics<br />
1. Course title<br />
Organization and Operation of Public Adm<strong>in</strong>istration<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEL040<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
5 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
<strong>english</strong><br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc eng<strong>in</strong>eer, Brygida Klemens, b.klemens@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Theoretical preparation from other <strong>courses</strong>, i.e. Local and Regional Policy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students learn how to use knowledge about public adm<strong>in</strong>istration structures <strong>in</strong> professional work and how<br />
to move <strong>in</strong> polish <strong>in</strong>stitutions.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Idea of public adm<strong>in</strong>istration,<br />
Central and territorial adm<strong>in</strong>istration,<br />
Local government <strong>in</strong> Poland (prov<strong>in</strong>ce “voivodship”, county, borough) and characteristic,<br />
Subjects and <strong>in</strong>stitutions,<br />
Contemporary public adm<strong>in</strong>istration system,<br />
Procedures of decisions and appeals <strong>in</strong> central government,<br />
Procedures of decisions and appeals <strong>in</strong> local government (e.g.: bus<strong>in</strong>ess, local taxes, environmental<br />
protection, crisis management, local register, passport procedure, marriage certificate, first name<br />
chang<strong>in</strong>g, tender procedure, control over local government),<br />
Local government tasks,<br />
Low, ethics and staff <strong>in</strong> public adm<strong>in</strong>istration.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
- credit based on students participation <strong>in</strong> classes,<br />
- project,<br />
- activity.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
R.B. Denhardt, J.V. Denhardt, Public Adm<strong>in</strong>istration. An Action Orientation, Thomson Wadsworth,<br />
Belmont USA 2009;<br />
acts
1. Course title<br />
Organizational Behavior<br />
2. Course Code<br />
ZZL014<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Liliana Hawrysz PhD Eng., l.hawrysz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
1. Course title<br />
Organizational Culture<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
2 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 30<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g essence and the mechanism of organization behavior, their conditions and <strong>in</strong>fluence on<br />
organization and management<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Essence, <strong>in</strong>ternal and external conditions of organizational behaviors, authority and leadership at<br />
organization, conflict: <strong>in</strong>terpersonal, <strong>in</strong>ternal and between groups, communication <strong>in</strong> organization,<br />
stress: reason, symptoms and methods to overcome the stress.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
On the basis of participation <strong>in</strong> discussions<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
9. S.R. Robb<strong>in</strong>s, T.A. Judge, Organizational Behavior<br />
10. J.R., Jr Schermerhorn, J.G.Hunt, R.N. Osborn, Organizational Behavior<br />
11. M.A. Hitt, C.Ch. Miller, A. Colella, Organizational Behavior: A Strategic Approach<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL045<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
6 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Liliana Hawrysz PhD Eng., l.hawrysz@po.opole.pl,<br />
MSc. Zofia Wieszczeczyńska, z.wieszczeczynska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basics of Management; knowledge about organization, structure of organization<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g essence of the organizational culture, understand<strong>in</strong>g differences between national cultures.<br />
Ma<strong>in</strong> goal is for the students to be able to describe cultural differences and their <strong>in</strong>fluence on the<br />
Organizations <strong>in</strong> different countries.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURES:
Organizational culture, def<strong>in</strong>ition, types and profiles of culture, national cultures and organizational cultures,<br />
culture shock , leadership <strong>in</strong> organization and national culture, the seven cultures of capitalism, chang<strong>in</strong>g of<br />
culture.<br />
CLASSES:<br />
- Def<strong>in</strong>ition of Organizational Culture<br />
- Culture Typologies: Deal & Kennedy, Handy & Harrison, Hofstede, Cameron & Qu<strong>in</strong>n, Sikorski<br />
- Cultural shock<br />
- Motivation <strong>in</strong> Organization: theories and examples: Mayo, Maslow, Herzberg, McGregor, MCClelland,<br />
Vroom, Sk<strong>in</strong>ner, Alderfer<br />
- National culture and the <strong>in</strong>fluence on the Organization<br />
- Difference of organizational culture <strong>in</strong> countries<br />
- Differences between behavior <strong>in</strong> exemplary countries<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
On the basis of participation <strong>in</strong> discussions.<br />
Test and grade from work<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> groups<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
J.Mart<strong>in</strong>, Cultures <strong>in</strong> Organizations: Three Perspectives<br />
E.H. Sche<strong>in</strong>, Organizational Culture and Leadership<br />
Ch.M. Hampden- Turner, F.Trompenaars, Build<strong>in</strong>g Cross-Cultural Competence: How to Create Wealth from<br />
Conflict<strong>in</strong>g Values<br />
Kim S. Cameron Robert E. Qu<strong>in</strong>n. - Organizational Culture<br />
Ch. M. Hampden-Turner & Alfons Trompenaars – Seven cultures of capitalism<br />
Ch. M. Hampden-Turner & Alfons Trompenaars - The seven dimensions of culture, the importance of cultural<br />
differences<br />
1. Course title<br />
Regional Policy<br />
2. Course Code<br />
ZZM036<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 2<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
3 (master – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
<strong>english</strong><br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc eng<strong>in</strong>eer, Brygida Klemens, b.klemens@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Theoretical preparation from other <strong>courses</strong>, i.e. Microeconomic, Macroeconomics, Low<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students learn about regional analysis <strong>in</strong>struments.<br />
Students are acqua<strong>in</strong>t with basics and pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of regional policy practically.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
- Def<strong>in</strong>itions of regions.<br />
- Euroregions.<br />
- General <strong>in</strong>formation about regional structures.<br />
- Local management units and regions.<br />
- Ma<strong>in</strong> problems of regional development.<br />
- Competitiveness of regions.<br />
- Social-economic regional strategies.<br />
- Economic and social results of regional cooperation.<br />
This knowledge is teach<strong>in</strong>g with use of m<strong>in</strong>d mapp<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
15. Assessment methods
- students participation <strong>in</strong> classes,<br />
- project,<br />
- m<strong>in</strong>d maps (2)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
G. Gorzelak, Regional and Local Potential for transformation <strong>in</strong> Poland, European Institute for Regional and Local<br />
Studies, Warsaw 1998<br />
European Union, Regional Policy: Work<strong>in</strong>g for the regions, Brussels, 2001<br />
1. Course title<br />
Society and Culture of Europe I<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEL007a<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dorota Schreiber – Kurpiers, PhD, d.schreiber-kurpiers@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students will:<br />
use the ma<strong>in</strong> sociological and anthropological terms;<br />
analyze the social processes <strong>in</strong> comparative context;<br />
understand of the cultural aberration of Europe and the common groundwork of European civilization;<br />
analyze of social phenomenon based on concepts and models;<br />
understand of the historical develop<strong>in</strong>g of Europe (Europe as the social-cultural whole);<br />
understand the social-cultural aspects of <strong>in</strong>tegrations processes.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURE:<br />
1. Nation and State. Political Nation and Cultural Nation. (Germany and France)<br />
2. Power Symbols. National Symbols<br />
3. Symbol and Sign. Turner, Roland Barthes, Paul Ricoeur<br />
4. Rites and Rituals<br />
5. Gender<br />
6. M<strong>in</strong>ority. Sexual m<strong>in</strong>ority <strong>in</strong> Europe.<br />
7. Family and K<strong>in</strong>ship <strong>in</strong> Europe.<br />
8. Myths. Levi-Strauss<br />
9. Social Sigma. Red Hair – as the Process of Destigmatisation.<br />
10. Archetype. The Image of the Vampire <strong>in</strong> Europe and its Sexualization<br />
CLASSES:<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
-<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
-<br />
1. Course title<br />
Society and Culture of Europe II<br />
2. Course code<br />
ZEL007b<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
2 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English, german<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Dorota Schreiber – Kurpiers, PhD, d.schreiber-kurpiers@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students will:<br />
use the ma<strong>in</strong> sociological and anthropological terms;<br />
analyze the social processes <strong>in</strong> comparative context;<br />
understand of the cultural aberration of Europe and the common groundwork of European civilization;<br />
analyze of social phenomenon based on concepts and models;<br />
understand of the historical develop<strong>in</strong>g of Europe (Europe as the social-cultural whole);<br />
understand the social-cultural aspects of <strong>in</strong>tegrations processes.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURE:<br />
1. „The Mission of Europe”<br />
2. Colonialism and its <strong>in</strong>fluence on the European economics.<br />
3. Colonialism and its Influence on the European Culture.<br />
4. Social Conflicts. Classical Theories.<br />
