Neurobiology of Learning and Memory - Institut für Bienenkunde
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory - Institut für Bienenkunde
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory - Institut für Bienenkunde
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Neurobiology</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Learning</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Memory</strong><br />
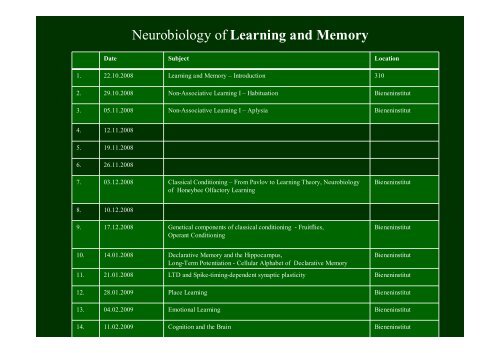
Date Subject Location<br />
1. 22.10.2008 <strong>Learning</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Memory</strong> – Introduction 310<br />
2. 29.10.2008 Non-Associative <strong>Learning</strong> I – Habituation Bieneninstitut<br />
3. 05.11.2008 Non-Associative <strong>Learning</strong> I – Aplysia Bieneninstitut<br />
4. 12.11.2008<br />
5. 19.11.2008<br />
6. 26.11.2008<br />
7. 03.12.2008 Classical Conditioning – From Pavlov to <strong>Learning</strong> Theory, <strong>Neurobiology</strong><br />
<strong>of</strong> Honeybee Olfactory <strong>Learning</strong><br />
8. 10.12.2008<br />
9. 17.12.2008 Genetical components <strong>of</strong> classical conditioning - Fruitflies,<br />
Operant Conditioning<br />
10. 14.01.2008 Declarative <strong>Memory</strong> <strong>and</strong> the Hippocampus,<br />
Long-Term Potentiation - Cellular Alphabet <strong>of</strong> Declarative <strong>Memory</strong><br />
Bieneninstitut<br />
Bieneninstitut<br />
Bieneninstitut<br />
11. 21.01.2008 LTD <strong>and</strong> Spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity Bieneninstitut<br />
12. 28.01.2009 Place <strong>Learning</strong> Bieneninstitut<br />
13. 04.02.2009 Emotional <strong>Learning</strong> Bieneninstitut<br />
14. 11.02.2009 Cognition <strong>and</strong> the Brain Bieneninstitut
<strong>Neurobiology</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Learning</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Memory</strong><br />
Sensitization<br />
Pr<strong>of</strong>. Dr. Bernd Grünewald<br />
www.institut-fuer-bienenkunde<br />
b.gruenewald@bio.uni-frankfurt.de
Eric K<strong>and</strong>el & wife
habituation vs sensitization<br />
both: learning about the properties <strong>of</strong> a<br />
single stimulus.<br />
habituation:<br />
decreases <strong>of</strong> responsiveness produced<br />
by repeated (or continuous) stimulation.<br />
sensitization:<br />
increases <strong>of</strong> responsiveness.<br />
(Domjan & Burkhard, 1985)
A marine snail is a model system for the<br />
study <strong>of</strong> cellular mechanisms <strong>of</strong> learning<br />
Aplysia californica
Gill Withdrawal Reflex
Sensitization <strong>of</strong> the reflex
Sensitization - neural circuitry
Neural network underlying behavioural sensitization
Cellular mechanisms <strong>of</strong> sensitization - Facilitation<br />
Sensitizing stimulus has five distinct effects on the SN‐MN synapse:<br />
•Increase <strong>of</strong> epsp amplitude<br />
•Increase <strong>of</strong> membrane resistance<br />
•Increase <strong>of</strong> SN excitability<br />
•Enhancement <strong>of</strong> action potential duration (spike broadening)<br />
•Increase <strong>of</strong> transmitter release
Cellular mechanisms <strong>of</strong> sensitization - Facilitation
Cellular mechanisms <strong>of</strong> sensitization – STF vs LTF
A cellular model <strong>of</strong> presynaptic facilitation
Do Facilitation <strong>and</strong> Classical conditioning utilize the<br />
same cellular machinery?
Do Facilitation <strong>and</strong> Classical conditioning utilize the<br />
same cellular machinery?
Do Facilitation <strong>and</strong> Classical conditioning utilize the<br />
same cellular machinery?