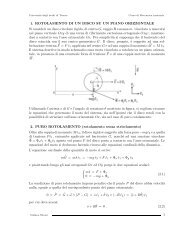
1. DISCUSSIONE DI WEIERSTRASS Si considera un punto ...
1. DISCUSSIONE DI WEIERSTRASS Si considera un punto ...
1. DISCUSSIONE DI WEIERSTRASS Si considera un punto ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Università degli studi di Trento Corso di Meccanica razionale 2<br />
equindi:<br />
il che completa la dimostrazione.<br />
c = Q −1<br />
<br />
x0 − x<br />
<br />
1/2<br />
S<br />
2arcsin<br />
,<br />
x − x D S<br />
Caso SD<br />
◦ Due fasi di moto, <strong>un</strong>a retrograda ed <strong>un</strong>a progressiva.<br />
◦ Regione accessibile: {x ∈ R : x S ≤ xx S }, conx S meta asintotica.<br />
◦ Legge oraria:<br />
t − t0 =<br />
x(t)<br />
x0<br />
1<br />
Φ(u) du ∀x(t) ∈ (x S , +∞) .<br />
◦ Intervallo J(t0,x0,v0) didefinizione della soluzione massimale:<br />
+∞ <br />
1<br />
−∞ ,t0 + du ,<br />
Φ(u)<br />
in cui l’integrale generalizzato può essereomenoconvergente.<br />
x0<br />
Caso DS<br />
◦ Due fasi di moto, <strong>un</strong>a retrograda ed <strong>un</strong>a progressiva.<br />
◦ Regione accessibile: {x ∈ R : x S