Integrità strutturale di ruote ferroviarie: procedure per la ... - AIAS
Integrità strutturale di ruote ferroviarie: procedure per la ... - AIAS
Integrità strutturale di ruote ferroviarie: procedure per la ... - AIAS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
XXXIV CONVEGNO NAZIONALE <strong>AIAS</strong> – MILANO, 14-17 SETTEMBRE 2005<br />
nello schema <strong>di</strong> Figura 11. Le analisi numeriche simu<strong>la</strong>no un ciclo <strong>di</strong> contatto completo, ottenuto<br />
variando <strong>la</strong> <strong>di</strong>stanza tra l’asse del<strong>la</strong> cricca e quello del<strong>la</strong> <strong>di</strong>stribuzione <strong>di</strong> pressione.<br />
p<br />
(MPa)<br />
Figura 10: andamento s<strong>per</strong>imentale delle pressioni <strong>di</strong><br />
contatto utilizzato nelle analisi (F=10000 N) [14].<br />
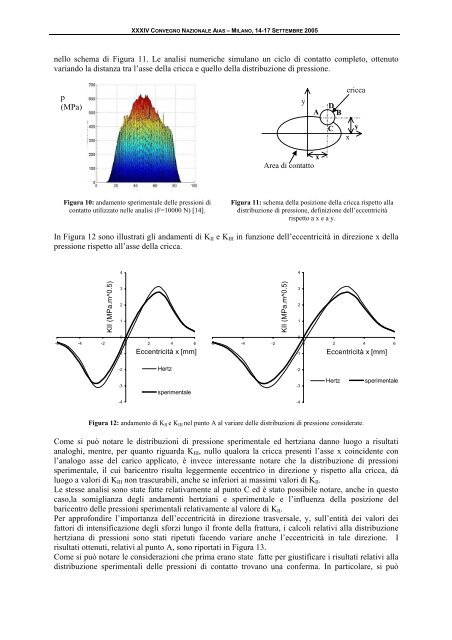
Figura 11: schema del<strong>la</strong> posizione del<strong>la</strong> cricca rispetto al<strong>la</strong><br />
<strong>di</strong>stribuzione <strong>di</strong> pressione, definizione dell’eccentricità<br />
rispetto a x e a y.<br />
In Figura 12 sono illustrati gli andamenti <strong>di</strong> KII e KIII in funzione dell’eccentricità in <strong>di</strong>rezione x del<strong>la</strong><br />
pressione rispetto all’asse del<strong>la</strong> cricca.<br />
KII (MPa.m^0.5)<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
-6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6<br />
-1<br />
-2<br />
-3<br />
-4<br />
Eccentricità x [mm]<br />
Hertz<br />
s<strong>per</strong>imentale<br />
0<br />
-6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6<br />
Figura 12: andamento <strong>di</strong> K II e K III nel punto A al variare delle <strong>di</strong>stribuzioni <strong>di</strong> pressione considerate.<br />
Come si può notare le <strong>di</strong>stribuzioni <strong>di</strong> pressione s<strong>per</strong>imentale ed hertziana danno luogo a risultati<br />
analoghi, mentre, <strong>per</strong> quanto riguarda KIII, nullo qualora <strong>la</strong> cricca presenti l’asse x coincidente con<br />
l’analogo asse del carico applicato, è invece interessante notare che <strong>la</strong> <strong>di</strong>stribuzione <strong>di</strong> pressioni<br />
s<strong>per</strong>imentale, il cui baricentro risulta leggermente eccentrico in <strong>di</strong>rezione y rispetto al<strong>la</strong> cricca, dà<br />
luogo a valori <strong>di</strong> KIII non trascurabili, anche se inferiori ai massimi valori <strong>di</strong> KII.<br />
Le stesse analisi sono state fatte re<strong>la</strong>tivamente al punto C ed è stato possibile notare, anche in questo<br />
caso,<strong>la</strong> somiglianza degli andamenti hertziani e s<strong>per</strong>imentale e l’influenza del<strong>la</strong> posizione del<br />
baricentro delle pressioni s<strong>per</strong>imentali re<strong>la</strong>tivamente al valore <strong>di</strong> KII.<br />
Per approfon<strong>di</strong>re l’importanza dell’eccentricità in <strong>di</strong>rezione trasversale, y, sull’entità dei valori dei<br />
fattori <strong>di</strong> intensificazione degli sforzi lungo il fronte del<strong>la</strong> frattura, i calcoli re<strong>la</strong>tivi al<strong>la</strong> <strong>di</strong>stribuzione<br />
hertziana <strong>di</strong> pressioni sono stati ripetuti facendo variare anche l’eccentricità in tale <strong>di</strong>rezione. I<br />
risultati ottenuti, re<strong>la</strong>tivi al punto A, sono riportati in Figura 13.<br />
Come si può notare le considerazioni che prima erano state fatte <strong>per</strong> giustificare i risultati re<strong>la</strong>tivi al<strong>la</strong><br />
<strong>di</strong>stribuzione s<strong>per</strong>imentali delle pressioni <strong>di</strong> contatto trovano una conferma. In partico<strong>la</strong>re, si può<br />
KII (MPa.m^0.5)<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
-1<br />
-2<br />
-3<br />
-4<br />
y<br />
x<br />
Area <strong>di</strong> contatto<br />
D<br />
A B<br />
C<br />
cricca<br />
x<br />
y<br />
Eccentricità x [mm]<br />
Hertz s<strong>per</strong>imentale