5. Social Conflicts and the different but possible scenarios. Hunt<strong>in</strong>g for Witches. (Keith Thomas)<br />
6. The Fill<strong>in</strong>g of Mortification <strong>in</strong> Europe. From the Historical Po<strong>in</strong>t of View.<br />
7. Migration <strong>in</strong> Europe. From the Historical Po<strong>in</strong>t of View.<br />
8. Ethnicity. (Eriksen)<br />
9. Ethnonationalism<br />
10. Religious diversity <strong>in</strong> Europe. Judaism<br />
11. Religious diversity <strong>in</strong> Europe. Christianity<br />
12. The perception of the Arabic culture <strong>in</strong> Europe. From historical po<strong>in</strong>t of view.<br />
13. New Religions <strong>in</strong> Europe<br />
14. Religion and War<br />
15. European Cultural Policy.<br />
CLASSES:<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
-<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
-<br />
1. Course title<br />
Sociology and Psychology of Management<br />
2. Course Code<br />
ZZL040<br />
4. Type of course<br />
elective<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2, 1<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
5. Semester<br />
5 (first – degree studies)<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30, 15
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Kornelia Polek-Duraj, k.polek-duraj@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the course is to acquire students' basic knowledge of sociology and psychology, management,<br />
and expand their awareness of social skills needed to lead a team of Staff. Obta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g credit course the<br />
student should know the basic mechanisms and organizational behavior, and pathology (eg. mobb<strong>in</strong>g). The<br />
program also <strong>in</strong>cluded the subject of effective management, leadership, and the operationalization of the<br />
concept of corporate social responsibility.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
1. Man <strong>in</strong> the process management<br />
2. Features and capacity utilization of workers<br />
3. Motivation (psychological aspects)<br />
4. Psychological difficulties <strong>in</strong> the management (stress, burn-out syndrome)<br />
5. The endorsement management<br />
6. Teams <strong>in</strong> the process management<br />
7. Grounds and effectiveness of the team (sociological)<br />
8. Communicat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> groups and organizations<br />
9. Develop<strong>in</strong>g creativity and presentation skills<br />
10. Entrepreneurship <strong>in</strong> the management band<br />
11. Managerial tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g (sensitivity tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g, work tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g)<br />
12. Conflict management<br />
13. Pathology <strong>in</strong> the organization<br />
14. Social responsibility standards for companies<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar is conducted <strong>in</strong> the form of these exercises, case studies and troubleshoot<strong>in</strong>g tasks.<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Carsten K.W. De Dreu, Michele J. Gelfand, THE PSYCHOLOGY OF CONFLICT AND CONFLICT MANAGEMENT IN<br />
ORGANIZATIONS. Psychology Press.<br />
Conny Antoni, Guido Hertel, TEAM INNOVATION, KNOWLEDGE AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT.<br />
Katz, John Wiley & Sons, THE SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OF ORGANIZATIONS, 2ND EDITION .<br />
W. RATYŃSKI, PSYCHOLOGICZNE I SOCJOLOGICZNE ASPEKTY ZARZĄDZANIA. WYDAWNICTWO C. H. BECK,<br />
WARSZAWA 2005.<br />
J. F. TERLAK, PSYCHOLOGIA ORGANIZACJI I ZARZĄDZANIA. WYDAWNICTWO DIFIN, WARSZAWA 2005.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Strategic Management<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZM006<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
2 (master – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Liliana Hawrysz PhD Eng., l.hawrysz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g essence and the mechanism of strategic management, understand<strong>in</strong>g method of strategic
analyz<strong>in</strong>g and plann<strong>in</strong>g, us<strong>in</strong>g method of strategic analyz<strong>in</strong>g and plann<strong>in</strong>g to solve management problems<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Strategy, global and local context strategy, strategic mission and goals of organization, method of<br />
strategy analyz<strong>in</strong>g<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
On the basis of participation <strong>in</strong> discussions<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
M. A. Hitt, R. D. Ireland, R. E. Hoskisson, Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization,<br />
Concepts and Cases<br />
G. Dess, G.T. (Tom) Lumpk<strong>in</strong>, A. Eisner, Strategic Management<br />
Ch. Hill, G. Jones, Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach<br />
1. Course title<br />
EU`s Common Foreign and Security Policy<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZEM004<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1 (muster – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 1<br />
30, 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
<strong>english</strong><br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc Filip Tereszkiewicz, f.tereszkiewicz@poczta.po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
It will not be necessary to have taken any sem<strong>in</strong>ars<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Students learn how to put projects <strong>in</strong>to practise.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURES:<br />
The historical development of CFSP; what does the EU seek to achieve through the CFSP? What part does it play<br />
<strong>in</strong> the overall framework of EU external relations?<br />
The legal nature of the CFSP: to what extent is it part of Union law? Do the general EU pr<strong>in</strong>ciples e.g. direct effect<br />
and primacy apply? What is the role of the ECJ?<br />
CFSP <strong>in</strong>struments: unilateral <strong>in</strong>struments and <strong>in</strong>ternational agreements; legal nature, objectives, policy<br />
framework. Role of 'soft law' e.g. guidel<strong>in</strong>es, Council Conclusions.<br />
CLASSES:<br />
CSDP <strong>in</strong>struments: civilian and military missions - one or two case studies.<br />
Relationship between CFSP and other EU external policies: legal rules, legal basis questions, and policy<br />
coherence. Is the CFSP an overall fram<strong>in</strong>g policy or a specific group of <strong>in</strong>struments for specific tasks? What (if<br />
any) are the dist<strong>in</strong>ctive CFSP objectives?<br />
Relationship between EU and NATO, UN: how does the CFSP/CSDP affect the development of the EU as an<br />
<strong>in</strong>ternational actor?<br />
Flexibility and enhanced cooperation <strong>in</strong> CFSP and CSDP: decision-mak<strong>in</strong>g flexibility; role of enhanced<br />
cooperation; permanent structured cooperation <strong>in</strong> defence; the special position of Denmark;<br />
Institutional framework and decision-mak<strong>in</strong>g: role of European Parliament; role of EEAS; role of High<br />
Representative. The position of the Member States: is there a genu<strong>in</strong>ely 'common' foreign policy?<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
One essay at 2 000 - 2 500 word maximum<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Ch. Bretherton, J. Vogler, The European Union as a Global Actor, NY 2008,<br />
S. Keukeleire, J. MacNaughtan, The Foreign Policy of the European Union, Bas<strong>in</strong>gstoke 2008,<br />
K. E. Smith, European Union Foreign Policy <strong>in</strong> a Chang<strong>in</strong>g World, Cambridge 2009,
M. E. Smith, Europe`s Foreign and Security Policy. The Institutionalization of Cooperation, Cambridge 2005,<br />
1. Course title<br />
Quality Management<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
ZZL017<br />
Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 (first – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
7<br />
-<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2, 2<br />
30, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph. D. Elżbieta Karaś, e.karas@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Knowledge of basic enterprise management<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Prepar<strong>in</strong>g students to f<strong>in</strong>d ways of solv<strong>in</strong>g problems <strong>in</strong> area of quality management and to use basic<br />
methods and techniques.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
LECTURE:<br />
1. Introduction – theoretic basis of quality management<br />
2. Quality management methods used <strong>in</strong> enterprises<br />
3. Tools of quality improvement<br />
4. Quality management and standardization accord<strong>in</strong>g to ISO series 9000<br />
5. Standardization documentation<br />
6. Audit<strong>in</strong>g and certification of quality management systems<br />
7. Practical implementation of quality management system<br />
8. Concept of quality costs<br />
9. A human aspect of quality management<br />
SEMINAR:<br />
1. Fundamental issues of quality management<br />
2. Method of self-assessment by quality criteria<br />
3. Method of process mapp<strong>in</strong>g<br />
4. Just-<strong>in</strong>-time system<br />
5. Ishikawa’s and Pareto’s diagrams<br />
6. FMEA – failure mode and effect analysis<br />
7. QFD – quality function deployment<br />
8. Creat<strong>in</strong>g documentation accord<strong>in</strong>g to ISO 9000 standards<br />
9. Guidel<strong>in</strong>es for benchmark<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> enterprise<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture and multimedia presentations, group discussions, case studies.<br />
Prepar<strong>in</strong>g papers, solv<strong>in</strong>g case studies, f<strong>in</strong>al test<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Imai M.: Kaizen. The Key to Japan’s Competitive Success, New York 2007<br />
Hoyle D.: ISO 9000 Quality Systems Handbook, Oxford 2003<br />
Liker J. K.: Toyota Way, New York 2003<br />
Oakland J.: Quality Management, Oxford 2004<br />
1. Course title<br />
Value-Based Management<br />
2. Course code 3. Form of class
ZZM034 Lecture, classes<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
