Límites de Funciones
Límites de Funciones
Límites de Funciones
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
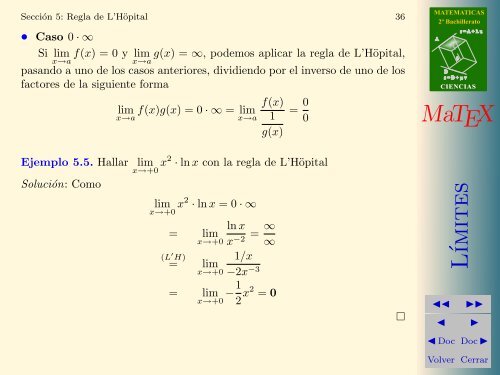
Sección 5: Regla <strong>de</strong> L’Höpital 36<br />
• Caso 0 · ∞<br />
Si lim f(x) = 0 y lim g(x) = ∞, po<strong>de</strong>mos aplicar la regla <strong>de</strong> L’Höpital,<br />
x→a x→a<br />
pasando a uno <strong>de</strong> los casos anteriores, dividiendo por el inverso <strong>de</strong> uno <strong>de</strong> los<br />
factores <strong>de</strong> la siguiente forma<br />
f(x)<br />
lim f(x)g(x) = 0 · ∞ = lim<br />
x→a x→a 1<br />
g(x)<br />
= 0<br />
0<br />
Ejemplo 5.5. Hallar lim<br />
x→+0 x2 · ln x con la regla <strong>de</strong> L’Höpital<br />
Solución: Como<br />
lim<br />
x→+0 x2 · ln x = 0 · ∞<br />
ln x ∞<br />
= lim =<br />
x→+0 x−2 ∞<br />
(L ′ H) 1/x<br />
= lim<br />
x→+0 −2x−3 = lim<br />
x→+0 −1<br />
2 x2 = 0<br />
<br />
MATEMATICAS<br />
2º Bachillerato<br />
A<br />
d<br />
B<br />
s = B + m v<br />
r = A + l u<br />
CIENCIAS<br />
MaTEX<br />
<strong>Límites</strong><br />
◭◭ ◮◮<br />
◭ ◮<br />
◭ Doc Doc ◮<br />
Volver Cerrar