6 - World Journal of Gastroenterology
6 - World Journal of Gastroenterology
6 - World Journal of Gastroenterology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
%<br />
Table 4 Positive predictive value and negative predictive value in percentage at 95% confidence interval <strong>of</strong> serum M2-pyruvate<br />
kinase using various cut-<strong>of</strong>f value settings for different colorectal lesions compared with 158 normal people in colorectal cancer<br />
mass screening in Hangzhou, China, 2006-2008 (95% CI)<br />
M2-PK<br />
(U/mL)<br />
2.00 49.73<br />
(42.57-56.90)<br />
2.50 55.35<br />
(47.62-63.07)<br />
3.00 60.71<br />
(52.62-68.80)<br />
3.50 62.31<br />
(53.98-70.64)<br />
4.00 64.96<br />
(56.31-73.60)<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
Sens Spec<br />
CRC<br />
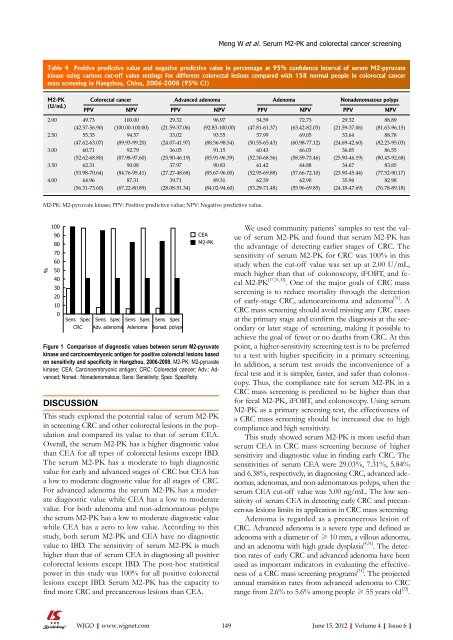
Figure 1 Comparison <strong>of</strong> diagnostic values between serum M2-pyruvate<br />
kinase and carcinoembryonic antigen for positive colorectal lesions based<br />
on sensitivity and specificity in Hangzhou, 2006-2008. M2-PK: M2-pyruvate<br />
kinase; CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen; CRC: Colorectal cancer; Adv.: Advanced;<br />
Nonad.: Nonadenomatous; Sens: Sensitivity; Spec: Specificity.<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
Colorectal cancer Advanced adenoma Adenoma Nonadenomatous polyps<br />
PPV NPV PPV NPV PPV NPV PPV NPV<br />
Sens Spec<br />
Adv. adenoma<br />
100.00<br />
(100.00-100.00)<br />
94.57<br />
(89.93-99.20)<br />
92.79<br />
(87.98-97.60)<br />
90.08<br />
(84.76-95.41)<br />
87.31<br />
(67.22-80.89)<br />
Sens Spec<br />
Adenoma<br />
29.32<br />
(21.59-37.06)<br />
33.02<br />
(24.07-41.97)<br />
36.05<br />
(25.90-46.19)<br />
37.97<br />
(27.27-48.68)<br />
39.71<br />
(28.08-51.34)<br />
Sens Spec<br />
Nonad. polvps<br />
96.97<br />
(92.83-100.00)<br />
93.55<br />
(88.56-98.54)<br />
91.15<br />
(85.91-96.39)<br />
90.83<br />
(85.67-96.00)<br />
89.31<br />
(84.02-94.60)<br />
CEA<br />
M2-PK<br />
This study explored the potential value <strong>of</strong> serum M2-PK<br />
in screening CRC and other colorectal lesions in the population<br />
and compared its value to that <strong>of</strong> serum CEA.<br />
Overall, the serum M2-PK has a higher diagnostic value<br />
than CEA for all types <strong>of</strong> colorectal lesions except IBD.<br />
The serum M2-PK has a moderate to high diagnostic<br />
value for early and advanced stages <strong>of</strong> CRC but CEA has<br />
a low to moderate diagnostic value for all stages <strong>of</strong> CRC.<br />
For advanced adenoma the serum M2-PK has a moderate<br />
diagnostic value while CEA has a low to moderate<br />
value. For both adenoma and non-adenomatous polyps<br />
the serum M2-PK has a low to moderate diagnostic value<br />
while CEA has a zero to low value. According to this<br />
study, both serum M2-PK and CEA have no diagnostic<br />
value to IBD. The sensitivity <strong>of</strong> serum M2-PK is much<br />
higher than that <strong>of</strong> serum CEA in diagnosing all positive<br />
colorectal lesions except IBD. The post-hoc statistical<br />
power in this study was 100% for all positive colorectal<br />
lesions except IBD. Serum M2-PK has the capacity to<br />
find more CRC and precancerous lesions than CEA.<br />
54.59<br />
(47.81-61.37)<br />
57.99<br />
(50.55-65.43)<br />
60.43<br />
(52.30-68.56)<br />
61.42<br />
(52.95-69.88)<br />
62.39<br />
(53.29-71.48)<br />
