TPA 01_Caratteristiche delle acque reflue - Dipartimento di ...
TPA 01_Caratteristiche delle acque reflue - Dipartimento di ...
TPA 01_Caratteristiche delle acque reflue - Dipartimento di ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
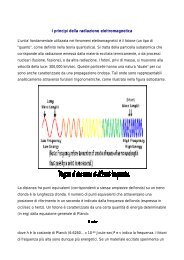
<strong>Caratteristiche</strong> fisiche<br />
Ciascuna frazione <strong>di</strong> soli<strong>di</strong> si <strong>di</strong>stingue in:<br />
SOLIDI VOLATILI<br />
SOLIDI NON VOLATILI<br />
Soli<strong>di</strong> volatili ⇒ FRAZIONE ORGANICA<br />
<strong>Caratteristiche</strong> <strong>delle</strong> <strong>acque</strong> <strong>reflue</strong><br />
Costituiscono la frazione che <strong>di</strong>venta volatile se sottoposta a<br />
calcinazione, ovvero riscaldamento in muffola a 550 °C, rappresenta<br />
con buona approssimazione la porzione <strong>di</strong> sostanza organica presente.<br />
Soli<strong>di</strong> non volatili (residuo fisso) ⇒ FRAZIONE INORGANICA<br />
Costituiscono i residui soli<strong>di</strong> della calcinazione e quin<strong>di</strong> rappresentano,<br />
con la medesima approssimazione, la porzione inorganica del campione.<br />
Nota: in effetti a 350 °C il carbonato <strong>di</strong> magnesio si decompone in MgO e CO2