- Page 1 and 2: Thiophilic Adsorption Chromatograph
- Page 3 and 4: Thiophilic Adsorption 3 8. Methanol
- Page 5 and 6: Thiophilic Adsorption 5 2.4. Reagen
- Page 7 and 8: Thiophilic Adsorption 7 3. The numb
- Page 9 and 10: Thiophilic Adsorption 9 (the ratio
- Page 11 and 12: Thiophilic Adsorption 11 0 5 10 15
- Page 13 and 14: Thiophilic Adsorption 3.7. T-Gel Co
- Page 15: Thiophilic Adsorption 15 17. Morris
- Page 18 and 19: 18 Yip and Hutchens Stationary phas
- Page 20 and 21: 20 Yip and Hutchens 12 1 .o ? c 0.8
- Page 22 and 23: 0 20 40 60 80 100 Time (mln) Yip an
- Page 24 and 25: 24 Yip and Hutchens 2. 5-10 cm inne
- Page 26 and 27: 26 Yip and Hutchens 3.4. Column Reg
- Page 28 and 29: 28 Yip and Hutchens 3. HEPES can be
- Page 30 and 31: 30 Yip and Hutchens 7. Hutchens, T.
- Page 33 and 34: CHAF’TER 3 Histidine Ligand Affin
- Page 35 and 36: Histidine Ligand Affinity Chromatog
- Page 37 and 38: Histidine Ligand Affinity Chromatog
- Page 39 and 40: Histidine Ligand Affinity Chromatog
- Page 41 and 42: Histidine Ligand Affinity Chromatog
- Page 43 and 44: Histidine Ligand Affbaity Chromatog
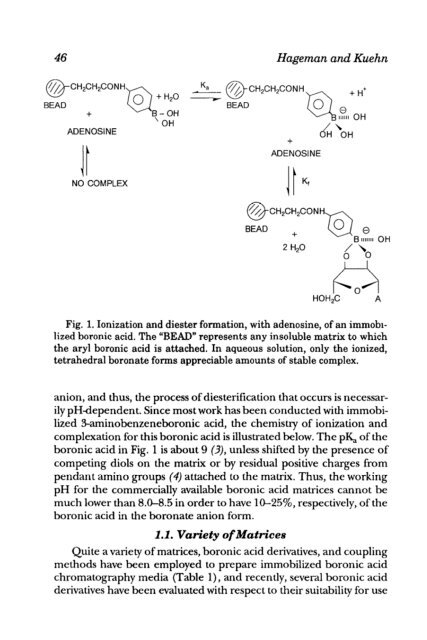
- Page 45: &AP!t’ER 4 Boronic Acid Matrices
- Page 49 and 50: Boronic Acid Matrices 49 amide, aga
- Page 51 and 52: Boronic Acid Matrices 51 Table 3 Bm
- Page 53 and 54: Boronic Acid Matrices 53 Table 5 En
- Page 55 and 56: Boronic Acid Matrices 55 hydroxyeth
- Page 57 and 58: Boronic Acid Matrices 57 solutions
- Page 59 and 60: Boronic Acid Matrices 9. The follow
- Page 61 and 62: Boronic Acid Matrices by coupling 3
- Page 63 and 64: Boronic Acid Matrices 63 beads, whi
- Page 65 and 66: Boronic Acid Matrices 65 rylamide g
- Page 67 and 68: Boronic Acid Matrices 67 Sephadex,
- Page 69 and 70: Boronic Acid Matrices 69 30. Plzer,
- Page 71: Boronic Acid Matrices 71 61. Hjerte
- Page 74 and 75: 74 Battey and Venis 2. Materials 1.
- Page 76 and 77: 76 Battey and Venis strained throug
- Page 78 and 79: 78 Battey and Venis Fig. 2. SDS-PAG
- Page 80 and 81: 80 Battey and Venis 6. Laemmh, U. K
- Page 82 and 83: Lectm Concanavahn A (tin A) L.kms c
- Page 84 and 85: 84 West and Goldring 2. Materials 2
- Page 86 and 87: 86 West and Goldring 6. Wash the co
- Page 88 and 89: 88 West and Gbldring 4. Sharma, S.