M2-PK: M2-pyruvate kinase; PPV: Positive predictive value; NPV: Negative predictive value.<br />
Meng W et al . Serum M2-PK and colorectal cancer screening<br />
72.73<br />
(63.42-82.03)<br />
69.05<br />
(60.98-77.12)<br />
66.03<br />
(58.59-73.46)<br />
64.88<br />
(57.66-72.10)<br />
62.90<br />
(55.96-69.85)<br />
29.32<br />
(21.59-37.06)<br />
33.64<br />
(24.69-42.60)<br />
36.05<br />
(25.90-46.19)<br />
34.67<br />
(23.90-45.44)<br />
35.94<br />
(24.18-47.69)<br />
88.89<br />
(81.63-96.15)<br />
88.78<br />
(82.23-95.03)<br />
86.55<br />
(80.43-92.68)<br />
83.85<br />
(77.52-90.17)<br />
82.98<br />
(76.78-89.18)<br />
We used community patients’ samples to test the value<br />
<strong>of</strong> serum M2-PK and found that serum M2-PK has<br />
the advantage <strong>of</strong> detecting earlier stages <strong>of</strong> CRC. The<br />
sensitivity <strong>of</strong> serum M2-PK for CRC was 100% in this<br />
study when the cut-<strong>of</strong>f value was set up at 2.00 U/mL,<br />
much higher than that <strong>of</strong> colonoscopy, iFOBT, and fecal<br />
M2-PK [17,31,32] . One <strong>of</strong> the major goals <strong>of</strong> CRC mass<br />
screening is to reduce mortality through the detection<br />
<strong>of</strong> early-stage CRC, adenocarcinoma and adenoma [31] . A<br />
CRC mass screening should avoid missing any CRC cases<br />
at the primary stage and confirm the diagnosis at the secondary<br />
or later stage <strong>of</strong> screening, making it possible to<br />
achieve the goal <strong>of</strong> fewer or no deaths from CRC. At this<br />
point, a higher-sensitivity screening test is to be preferred<br />
to a test with higher specificity in a primary screening.<br />
In addition, a serum test avoids the inconvenience <strong>of</strong> a<br />
fecal test and it is simpler, faster, and safer than colonoscopy.<br />
Thus, the compliance rate for serum M2-PK in a<br />
CRC mass screening is predicted to be higher than that<br />
for fecal M2-PK, iFOBT, and colonoscopy. Using serum<br />
M2-PK as a primary screening test, the effectiveness <strong>of</strong><br />
a CRC mass screening should be increased due to high<br />
compliance and high sensitivity.<br />
This study showed serum M2-PK is more useful than<br />
serum CEA in CRC mass screening because <strong>of</strong> higher<br />
sensitivity and diagnostic value in finding early CRC. The<br />
sensitivities <strong>of</strong> serum CEA were 29.03%, 7.31%, 5.84%<br />
and 6.38%, respectively, in diagnosing CRC, advanced adenomas,<br />
adenomas, and non-adenomatous polyps, when the<br />
serum CEA cut-<strong>of</strong>f value was 5.00 ng/mL. The low sensitivity<br />
<strong>of</strong> serum CEA in detecting early CRC and precancerous<br />
lesions limits its application in CRC mass screening.<br />
Adenoma is regarded as a precancerous lesion <strong>of</strong><br />
CRC. Advanced adenoma is a severe type and defined as<br />
adenoma with a diameter <strong>of</strong> ≥ 10 mm, a villous adenoma,<br />
and an adenoma with high grade dysplasia [4,31] . The detection<br />
rates <strong>of</strong> early CRC and advanced adenoma have been<br />
used as important indicators in evaluating the effectiveness<br />
<strong>of</strong> a CRC mass screening programs [31] . The projected<br />
annual transition rates from advanced adenoma to CRC<br />
range from 2.6% to 5.6% among people ≥ 55 years old [33] .<br />
WJGO|www.wjgnet.com 149<br />
June 15, 2012|Volume 4|Issue 6|