4 (master – degree studies)<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1, 2<br />
15, 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Justyna Zygmunt, PhD, j.zygmunt@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of enterprise f<strong>in</strong>ancial activity and economy<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g the aspects of value-based management. Recognition of methods and measures applied <strong>in</strong><br />
company value pric<strong>in</strong>g processes.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The essence and the premises of company value pric<strong>in</strong>g. Value standards. Functions of company value<br />
pric<strong>in</strong>g. Factors affect<strong>in</strong>g company value. System and stages of value-based management. Classification of<br />
company value pric<strong>in</strong>g methods. Factors of value pric<strong>in</strong>g methods selection. Income methods. Assets based<br />
methods. Mixed and comparative methods. Internal and external measures of value creation efficiency.<br />
Strategic matrixes of value-based management. Intellectual capital <strong>in</strong> value-based management.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Constant evaluation of student’s work. F<strong>in</strong>al test <strong>in</strong> the end of semester. Duration and test date is given on<br />
the first class<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
R.A. Brealey, S.C. Myers, Capital Investment and Valuation, The McGraw Hill, New York 2003.<br />
A. Rappaport, Creat<strong>in</strong>g Shareholder Value, Free Press, 1997.<br />
A. Brook<strong>in</strong>g, Intellectual Capital: Core Assets for the Third Millennium Enterprise, Thomson Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Press,<br />
London 1996.<br />
A. Damodaran, Damodaran on Valuation. Security Analysis for Investment and Corporate<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>formation regard<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>courses</strong> taught at Faculty of Education Management should be consulted with the<br />
lecturers and/or Faculty coord<strong>in</strong>ator<br />
_____________________________________________________________<br />
FACULTY OF PRODUCTION ENGINEERING AND LOGISTICS<br />
5 Luboszycka Street, 45-036 Opole, Poland<br />
phone (+48 77) 453 84 47-9 w. 171, 172<br />
e-mail: wetii@po.opole.pl, http://www.eti.po.opole.pl
FIELDS OF STUDY � Education <strong>in</strong> Technology and Informatics (BSc, MSc)<br />
� Logistics (BSc )<br />
� Security Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g (BSc )<br />
FACULTY DEPARTMENTS � Mathematics and Physics<br />
� Mathematics and Computer Science Applications<br />
� Physics<br />
� Technology and Education<br />
� Applications of Chemistry and Mechanics<br />
� Technology and Work Environment Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Faculty Erasmus Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Hanna Ścięgosz, PhD; h.sciegosz@po.opole.pl<br />
COURSES IN ENGLISH<br />
Course<br />
code<br />
Course Name ECTS credits<br />
T001 Mathematical Analysis 6<br />
T002 Mathematical Statistics 6<br />
T003 Mathematics - L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra 6<br />
T004 Mathematical Model<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Technology m 4<br />
T005 Statistics 6<br />
T006 Production and Services Management 6<br />
T007 Differential Equations 5<br />
T008 Chemistry 6<br />
T009 Multivariate Data Analysis for Market<strong>in</strong>g Research 6<br />
T010 Quality Management 2<br />
T011 Market<strong>in</strong>g 4<br />
T012 Quality management of the production 3<br />
T013 Manag<strong>in</strong>g the service quality 3<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mathematical Analysis<br />
2. Course Code<br />
T001<br />
3. Form of class<br />
Lecture and sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1 st or above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week 9. Number of hours per semester
Lecture – 2<br />
Lecture – 30<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 1<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Hanna Ścięgosz PhD Eng., h.sciegosz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamental knowledge of mathematics, elementary functions, some experience with mathematical<br />
language and proofs.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
To <strong>in</strong>troduce students to differential and <strong>in</strong>tegral calculus of functions of one variable and several variables<br />
and to provide the background for more advanced <strong>courses</strong>.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Mapp<strong>in</strong>gs and their properties;<br />
� Sequences of numbers and limits of sequences;<br />
� Limits of one variable functions, cont<strong>in</strong>uity;<br />
� Differentiation of one variable functions and applications of the derivative;<br />
� Integration of one variable functions and applications;<br />
� Inf<strong>in</strong>ite series of numbers and functions, applications;<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>ear ord<strong>in</strong>ary differential equations with constant coefficients;<br />
� Differential calculus of functions of several variables.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written and oral assessment, <strong>in</strong>dividual elaborate<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) E. Zakon, Mathematical Analysis I, The Trillia Group, 2004<br />
b) B. S. Schroder, Mathematical Analysis: A Concise Introduction, JohnWiley&Sons,2008<br />
c) G.M. Fihtenholtz, Course <strong>in</strong> the Differential and Integral Calculus vol. I, II, III, Nauka, Moscow, 1969.<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: PowerPo<strong>in</strong>t and Derive 6.1 presentations, elaboration and discussion.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mathematical Statistics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T002<br />
Lecture, sem<strong>in</strong>ar, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
2 nd or above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture – 2<br />
Lecture – 30<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 1<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 15<br />
Laboratory – 1<br />
Laboratory – 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Hanna Ścięgosz PhD Eng., h.sciegosz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamental knowledge of mathematics, elementary functions, elementary course of mathematical analysis<br />
and probability.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
To provide students <strong>in</strong> fundamental concepts of stochastic mathematics and their apply<strong>in</strong>g to econometrics,<br />
edumetrics, technometrics, decision science, etc.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Statistical experiments and their graphical presentations;<br />
� Descriptive statistic;<br />
� Random variables and their distributions;
� Po<strong>in</strong>t and <strong>in</strong>terval estimation;<br />
� Test<strong>in</strong>g of parametric and non-parametric statistical hypothesis;<br />
� Correlation, l<strong>in</strong>ear and non-l<strong>in</strong>ear regression;<br />
� Time series.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written and oral assessment, <strong>in</strong>dividual elaborate<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) D. C. Montgomery, G. C. Runger, Applied Statistics and Probability for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers, John Wiley & Sons, 2003;<br />
b) D.Wackerly, W.Mendenhall, R.L.Scheaffer, Mathematical Statistics with Applications,2007;<br />
c) L. Wasserman, All of Statistics: A Concise Course <strong>in</strong> Statistical Inference, Spr<strong>in</strong>ger Sciences + Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Media,<br />
2004.<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: power-po<strong>in</strong>t presentation, elaborate and discussion;<br />
Laboratory: STATISTICA 7.0.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mathematics - L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T003<br />
Lecture and sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1 st or above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture – 2<br />
Lecture – 30<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 1<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Hanna Ścięgosz PhD Eng., h.sciegosz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamental and relatively basic knowledge of mathematics beyond arithmetic.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Profile of this lecture comes to know the algebraic notations and to apply them to solve some technical<br />
problems.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Complex numbers;<br />
� Rational functions, polynomials and partial fractions;<br />
� Matrices and determ<strong>in</strong>ants;<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>ear equations;<br />
� L<strong>in</strong>ear spaces;<br />
� Vector spaces;<br />
� Eigenvalues and eigenvectors;<br />
� Tree-dimensional geometry.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written and oral assessment, <strong>in</strong>dividual elaborate<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) K.R. Matthews, Elementary l<strong>in</strong>ear algebra, Univ. of Queensland, Press 1991<br />
b) D.J. W<strong>in</strong>ter, A Primer of L<strong>in</strong>ear Algebra, Macmillan, Press 1988<br />
c) M. Art<strong>in</strong>, Algebra, Prentice Hall, 1991<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: PowerPo<strong>in</strong>t, Derive 6.1 and e-learn<strong>in</strong>g presentations, elaborate and discussion.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Mathematical Model<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Technology
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T004<br />
laboratory/sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Elective<br />
5<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Andrzej Metelski PhD a.metelski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Mathematics 1, Mathematics 2<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Fundamentals of model<strong>in</strong>g physical processes us<strong>in</strong>g numerical methods and computer software.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Fundamentals of f<strong>in</strong>ite element method and Matlab<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Project: computer program (e.g. model<strong>in</strong>g heat conduction problem)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) J.V.Beck, B.Blackwell, J.R.St.Clair, Inverse heat conduction, a Wiley Interscience Publication, 1985.<br />