- Page 91 and 92: CHAPTER 7 Dye-Ligand Affinity Chrom
- Page 93 and 94: Dye-Ligand Chromatography 93 B Fig.
- Page 95 and 96: Dye-Ligand Chromatography 95 the eq
- Page 97 and 98:
Dye-L&and Chromatography 20 A,,, 1.
- Page 99 and 100:
Dye-Ligand Chromatography 99 leakag
- Page 101 and 102:
Dye-Ligand Chromatography or most o
- Page 103:
Dye-Ligand Chromatography 103 6. Sm
- Page 106 and 107:
106 Clonis tion in the size of the
- Page 108 and 109:
support Sdica, unmodified Hypersll
- Page 110 and 111:
110 Clonis 2. Materials 2.1. Coatin
- Page 112 and 113:
112 Clonis 6. Hydrochloric acid (1
- Page 114 and 115:
114 Clonis 2.3.2. Separation of BSA
- Page 116 and 117:
116 Clonis 3.1.4. Preparation of Al
- Page 118 and 119:
116 Clonis 3.2.4. Immobilization of
- Page 120 and 121:
120 Clonis TiME (m(n) - Fig, 1. Res
- Page 122 and 123:
122 Clonis 5. The carbodiimide-prom
- Page 125 and 126:
Immunoafflnity Chromatography Georg
- Page 127 and 128:
Immunoafinity Chromatography 127 OC
- Page 129 and 130:
Immunoafinity Chromatography 129 3.
- Page 131 and 132:
Immunoafinity Chromatography 131 3.
- Page 133:
Immunoafinity Chromatography 133 ho
- Page 136 and 137:
136 Pepper Table 1 Polyclonal Antib
- Page 138 and 139:
138 Pepper to see which functions b
- Page 140 and 141:
140 Pepper role in diagnosing probl
- Page 142 and 143:
142 Pepper Fig. 1. ELISA (A,B), RIA
- Page 144 and 145:
144 Pepper mum bound signal of 40%
- Page 146 and 147:
146 Pepper 10 30 50 70 90 110 130 1
- Page 148 and 149:
148 Pepper radioactive decay, the c
- Page 150 and 151:
150 AEl0 ELISA loo 10’ lo2 lo3 lo
- Page 152 and 153:
152 Pepper subclassed antibodies, w
- Page 154 and 155:
154 Pepper binding. Wash three time
- Page 156 and 157:
156 I A ANTMOOV AB3 (I$ =l xd”) B
- Page 158 and 159:
158 Pepper 3.4. Eluant Selection an
- Page 160 and 161:
160 Pepper tion reagents (18,44), w
- Page 162 and 163:
162 Pepper directly by adding a 125
- Page 164 and 165:
164 Pepper ant/gel are not very com
- Page 166 and 167:
Pepper ‘7. There are a number of
- Page 168 and 169:
168 Pepper 5. Miller, K. F., Bolt,
- Page 170 and 171:
170 Pepper 35. Lamoyi, E. and Nison
- Page 173 and 174:
&LWI’ER 11 Some Alternative Coupl
- Page 175 and 176:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 17
- Page 177 and 178:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 17
- Page 179 and 180:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 17
- Page 181 and 182:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 18
- Page 183 and 184:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 18
- Page 185 and 186:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 18
- Page 187 and 188:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 18
- Page 189 and 190:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 18
- Page 191 and 192:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 19
- Page 193 and 194:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 19
- Page 195 and 196:
Alternative Coupling Chemistries 19
- Page 197 and 198:
CHAPTER 12 Exploiting Weak Affiniti
- Page 199 and 200:
Exploiting Weak Affinities 199 The
- Page 201 and 202:
Exploiting Weak Affinities 201 4 Co
- Page 203 and 204:
Exploiting Weak Affinities 203 a P
- Page 205 and 206:
