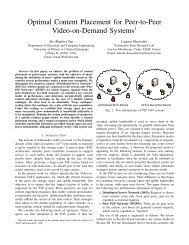
Introduction au calcul scientifique pour les EDP de la ... - Inria
Introduction au calcul scientifique pour les EDP de la ... - Inria
Introduction au calcul scientifique pour les EDP de la ... - Inria
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
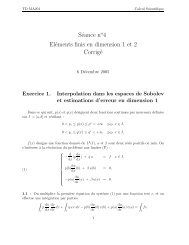
La mise en équationLoi <strong>de</strong> conservation : ∂θ + div ⃗q = 0.∂tLoi <strong>de</strong> conduction : ⃗q = −σ∇θ.Si on élimine ⃗q le problème à résoudre s’écrit:⎧Trouver θ(x, t) : Ω×]0, T [−→ R tel que:∂θ⎪⎨ ∂t − div( σ∇θ) = 0, x ∈ Ω, t > 0,σ ∂θ∂n = q l, (−⃗q · n = q l ) x ∈ Γ 1 , t > 0,θ = θ l , x ∈ Γ 0 , t > 0,⎪⎩θ(x, 0) = θ 0 (x), x ∈ Ω.Nature du problème⎧Trouver θ(x, t) : Ω×]0, T [−→ R tel que:∂θ⎪⎨ ∂t − div( σ∇θ) = 0, x ∈ Ω, t > 0,σ ∂θ∂n = q l, x ∈ Γ 1 , t > 0,θ = θ l , x ∈ Γ 0 , t > 0,⎪⎩θ(x, 0) = θ 0 (x), x ∈ Ω.Le temps faisant partie explicitement <strong>de</strong>s variab<strong>les</strong> duproblème, on a affaire à un problème d’évolution.Tant mathématiquement que numériquement,<strong>les</strong> variab<strong>les</strong> x et t jouent un rôle différent.<strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>au</strong> <strong>calcul</strong> <strong>scientifique</strong> <strong>pour</strong> <strong>les</strong> <strong>EDP</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> physique. – p.5/27<strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>au</strong> <strong>calcul</strong> <strong>scientifique</strong> <strong>pour</strong> <strong>les</strong> <strong>EDP</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> physique. – p.6/27Nature du problème⎧Trouver θ(x, t) : Ω×]0, T [−→ R tel que:∂θ⎪⎨ ∂t − div( σ∇θ) = 0, x ∈ Ω, t > 0,σ ∂θ∂n = q l, x ∈ Γ 1 , t > 0,θ = θ l , x ∈ Γ 0 , t > 0,⎪⎩θ(x, 0) = θ 0 (x), x ∈ Ω.L’équation <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> chaleur est le prototype <strong>de</strong>s équationsparaboliques qui modélisent <strong>les</strong> phénomènes <strong>de</strong> diffusion.El<strong>les</strong> interviennent <strong>au</strong>ssi en mécanique <strong>de</strong>s flui<strong>de</strong>s (milieuxporeux, diffusion <strong>de</strong> polluants), ou en finance (B<strong>la</strong>ck-Scho<strong>les</strong>).Ces équations seront abordées <strong>au</strong> cours 8.Les difficultés <strong>de</strong> l’analyse mathématique.Vu <strong>de</strong> très loin, le problème peut être mis sous <strong>la</strong> forme:Trouver u ∈ V tel que A u = doù V est un espace vectoriel (espace <strong>de</strong> fonctions), A est unopérateur linéaire, le vecteur u est <strong>la</strong> fonction inconnue θ et dreprésente <strong>les</strong> données (θ 0 , θ l , q l ).Ce<strong>la</strong> ressemble à un système linéaire.Les différences majeures, sources <strong>de</strong> difficultés, sont:L’espace fonctionnel V est <strong>de</strong> dimension infinie.L’opérateur A est un opérateur différentiel (non continudans <strong>de</strong>s topologies c<strong>la</strong>ssiques).De ce fait, <strong>les</strong> questions d’existence et d’unicité <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> solutionsont très délicates.<strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>au</strong> <strong>calcul</strong> <strong>scientifique</strong> <strong>pour</strong> <strong>les</strong> <strong>EDP</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> physique. – p.6/27<strong>Introduction</strong> <strong>au</strong> <strong>calcul</strong> <strong>scientifique</strong> <strong>pour</strong> <strong>les</strong> <strong>EDP</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> physique. – p.7/27