b) B.Mochnacki, J.S.Suchy, Numerical methods <strong>in</strong> computations of foundry processes, PFTA, Cracow 1995.<br />
c) O.C.Zienkiewicz, The f<strong>in</strong>ite element method, Butterworth-He<strong>in</strong>emann, Oxford, 2000.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Statistics<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T005<br />
Lecture, laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
II<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
Basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2h for lecture, 2h for laboratory<br />
30h for lecture, 30h for laboratory<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Anna Koziarska, a.koziarska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge <strong>in</strong> analysis and algebra, <strong>in</strong>tegration and differentiation of one variable functions.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Knowledge of the basic ideas of probability theory and its application. Knowledge and apprehension of<br />
descriptive statistic method and methods of mathematical statistics and conquest of ability of their<br />
application <strong>in</strong> practical questions.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Descriptive statistics (measures of central tendency: mode, median, mean, measures of dispersion: range,<br />
variance, standard deviation and many others, empirical distributions and its graphics illustrations);<br />
foundation of probability theory (basic concept and def<strong>in</strong>itions); random variables (discrete and cont<strong>in</strong>uous);<br />
discrete distributions; cont<strong>in</strong>uous distributions; conditional distributions examples; functions of random<br />
variables; important examples of distributions (the b<strong>in</strong>omial distribution, the Poisson distribution, the normal<br />
distribution, the chi-square distribution, the Student distribution, the F distribution); the Law of Large<br />
Numbers; the Central Limit Theorem; po<strong>in</strong>t estimation; set estimation (estimation the normal model,<br />
estimation <strong>in</strong> the two-sample normal model and others); hypothesis test<strong>in</strong>g (basic ideas and examples: tests<br />
<strong>in</strong> the normal model, tests <strong>in</strong> the two-sample normal model, nonparametric tests); pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of regression
and correlation analysis (as an example: l<strong>in</strong>ear correlation and regression).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Laboratory - written test (solv<strong>in</strong>g problems with the use of computer program (STATISTICS)).<br />
Lecture - written exam (solv<strong>in</strong>g problems with the use of the methods from the lecture)<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) J. P. Marques de Sá; Applied Statistics; Spr<strong>in</strong>ger-Verlag, Berl<strong>in</strong> Heidelberg 2007<br />
b) D. C. Montgomery, G. C. Runger; Applied Statistics and Probability for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers, J.Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2002<br />
c) H.Stark, J.W.Woods; Probability, Random Processes, and Estimation Theory for Eng<strong>in</strong>eers; Prentice-Hall; New<br />
Jersey 1986<br />
d) E. Mansfield; Statistics for Bus<strong>in</strong>ess and Economic: Methods and Applications; W.W. Norton & Company; New<br />
York, London 1987<br />
e) T. D. V. Sw<strong>in</strong>scow; Statistics at Square One, BMJ Books; 2002<br />
f) W. Feller; An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications, Vol.1,2; J.Wiley & Sons, Inc; 1968, 1971<br />
1. Course title<br />
Production and Services Management<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T006<br />
Lecture & sem<strong>in</strong>ary & laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
elective<br />
VI<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
lecture - 2h sem<strong>in</strong>ary - 2h laboratory - 1h<br />
Lecture - 30h sem<strong>in</strong>ar - 30 laboratory – 15h<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Jurczyk-Bunkowska Magdalena, m.jurczyk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Basic knowledge of Market<strong>in</strong>g and F<strong>in</strong>ancial Management<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of this course is to provide the students with a knowledge base on how to develop and run<br />
bus<strong>in</strong>esses more efficient. Dur<strong>in</strong>g the course the students will be <strong>in</strong>troduced to terms, methods, and current<br />
research topics with<strong>in</strong> the field of operation management. Although the ma<strong>in</strong> focus <strong>in</strong> the course is <strong>in</strong>dustry,<br />
almost all methods are general and therefore applicable <strong>in</strong> service trades like the hotel <strong>in</strong>dustry, consult<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
hospitals, public services etc.<br />
Students will understand the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and practice of factors which <strong>in</strong>fluence the capacity to compete<br />
effectively <strong>in</strong> manufactur<strong>in</strong>g and service operations.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
The Production and Operations Function and the Organisation, Production/Operations Strategy, Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and Controll<strong>in</strong>g the Operations, Production/Operations Management<br />
Production/Operations Management <strong>in</strong> Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g and Service Environments, Market<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
Product/Service Design, Product/Service: Variety and Value, Quality, Reliability, Product, Service, Operations<br />
and Competitive Strategies, Location and Design of the Plant or Facilities, Layout of the Facilities, Equipment<br />
Selection, Ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of the Facilities and Equipment, Production/Operation Systems Design, Work<br />
Measurement, Operations Control: An Introduction, Forecast<strong>in</strong>g, Capacity Management and Operations<br />
Schedul<strong>in</strong>g, Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Plann<strong>in</strong>g Case Study, Data Capture and Release, Inventory Management,<br />
Manufactur<strong>in</strong>g Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Control Systems, Project Management, Resource Allocation - L<strong>in</strong>ear<br />
Programm<strong>in</strong>g, Purchas<strong>in</strong>g, Despatch.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture – oral exam<strong>in</strong>ation; sem<strong>in</strong>ary participation; laboratory completion of <strong>in</strong>dividual project assignments<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Gideon Halevi: Handbook of Production Management Methods, Butterworth He<strong>in</strong>emann, 2001.<br />
b) Keith Lockyer, Alan Muhlemann, and J.S. Oakland: Production and Operations Management, F<strong>in</strong>ancial Times/<br />
Prentice Hall
c) Donald Waters: Operations Management. Product<strong>in</strong>g Goods and Services F<strong>in</strong>ancial Times/ Prentice Hall (now<br />
2th edition)<br />
d) Eliyahu M. Goldratt and Jeff Cox The Goal: A Process of Ongo<strong>in</strong>g Improvement, Gower Publish<strong>in</strong>g Ltd<br />
e) Chase, Richard B. (2006). Operations management for competitive advantage. McGraw-Hill/Irw<strong>in</strong>; 11 edition<br />
f) David Ray Anderson Dennis J. Sweeney Thomas Arthur Williams (2008): An Introduction to Management<br />
Science: Quantitative Approaches to Decision Mak<strong>in</strong>g, South-Western Educational Publish<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1. Course title<br />
Differential Equations<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T007<br />
Lecture and sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
optional<br />
3th or above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture – 1; Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 1<br />
Lecture – 15; Sem<strong>in</strong>ar – 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD Eng. Hanna Ścięgosz h.sciegosz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamental knowledge of mathematics, elementary functions, experience with mathematical language and<br />
proofs, calculus I.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
To <strong>in</strong>troduce students to methods of solv<strong>in</strong>g of differential equations and model<strong>in</strong>g via differential<br />
equations. To present their applications.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
� Introduction and First Def<strong>in</strong>itions;<br />
� First Order Differential Equations (Separable Equations, Homogeneous Equations, L<strong>in</strong>ear Equations, Bernoulli<br />
Equations, Darboux Equations, Riccati Equations, Exact and Non-Exact Equations, Integrat<strong>in</strong>g Factor<br />
technique, Numerical Technique: Euler's Method, Existence and Uniqueness of Solutions, Picard Iterative<br />
Process)<br />
� Second Order Differential Equations (Reduction of Order, Euler-Cauchy Equations);<br />
� Higher Order L<strong>in</strong>ear Equations (Homogeneous L<strong>in</strong>ear Equations with Constant Coefficients, Non-<br />
Homogeneous L<strong>in</strong>ear Equations, Method of Undeterm<strong>in</strong>ed Coefficients, Method of Variation of Parameters,<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear Independence and the Wronskian);<br />
� Systems of Differential Equations (Second Order Equations and Systems, Euler's Method for Systems, L<strong>in</strong>ear<br />
Systems, Qualitative Analysis of L<strong>in</strong>ear Systems);<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Written and oral assessment, <strong>in</strong>dividual elaborate<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
P. Blanchard, R. L. Devaney, G. R. Hall, Differential equations, Cengage Learn<strong>in</strong>g, 2006;<br />
J. C. Rob<strong>in</strong>son, An <strong>in</strong>troduction to ord<strong>in</strong>ary differential equations, Cambridge University Press, 2004;<br />