-me Trade name Matrix Aldehyde Chlo
- Page 207 and 208:
Exploiting Weak Affinities 207 prof
- Page 209 and 210:
CHAPTER 13 Biospecific Affinity Elu
- Page 211 and 212:
Biospecific Affinity El&ion 211 mol
- Page 213 and 214:
Biospecific Affinity E&ion 213 stre
- Page 215 and 216:
Biospecijic Affinity Elution 215
- Page 217 and 218:
Biospecific Affinity Elution 217 0
- Page 219 and 220:
Blospectjic Affinity El&ion 219 thr
- Page 221:
Biospecific Affinity Elution 221 th
- Page 224 and 225:
224 Harris In considering applicati
- Page 226 and 227:
226 Harris pressures (10-40 bar) re
- Page 228 and 229:
228 Table 2 Cahbrahon Protems Suita
- Page 230 and 231:
230 Harris time (min) Fig. 2. Const
- Page 232 and 233:
232 Harris guard and/or separation
- Page 234 and 235:
234 Harris 15 20 25 time after inje
- Page 236 and 237:
236 Harris References 1. KopacieMnc
- Page 238 and 239:
238 Li and Hutchens This chapter pr
- Page 240 and 241:
240 Li and Hutchens !=RACl-lON NUMB
- Page 242 and 243:
242 Li and Hutchens Desired pH grad
- Page 244 and 245:
244 Li and Hutchens sample volume s
- Page 246 and 247:
9 6 Li and Hutchens 0 20 40 60 80 1
- Page 248 and 249:
248 Li and Hutchens of a focusmg bu
- Page 250 and 251:
250 Kenney DEAE SP CM QA PEI CBX Ta
- Page 252 and 253:
Table 2 Some Commercially Available
- Page 254 and 255:
254 Kenmy b. Gradient former (see N
- Page 256 and 257:
is eluted last from the cation exch
- Page 258 and 259:
Kenney bacteria and spores. This ki
- Page 260 and 261:
260 Cramer displacer front. The dis
- Page 262 and 263:
1.1. Methods Development in Displac
- Page 264 and 265:
264 Cramer I I I I I I I I I I I I
- Page 266 and 267:
266 Cramer obtained using the mathe
- Page 268 and 269:
268 Cramer during the introduction
- Page 270 and 271:
270 Cramer Problem Typical Problems
- Page 273 and 274:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 275 and 276:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 277 and 278:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 279 and 280:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 281 and 282:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 283 and 284:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 285:
Purification of DNA Binding Protein
- Page 288 and 289:
288 Sherwood Table 1 General Techni
- Page 290 and 291:
290 Sherwood risk of product proteo
- Page 292 and 293:
292 Sherwood ing 8000g and with a b
- Page 294 and 295:
Organrsm Endma chtysanthemz PSeUdo?
- Page 296 and 297:
296 Sherwood Table 5 Effect of Ioni
- Page 298 and 299:
298 Sherwood 2.1. Filtration Concen
- Page 300 and 301:
300 Sherwood 2.2.1. Precipitation b
- Page 302 and 303:
302 Sherwood Precipitate can be rem
- Page 304 and 305:
304 Sherwood 5. Hammond, P. M., Ram
- Page 307 and 308:
CHAFFER 20 Determination of Purity
- Page 309 and 310:
Purity and Yield 309 reason is that
- Page 311 and 312:
Purity and Yield 311 (l-3 mm thick)
- Page 313 and 314:
Purity and Yield 313 is phosphomoly
- Page 315 and 316:
Purity and Yield 315 A Acetyl CoA-
- Page 317 and 318:
Purity and Yield 317 3 MM filter pa
- Page 319 and 320:
Purity and Yield 319 Solution A, So
- Page 321 and 322:
Purity and Yield 321 ide solution.
- Page 323:
Purity and Yield 323 11. Layne, E.