Netzleiste | Netzkabel Power cable | Power bar Multiprise - In-Akustik
Netzleiste | Netzkabel Power cable | Power bar Multiprise - In-Akustik
Netzleiste | Netzkabel Power cable | Power bar Multiprise - In-Akustik
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
AC-1502 | AC-1502-P6 | AC-2502-P8<br />
<strong>Power</strong>-Bar /-Cord<br />
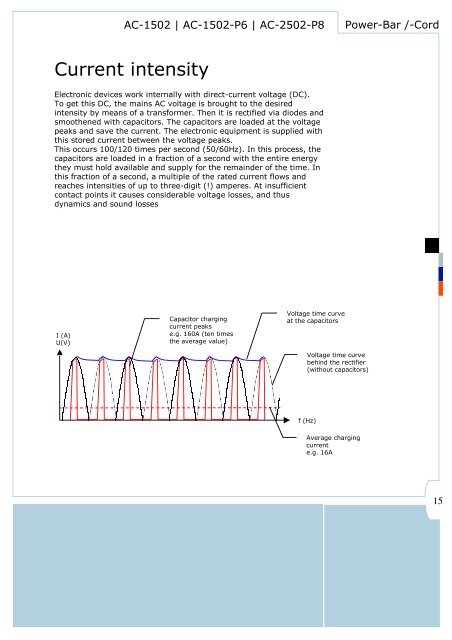
Current intensity<br />
Electronic devices work internally with direct-current voltage (DC).<br />
To get this DC, the mains AC voltage is brought to the desired<br />
intensity by means of a transformer. Then it is rectified via diodes and<br />
smoothened with capacitors. The capacitors are loaded at the voltage<br />
peaks and save the current. The electronic equipment is supplied with<br />
this stored current between the voltage peaks.<br />
This occurs 100/120 times per second (50/60Hz). <strong>In</strong> this process, the<br />
capacitors are loaded in a fraction of a second with the entire energy<br />
they must hold available and supply for the remainder of the time. <strong>In</strong><br />
this fraction of a second, a multiple of the rated current flows and<br />
reaches intensities of up to three-digit (!) amperes. At insufficient<br />
contact points it causes considerable voltage losses, and thus<br />
dynamics and sound losses<br />
U<br />
I<br />
U<br />
(A)<br />
(V)<br />
U(V)<br />
I (A)<br />
Capacitor charging<br />
current peaks<br />
e.g. 160A (ten times<br />
the average value)<br />
z.B. 160A (10-<br />
facher<br />
Voltage time curve<br />
at the capacitors<br />
Voltage time curve<br />
behind the rectifier<br />
(without capacitors)<br />
f (Hz)<br />
Average charging<br />
current<br />
e.g. 16A<br />
15