R. Bronson, E. J. Bredenste<strong>in</strong>er, Differential equations, McGraw-Hill Professional, 2003.<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation (uwagi dodatkowe)<br />
Sem<strong>in</strong>ar: PowerPo<strong>in</strong>t presentations, elaborate and discussion.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Chemistry<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T008<br />
Lectures, sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Compulsory<br />
1 st and above<br />
6. Numer of ECTS credits 7. Level of class
6 basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
lectures 2hours/week<br />
classes 1 hour/week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lectures 30<br />
Class (recitation) 15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. Janusz Pająk, j.pajak@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites -<br />
13. Objectives of the course -<br />
14. Objectives of the course<br />
To provide students withan understand<strong>in</strong>g of the bacic concepts of chemistry and basic chemical calculations<br />
15. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of chemistry,<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g stoichiometry, nomenclature, atomic structure, bond<strong>in</strong>g, redox reactions,<br />
periodicity, equilibria, electrochemistry, k<strong>in</strong>etics, <strong>in</strong>organic and organic compounds. The recitation hour –<br />
practice on chemical calculations and problem solv<strong>in</strong>g<br />
16. Assessment methods<br />
Written exams<br />
17. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture and class notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Multivariate Data Analysis for Market<strong>in</strong>g Research<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T009<br />
Lecture and laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
Elective<br />
5th or above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
Intermediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
Lecture – 2<br />
Lecture – 30<br />
Laboratory – 2<br />
Laboratory – 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Mariusz Kubus PhD, m.kubus@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
Fundamental knowledge of l<strong>in</strong>ear algebra and statistics.<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Descriptive and predictive model<strong>in</strong>g, extraction of knowledge from data for decision support <strong>in</strong> market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
managment.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
L<strong>in</strong>ear models for regression and discrim<strong>in</strong>ation, non-parametric methods of regression, classification and<br />
regression trees, <strong>in</strong>duction of logical rules, ensemble methods, m<strong>in</strong>imum distance based methods,<br />
cluster<strong>in</strong>g, corespondence analysis, feature selection. Application <strong>in</strong> Market<strong>in</strong>g and Management Science<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Lecture - written test<br />
Laboratory – <strong>in</strong>dividual elaborate<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a. Hand D., Mannila H., Smyth P. (2001), Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Data M<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g, The MIT Press.<br />
b. Hastie T., Tibshirani R., Friedman J. (2001), The Elements of Statistical Learn<strong>in</strong>g: Data M<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g, Inferance, and<br />
Prediction. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger, New York.<br />
c. Webb A.R. (2002), Statistical Pattern Recognition. 2 nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons.<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Laboratory: computation with a use of R
1. Course title<br />
Quality Management<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T010<br />
laboratory<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
III<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15 h<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English, Polish<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Katarzyna Hys, e-mail: k.hys@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
-<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Process approach <strong>in</strong> quality management systems with<strong>in</strong> an organization. Conformity assessment <strong>in</strong> the<br />
stage of design<strong>in</strong>g, manufactur<strong>in</strong>g and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Process approach <strong>in</strong> quality management systems with<strong>in</strong> an organization. Assumptions for process approach<br />
covered by PN-EN ISO 9001:2001. Def<strong>in</strong>itions related to processes. Human, equipment and material<br />
resources management. Processes distribution with<strong>in</strong> an organization. Methods of process determ<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
with<strong>in</strong> an organization. Documentation of the process-based quality management system. Declaration of<br />
conformity, technical criteria for conformity assessment Conformity assessment <strong>in</strong> the stage of design<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
manufactur<strong>in</strong>g and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of the selected <strong>in</strong>stallations. Design, manufactur<strong>in</strong>g and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance<br />
procedures related to regulations and standards <strong>in</strong> force. Assessment of approval tests. Responsibility<br />
related to ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of <strong>in</strong>stallations of high level of risk.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Individual project<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a) Hamrol A., Mantura W.: Zarządzanie jakością-teoria i praktyka, PWN, Warszawa 2002.<br />
b) Kraszewski R.: TQM teoria i praktyka. Toruń 2001.<br />
c) Lock D.: Zarządzanie jakością, PWN, Warszawa 2002. EN ISO 9001:2000<br />
d) Quality management systems - requirements.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T011<br />
project, exercises<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
4<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Katarzyna Hys, PhD Eng, tel.: + 48 77 42 34 039<br />
email: k.hys@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites
asic knowledge <strong>in</strong> the scope of the management<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Acqua<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g students with bases of market<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g cells, tasks, functions, strategies, <strong>in</strong>struments and<br />
essential methods are a purpose of the object. Exploit<strong>in</strong>g the wisdom <strong>in</strong> practice is significant - this process is<br />
be<strong>in</strong>g carried out on exercise classes as part of <strong>in</strong>dividual issues.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
• Description of the work of the market<strong>in</strong>g department: vision, mission of the department, organizational<br />
structure.<br />
• EVALUATION OF THE CURRENT MARKETING SITUATION OF THE ENTERPRISE: Market<strong>in</strong>g environment of the<br />
company. Offered products. Target market. Competition analysis. Analysis of chances and threats.<br />
• DEFINED MARKETING OBJECTIVES: Cells <strong>in</strong> a short span of time. Cells <strong>in</strong> the long term.<br />
• PROPOSALS OF MARKETING STRATEGIES: Chosen action <strong>in</strong> the sphere of the product, the price, distribution<br />
and promocji-mix.<br />
• OPERATIONAL PLANS: Schedule of action carried out. Duties and liabilities of the staff.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
exercises: active participation under the exercises, written report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g (for ex ample):<br />
• Hoyer, W.D. and MacInnis, D.J. (2001) Consumer Behaviour, 2nd Edition, USA: Houghton Miffl<strong>in</strong> Company<br />
• Baker, M. (2000) Market<strong>in</strong>g Management and Strategy, 3rd edition, Macmillan Bus<strong>in</strong>ess.<br />
• Booms, B.H. and Bitner, M.J. (1981), Market<strong>in</strong>g strategies and organisation structures for service firms, <strong>in</strong><br />
Market<strong>in</strong>g of Services, J. Donnelly and W.R. George (eds), American Market<strong>in</strong>g Association<br />
• Davies, M. (1998) Understand<strong>in</strong>g Market<strong>in</strong>g, 1st edition. Prentice Hall<br />
• Fill, C (2002) Market<strong>in</strong>g Communications, Contexts, strategies and applications, Prentice Hall<br />
• Kotler, P, Armstrong, G, Saunders, J and Wong, V, (2001), Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Market<strong>in</strong>g: Third European Edition,<br />
Prentice Hall, Harlow<br />
• Kotler, P. and Armstrong, G. (1997) Market<strong>in</strong>g An Introduction. Fourth Edition. New Jersey. Prent<strong>in</strong>ce Hall<br />
International<br />
• Kotler, P., Armstrong, G., Saunders, J. and Wong, V. (1999) Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of Market<strong>in</strong>g, 2nd Edition, New Jersey:<br />
Prentice Hall<br />
• Lauterborn, R.(1990), New market<strong>in</strong>g litany:4Ps passe; 4Cs take over, Advertis<strong>in</strong>g Age, Oct. 1:26<br />
• Lovelock (2001) Services Market<strong>in</strong>g, people, technology, strategy, Prentice Hall.<br />
• McCarthy, J. (1975), Basic Market<strong>in</strong>g: a managerial approach, Homewood, IL<br />
• McDonald, M. (2001) Market<strong>in</strong>g Plans. How to prepare them, how to use the. 4th edition, Butterworth<br />
He<strong>in</strong>enamm<br />
• Peter, J.P. and Olson, J.J. (1996) Consumer Behaviour and Market<strong>in</strong>g Strategy, USA: Irw<strong>in</strong><br />
1. Course title<br />
Quality management of the production<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T012<br />
project, exercises<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Katarzyna Hys, PhD Eng, tel.: + 48 77 42 34 039<br />
email: k.hys@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
basic knowledge <strong>in</strong> the scope of the management<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Purpose of the exercise: Methods support<strong>in</strong>g the quality management <strong>in</strong> the production <strong>in</strong> real conditions (<strong>in</strong><br />
the given enterprise).
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Apply<strong>in</strong>g chosen methods of estimation of the product quality:<br />
• Quality Function Deployment (QFD),<br />
• Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA),<br />
• Compla<strong>in</strong>t resolution (procedure),<br />
• Strategic scorecard (BSC),<br />
• Rank<strong>in</strong>g of Suppliers accord<strong>in</strong>g to beloveds of criteria,<br />
• Audits (list of test questions, check list).<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
exercises: active participation under the exercises, written report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g (for ex ample):<br />
• Quality Associates International's History of FMEA<br />
• E. Fadlovich, Perform<strong>in</strong>g Failure Mode and Effect Analysis [1]<br />
• http://www.asq.org/learn-about-quality/process-analysis-tools/overview/fmea.html<br />
• Kmenta, Steven; Koshuke Ishii (November 2004). "Scenario-Based Failure Modes and Effects Analysis Us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Expected Cost". Journal of Mechanical Design 126 (6): 1027.<br />
• Richard Denney. 2005. Succeed<strong>in</strong>g with Use Cases: Work<strong>in</strong>g Smart to Deliver Quality, Addison-Wesley Object<br />
Technology Series, Addison-Wesley Professional, ISBN 0321316436<br />
• HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW, The House of Quality by John R. Hauser and Don Claus<strong>in</strong>g, May-June 1988<br />
• QFD FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about QFD<br />
• http://www.webducate.net/qfd/<br />
• QFD Onl<strong>in</strong>e - Free House of Quality (QFD) Templates for Excel<br />
• "What is QFD?" - White paper expla<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g what QFD is and how to use it.<br />
• 2GC Limited (2009), "2GC Balanced Scorecard Usage Survey 2009", “FAQ Answer: What is the Balanced<br />
Scorecard?”.<br />
• Art Schneiderman, "The First Balanced Scorecard"<br />
• "The Balanced Scorecard - Measures that Drive Performance", Harvard Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Review, Feb. 1992<br />
• Maisel, L.S., “Performance measurement: the balanced scorecard approach”, Journal of Cost Management,<br />
Vol. 6 No. 2, 1992, pp. 47-52.<br />
• "Performance Drivers: A practical guide to us<strong>in</strong>g the Balanced Scorecard", Nils-Goran Olve, JanRoy, Magnus<br />
Wetter. John Wiley & Sons, 1999<br />
• e.g. Brignall, S. (2002) "The UnBalanced Scorecard: a Social and Environmental Critique", Proceed<strong>in</strong>gs, Third<br />
International Conference on Performance Measurement and Management (PMA 2002) Boston, MA, USA July<br />
2002; Butler A. Letza S.R. and Neale B. (1997).<br />
• Cobbold, I. and Lawrie, G. (2002a). “The Development of the Balanced Scorecard as a Strategic Management<br />
Tool”. Performance Measurement Association 2002<br />
• Kaplan R.S. and Norton D.P. (2000). The Strategy Focused Organization, HBS Press, USA.<br />
1. Course title<br />
Manag<strong>in</strong>g the service quality<br />
2. Course Code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
T013<br />
project, exercises<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4 and above<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
1<br />
15<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>strucion<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Katarzyna Hys, PhD Eng, tel.: + 48 77 42 34 039<br />
email: k.hys@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites
asic knowledge <strong>in</strong> the scope of the management<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Understand<strong>in</strong>g the be<strong>in</strong>g of the service quality is a purpose of classes. Gett<strong>in</strong>g acqua<strong>in</strong>ted with types of services<br />
and characteristic features of services. Dist<strong>in</strong>guish<strong>in</strong>g types of services and the guild of services for <strong>in</strong>dividual types<br />
of the market: B2B and B2C. Exam<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and know<strong>in</strong>g requirements of customers for services of different type.<br />
Form<strong>in</strong>g the semantic profile for competence of the service staff. The evaluation and the measurement of the<br />
service quality of methods with the help chosen.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
• def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g and classify<strong>in</strong>g services.<br />
• design<strong>in</strong>g and present<strong>in</strong>g services.<br />
• services provid<strong>in</strong>g company – <strong>in</strong>ternal and outside condition<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
• the service contact and the buy<strong>in</strong>g decision process of the service.<br />
• apply<strong>in</strong>g the mix concept of market<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> services.<br />
• issues of the quality <strong>in</strong> services.<br />
• problems and manners of the evaluation of the service quality.<br />
• competence of employees of service companies.<br />
• offer of production services – the questionnaire form and comparison.<br />
• bluepr<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g for production services.<br />
• servperf for general-public services.<br />
• quota evaluation for consumer services.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
exercises: active participation under the exercises, written report<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g (for ex ample):<br />
• Baker, E. R. and Fisher, M. J., Organiz<strong>in</strong>g for Quality Management - Handbook of Software Quality Assurance,<br />
Artech House Inc., pp. 1-34, 2008<br />
• Balog, A., Badulescu, G., Badulescu, R. and Petrescu, F. E-ServEval: a system for quality evaluation of the onl<strong>in</strong>e<br />
public services, Revista Informatica Economica, Bucharest, no. 2(46), 2008<br />
• Fotache, M. Probleme generale ale managementului cunost<strong>in</strong>telor, ISIS 2002, Iassy, 24-26 October, 2002<br />
• Gareis, R. Professional Project Portfolio Management, IPMA World Congress, Berl<strong>in</strong>, 2002<br />
• Järv<strong>in</strong>en, R. and Leht<strong>in</strong>en, U. Services, e-Services and e-Service Innovations, Comb<strong>in</strong>ation of Theoretical and<br />
Practical Knowledge Frontiers of e-bus<strong>in</strong>ess research, Tampere University of Technology and University of<br />
Tampere, 2004, pp. 78-89<br />
• Kalle, K. Bus<strong>in</strong>ess Strategies for Information Technology Management, Idea Group Publish<strong>in</strong>g, 2003<br />
• Louise, E. Are we manag<strong>in</strong>g our knowledge?, Science, Innovation and Electronic Information Division<br />
Statistics, Canada, 2000<br />
• Neagu, D. The <strong>in</strong>telligent enterprise <strong>in</strong> Knowledge Society, <strong>in</strong> proceed<strong>in</strong>gs of “Knowledge Technologies <strong>in</strong><br />
Bus<strong>in</strong>ess and Management”, Iassy, June 6, 2003<br />
• Pocatilu, P. IT Projects Management Metrics Informatica Economica Journal, Bucharest, no.4(44), 2007, pp.<br />
122-125<br />
• Rust, R. T. and Kannan, P. K. e-Service: New Direction <strong>in</strong> Theory and Practice, Armonk NY, 2002<br />
• Scupola, A. E-Services: Def<strong>in</strong>ition, Characteristics and Taxonomy, Journal of Electronic Commerce <strong>in</strong><br />
Organizations, Guest Editorial Preface, 2008<br />
• Sukasame, N. E-Service Quality: A Paradigm for Competitive Success of E-Commerce Entrepreneurs, The<br />
N<strong>in</strong>th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS-2005), 2005<br />
• Whitman, M. E. and Woszczynski, A. B. The Handbook of Information Systems Research, Idea Group<br />
Publish<strong>in</strong>g, 2004<br />
• Quality Management Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, [Onl<strong>in</strong>e], Available:<br />
http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_catalogue/management_standards/iso_9000_iso_14000/qmp.htm<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>formation regard<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>courses</strong> taught at Faculty of Production Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and Logistics should be<br />
consulted with the lecturers and/or Faculty coord<strong>in</strong>ator
_____________________________________________________________<br />
FACULTY OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND PHYSIOTHERAPY<br />
76 Prószkowska Street, 45-758 Opole, Poland<br />
phone (+48 77) 40 00 405, e-mail: wwfif@po.opole.pl<br />
FIELDS OF STUDY � Physiotherapy (BSc, MSc)<br />
� Physical Education (BSc, MSc)<br />
� Tourism and Recreation (BSc, MSc)
FACULTY DEPARTMENTS � Physiotherapy<br />
� Biological Sciences<br />
� Biochemistry and Physiology<br />
� Fundamentals of Physiotherapy<br />
� Cl<strong>in</strong>ical Physiotherapy<br />
� Physical Education<br />
� Humanistic Science<br />
� Physical Education and Sport<br />
� Methodology of Physical Education<br />
� Individual Sports<br />
� Tourism and Recreation<br />
� Culture Bases of Tourism<br />
� Geography and Tourism Market<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Faculty Erasmus Coord<strong>in</strong>ator Jacek Soboń, PhD; therapy73@o2.pl<br />
COURSES IN ENGLISH<br />
Course<br />
code<br />
Course Name<br />
ECTS<br />
credits<br />
F001 Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Cardiology 3<br />
F002 Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Orthopedics<br />
and Traumatology<br />
3<br />
F003 Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Neurology and<br />
Neurosurgery<br />
4<br />
F004 Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Rheumatology 2<br />
F005 Physical Therapy 6<br />
F006 Therapeutic Massage 2<br />
F007 K<strong>in</strong>esiology 2<br />
F008 Prosthetics and Orthotics 2<br />
F009 Economics 5<br />
F010 Management 5<br />
F011 Tourism Geography 6<br />
F012 Eco- and Agro- Tourism 4<br />
F013 Ecology 5<br />
F014 Biomechanics 3<br />
F015 Theory and Methodology of Individual Sports - Swimm<strong>in</strong>g 3<br />
F016 Methodology and Didactics of Physical Education 2<br />
F017 Theory and Methodology of Team Sport – Basketball 2<br />
F018 Human K<strong>in</strong>etics/ Anthropomotorics 4<br />
F019 Theory and Methodology of Team Sport – Volleyball 2<br />
F020 Theory and Methodology of Individual Sports – Gymnastics 3<br />
F021 Summer Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Camp 2<br />
F022 Psychology 6
F023 Theory and Methodology of Individual Sports – Athletics 3<br />
1. Course title<br />
Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Cardiology<br />
2. Course code<br />
F001<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD J. Soboń / contact: therapy73@o2.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
3<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course is shaped to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with programm<strong>in</strong>g of rehabilitation process, its control and<br />
adjustment of physiotherapeutic process to the purpose of complex rehabilitation.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Students are acqua<strong>in</strong>ted with tak<strong>in</strong>g a patient history, the skills on diagnostic exam<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>in</strong> circularly<br />
diseases, <strong>in</strong>terpret<strong>in</strong>g of efficiency tests, qualify<strong>in</strong>g of relevant cardiologic rehabilitation models, keep<strong>in</strong>g of<br />
physiotherapeutic documentation.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Orthopedics and<br />
Traumatology<br />
2. Course code<br />
F002<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc Grzegorz Skiba, g.skiba@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
3<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Diagnostic and functional <strong>in</strong>vestigation as the basis of creation, verification and modification the<br />
rehabilitation programme.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Fundamentals of programm<strong>in</strong>g the rehabilitation process, controll<strong>in</strong>g its course and adjustment a<br />
physiotherapeutic treatment for purpose of the complex rehabilitation the adults, children and youth be<strong>in</strong>g
diseased of various dysfunctions. Select<strong>in</strong>g of the physiotherapeutic procedure and methods accord<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
cl<strong>in</strong>ical diagnosis, illness period and functional stage of rehabilitee. Monitor<strong>in</strong>g of results and keep<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
documents.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Neurology and<br />
Neurosurgery<br />
2. Course code<br />
F003<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD J. Soboń / contact: therapy73@o2.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
2<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Diagnostic and functional <strong>in</strong>vestigation as the basis of creation, verification and modification the<br />
rehabilitation programme.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Fundamentals of programm<strong>in</strong>g the rehabilitation process, controll<strong>in</strong>g its course and adjustment a<br />
physiotherapeutic treatment for purpose of the complex rehabilitation the adults, children and youth be<strong>in</strong>g<br />
diseased of various dysfunctions. Select<strong>in</strong>g of the physiotherapeutic procedure and methods accord<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
cl<strong>in</strong>ical diagnosis, illness period and functional stage of rehabilitee. Monitor<strong>in</strong>g of results and keep<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
documents.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Functional Diagnostics and Rehabilitation Programm<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Rheumatology<br />
2. Course code<br />
F004<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
2<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
30
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D J. Łuniewski / contact: j.luniewski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
Diagnostic and functional research as a basis of creation, verification and modification the rehabilitation<br />
programme.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Basics of programm<strong>in</strong>g the rehabilitation process, controll<strong>in</strong>g its course and adapt<strong>in</strong>g the physiotherapeutic<br />
treatment to the aims complex rehabilitation of children and adults. Selection of physiotherapeutic<br />
procedures and methods appropriately for cl<strong>in</strong>ical recognition. Results control, keep<strong>in</strong>g documentary.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Physical Therapy<br />
2. Course code<br />
F005<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D J. Łuniewski / contact: j.luniewski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
3<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The subject programme <strong>in</strong>troduces knowledge from range of different k<strong>in</strong>d of energy used <strong>in</strong> physical<br />
therapy<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Therapeutic Massage<br />
2. Course code<br />
F006<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week 9. Number of hours per semester
2 30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D J. Łuniewski / contact: j.luniewski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The subject programme <strong>in</strong>troduces knowledge from range of massage theory and practical skills<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
K<strong>in</strong>esiology<br />
2. Course code<br />
F007<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD J. Soboń / contact: therapy73@o2.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The subject programme <strong>in</strong>cludes basic knowledge of a normal and functional anatomy. A theoretical and<br />
practical knowledge is provided <strong>in</strong> particular aspect of function<strong>in</strong>g a passive and active human motor and<br />
nervous system. The goal is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with a human body build and the organism structure<br />
focused on the active and passive motor systems<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Prosthetics and Orthotics<br />
2. Course code<br />
F008<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
2<br />
6. ECTS credits 7. Level of class
2 advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
4<br />
60<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
MSc Grzegorz Skiba, g.skiba@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The semester course of studies comb<strong>in</strong>es lectures and classes on the role of orthopedic subjects <strong>in</strong><br />
rehabilitation, especially as a remedy <strong>in</strong> physiotherapy. The aim is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students how to recognize<br />
patient problems, assess <strong>in</strong>dividual needs, design and construct appliances, fit the device and adjust to the<br />
<strong>in</strong>dividual patient. Structure and function of prosthetic appliances, repairs and ma<strong>in</strong>tenance. Select<br />
appropriate materials and deal with the emotional difficulties of patients. Arrangements for orthopedic<br />
supply, recognition, distribution and payment<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Practical consultation <strong>in</strong> the hospital<br />
1. Course title<br />
Economics<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F009<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
5<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
mgr Maja Zagórna-Goplańska e-mail: m.zagorna-goplanska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
General objective: convey<strong>in</strong>g selected elements of the knowledge on Economics<br />
Specific objectives: provid<strong>in</strong>g with the knowledge on: basic pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and economic categories; free market<br />
economy; subjects of management process; subject structure of the goods market and services; gross<br />
national product account; <strong>in</strong>flation; labour market and unemployment; contemporary bank<strong>in</strong>g system;<br />
national policy of stabilisation; contemporary problems of world economic policy; economic system of<br />
European Community<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes
1. Course title<br />
Management<br />
2. Course code<br />
F010<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Msc M. Tataruch / contact: m.tataruch@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
1<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
General objective: convey<strong>in</strong>g the selected elements of the knowledge regard<strong>in</strong>g organisation and<br />
management<br />
Specific objectives: develop<strong>in</strong>g the knowledge <strong>in</strong> range of the basic management function, plann<strong>in</strong>g and<br />
organisation, motivat<strong>in</strong>g and controll<strong>in</strong>g; develop<strong>in</strong>g the knowledge of concepts <strong>in</strong> human resources<br />
management, means and hardware management, standardised systems’ management, contemporary<br />
concepts and methods of management<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Tourism Geography<br />
2. Course code<br />
F011<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
6<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD B. Woś / contact: b.wos@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
2<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The purpose of this course is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with several methods of evaluation natural environment<br />
attractiveness for tourism. A focus is given on natural scenery and cultural attractiveness of Poland,<br />
especially the tourism regionalization. However, the lectures are not limited to Poland’s territory; but<br />
consecutively they cover an attractiveness of the European tourism and some overseas countries<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Test exam<strong>in</strong>ation
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Eco- and Agro- Tourism<br />
2. Course code<br />
F012<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD B. Woś / contact: b.wos@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The purpose of this course is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with alternative forms and conditions of recreation <strong>in</strong> ecotourism<br />
and agro-tourism friendly environment. Develop the knowledge and skills needed to better<br />
understand<strong>in</strong>g the complexity of theoretical problems, practical issues and effective use them <strong>in</strong> practice<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium and presentation of student’s skills <strong>in</strong> practice<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Ecology<br />
2. Course code<br />
F013<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
5<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
PhD B. Woś / contact: b.wos@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
basic<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The purpose of this course is to develop students’ knowledge and ecological awareness for environmental<br />
protection promotion and shap<strong>in</strong>g pro-ecological attitude <strong>in</strong> society. Upon completion of the subject,<br />
students will be able to: reason the environmental protection; f<strong>in</strong>d out and trace the conflict of <strong>in</strong>terests<br />
between an economic growth and the protection of nature; develop the knowledge towards shap<strong>in</strong>g an idea<br />
and protective actions and to identify good practice <strong>in</strong> the subject; enhance the basic concepts and<br />
mechanisms of regard<strong>in</strong>g the ecology protection; develop the knowledge <strong>in</strong> area of ecological philosophy<br />
and ethics; have competence towards the ecological actions <strong>in</strong> civic capacity<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium and presentation of student’s skills <strong>in</strong> practice<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Biomechanics<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F014<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
6<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
advanced<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
3<br />
45<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Prof. M. Kuczyński / contact: m.kuczynski@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the course is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with the basic concepts of theoretical and applied<br />
biomechanics as well as their application to movement study and human motor analysis with particular<br />
emphasis on exercise, sports and physical activity<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, f<strong>in</strong>al exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Theory and Methodology of Individual Sports - Swimm<strong>in</strong>g<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F015<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D B. Maszkowska / contact: b.wojciechowska-maszkowska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The ma<strong>in</strong> aim of the course is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with: up-to-date methods of teach<strong>in</strong>g swimm<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
children and youth; regulations and rules b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g dur<strong>in</strong>g a swimm<strong>in</strong>g competition, especially <strong>in</strong> water-polo<br />
and div<strong>in</strong>g; the procedure and action <strong>in</strong> case of threat of the human life <strong>in</strong> water<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, theory and practice<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Activities at the swimm<strong>in</strong>g pool<br />
1. Course title<br />
Methodology and Didactics of Physical Education<br />
2. Course code<br />
F016<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
1<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D M. Jagusz / contact: m.jagusz@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
2<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
15<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the course to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, range and tasks of physical education <strong>in</strong> primary<br />
and secondary school and to qualify them to become a competent and professional PE teacher. Students will<br />
ga<strong>in</strong> the competencies <strong>in</strong> methodology, organization and plann<strong>in</strong>g of educational process as well as the<br />
creativity and skills to l<strong>in</strong>k up an <strong>in</strong>dividual research development with pedagogical practice<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Theory and Methodology of Team Sport - Basketball<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F017<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
4<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
17. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
18. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
19. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D D. Nawarecki / contact: d.nawarecki@po.opole.pl<br />
20. Prerequisites<br />
21. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the course is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with a theory and teach<strong>in</strong>g methodology of basketball game.<br />
The course is dedicated to present<strong>in</strong>g its position and function <strong>in</strong> the curriculum of comprehensive<br />
education, and the ma<strong>in</strong> tasks are related to gett<strong>in</strong>g the knowledge of teach<strong>in</strong>g methodology, master<strong>in</strong>g the
elements technique and tactics of play<strong>in</strong>g the basketball game<br />
22. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
23. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, f<strong>in</strong>al exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
24. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
25. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Activities at the gym<br />
1. Course title<br />
Human K<strong>in</strong>etics/ Anthropomotorics<br />
2. Course code<br />
F018<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
4<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
3<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D Z. Borysiuk / contact: z.borysiuk@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
<strong>in</strong>termediate<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
45<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The aim of the course is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with problems and the theory of motor abilities as a scientific<br />
issue cover<strong>in</strong>g the whole aspect of human motor activities <strong>in</strong> its complex and conditions. The ma<strong>in</strong> task is to<br />
present the essence of the problems, structure, changeability and conditions of human motor abilities<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, f<strong>in</strong>al exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Theory and Methodology of Team Sport - Volleyball<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F019<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
2<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D D. Borzucka / contact: d.borzucka@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The subject programme covers the basic knowledge of methodology and specific exercises of the volleyball
techniques, methods and forms of teach<strong>in</strong>g volleyball, master<strong>in</strong>g practical elements and techniques for<br />
play<strong>in</strong>g volleyball, knowledge and skills to enforc<strong>in</strong>g regulations of the game. A particular focus is given on<br />
assimilation knowledge concern<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dividual and team tactics at the volleyball meet<strong>in</strong>g<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, f<strong>in</strong>al exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Activities at the gym<br />
1. Course title<br />
Theory and Methodology of Individual Sports - Gymnastics<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F020<br />
consultation<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
1<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
3<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
4<br />
60<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D K. Sojka-Krawiec / contact: k.sojka-krawiec@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The purpose of the course is to prepare students to teach<strong>in</strong>g work on gymnastics at all level schools, nonschool<br />
establishments as well as at the higher education <strong>in</strong>stitutions. Division of gymnastics and gymnastic<br />
exercises, their role <strong>in</strong> shap<strong>in</strong>g of general physical fitness and assimilation of term<strong>in</strong>ology for exercise<br />
plann<strong>in</strong>g. Key features of the forms of agility exercises, system and methodology of teach<strong>in</strong>g various<br />
exercises. PE at school and ma<strong>in</strong> issues of methodology<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, f<strong>in</strong>al exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
17. Additional <strong>in</strong>formation<br />
Activities at the gym<br />
1. Course title<br />
Summer Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Camp<br />
2. Course code<br />
F021<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
2<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
4<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Msc L. Kosińska / contact: l.kos<strong>in</strong>ska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The programme <strong>in</strong>troduces knowledge from swimm<strong>in</strong>g, sail<strong>in</strong>g and games - theory and practical skills<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, written and practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
1. Course title<br />
Psychology<br />
2. Course code<br />
3. Form of class<br />
F022<br />
sem<strong>in</strong>ar<br />
4. Type of course<br />
5. Semester<br />
compulsory<br />
3<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
7. Level of class<br />
6<br />
basic<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
2<br />
30<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D A. Rogowska / contact: a.rogowska@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course <strong>in</strong>troduces basic issues necessary to understand human psyche and behaviour, especially <strong>in</strong> sport<br />
doma<strong>in</strong>. It also presents <strong>in</strong>formation that helps to better understand mechanisms and pr<strong>in</strong>ciples underly<strong>in</strong>g<br />
the cognitive and educational processes - lead<strong>in</strong>g to optimum physical, mental and social development of<br />
children and youth. The class will cover a selection of methods and tools that serve to measure various<br />
psychical phenomena.<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
Psychology as a science – def<strong>in</strong>ition, goals and tasks of psychology. Fields of specialization <strong>in</strong> psychology.<br />
Psychology of sport. Methods of psychological research. Ma<strong>in</strong> foundation of psychological theories<br />
(comparative analysis): biological approach, behaviorism, psychoanalytic psychology, humanistic psychology,<br />
cognitive psychology. Cognitive process - sensations and perception, attention, imag<strong>in</strong>ation, memory,<br />
reason<strong>in</strong>g and solv<strong>in</strong>g problems. Individual differences and their relationships with sport activity: capacity,<br />
ability and talent, <strong>in</strong>telligence, temperament, personality (trait theory). The nature and nurture of behavior.<br />
Mean<strong>in</strong>g of motivation <strong>in</strong> our life: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, stimulus seek<strong>in</strong>g and arousal concept,<br />
<strong>in</strong>centive role of award and punishments, achievement motivation. Emotion and stress: def<strong>in</strong>itions and<br />
components of emotion, behavioral expression of emotion, the ma<strong>in</strong> theories of emotion, stress and illness,<br />
strategies of advis<strong>in</strong>g with the stress (mental tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> sport). Social psychology: attitudes and actions,<br />
biases <strong>in</strong> attribution process, social <strong>in</strong>fluence (conformity, group <strong>in</strong>fluence), prejudice and aggression.<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, f<strong>in</strong>al exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Myers, David G, Psychology. New York 2004: Worth Publishers.<br />
• Ross, Glenn F, The Psychology of Tourism. Melbourne 1998: Hospitality Press.<br />
• Dosil, Joaquín (Ed.), The Sport Psychologist's Handbook: a Guide for Sport-Specific Performance<br />
Enhancement. Chichester 2006: John Wiley & Sons.
1. Course title<br />
Theory and Methodology of Individual Sports - Athletics<br />
2. Course code<br />
F023<br />
4. Type of course<br />
compulsory<br />
6. ECTS credits<br />
3<br />
8. Number of hours per week<br />
4<br />
10. Language of <strong>in</strong>struction<br />
English<br />
11. Name and contact <strong>in</strong>formation of the lecturer<br />
Ph D R. Tataruch / contact: r.tataruch@po.opole.pl<br />
12. Prerequisites<br />
3. Form of class<br />
consultation<br />
5. Semester<br />
2<br />
7. Level of class<br />
advanced<br />
9. Number of hours per semester<br />
60<br />
13. Objectives of the course<br />
The course objective is to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with a technique and teach<strong>in</strong>g methodology of the athletic<br />
exercises as well as to develop the skills for implement<strong>in</strong>g them <strong>in</strong> classes, and to acqua<strong>in</strong>t students with<br />
basic methods of athletic tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g. Methodology of <strong>in</strong>dividual sports<br />
14. Teach<strong>in</strong>g program<br />
To be provided by the lecturer<br />
15. Assessment methods<br />
Credit colloquium, practical exam<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
16. Recommended read<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Lecture notes<br />
Further <strong>in</strong>formation regard<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>courses</strong> taught at Faculty of Physical Education and Physiotherapy should be<br />
consulted with the lecturers and/or Faculty coord<strong>in</strong>ator<br />
_____________________________________________________________