B.Tech. Biotechnology (Molecular & Cellular ... - Shiats.edu.in
B.Tech. Biotechnology (Molecular & Cellular ... - Shiats.edu.in
B.Tech. Biotechnology (Molecular & Cellular ... - Shiats.edu.in
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
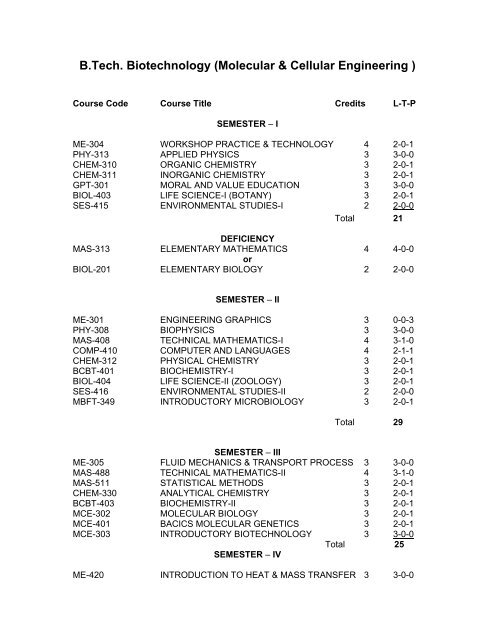
B.<strong>Tech</strong>. <strong>Biotechnology</strong> (<strong>Molecular</strong> & <strong>Cellular</strong> Eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g )Course Code Course Title Credits L-T-PSEMESTER – IME-304 WORKSHOP PRACTICE & TECHNOLOGY 4 2-0-1PHY-313 APPLIED PHYSICS 3 3-0-0CHEM-310 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3 2-0-1CHEM-311 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3 2-0-1GPT-301 MORAL AND VALUE EDUCATION 3 3-0-0BIOL-403 LIFE SCIENCE-I (BOTANY) 3 2-0-1SES-415 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-I 2 2-0-0Total 21DEFICIENCYMAS-313 ELEMENTARY MATHEMATICS 4 4-0-0orBIOL-201 ELEMENTARY BIOLOGY 2 2-0-0SEMESTER – IIME-301 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 3 0-0-3PHY-308 BIOPHYSICS 3 3-0-0MAS-408 TECHNICAL MATHEMATICS-I 4 3-1-0COMP-410 COMPUTER AND LANGUAGES 4 2-1-1CHEM-312 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 3 2-0-1BCBT-401 BIOCHEMISTRY-I 3 2-0-1BIOL-404 LIFE SCIENCE-II (ZOOLOGY) 3 2-0-1SES-416 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-II 2 2-0-0MBFT-349 INTRODUCTORY MICROBIOLOGY 3 2-0-1Total 29SEMESTER – IIIME-305 FLUID MECHANICS & TRANSPORT PROCESS 3 3-0-0MAS-488 TECHNICAL MATHEMATICS-II 4 3-1-0MAS-511 STATISTICAL METHODS 3 2-0-1CHEM-330 ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY 3 2-0-1BCBT-403 BIOCHEMISTRY-II 3 2-0-1MCE-302 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 3 2-0-1MCE-401 BACICS MOLECULAR GENETICS 3 2-0-1MCE-303 INTRODUCTORY BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 3-0-0Total 25SEMESTER – IVME-420 INTRODUCTION TO HEAT & MASS TRANSFER 3 3-0-0
EEE-301 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 4 2-1-1COMP-510 FOUNDATION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 4 2-1-1BCBT 408 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS 3 3-0-0BCBT-404 ENZYMOLOGY & ENZYME TECHNOLOGY 3 2-0-1GPB-412 GENETICS 3 2-0-1MCE-406 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES 3 2-0-1& INSTRUMENTATIONMCE-402 INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 2-0-1Total 26JSBB-400 TRAINING-I 1 0-0-2SEMESTER – VECE-430 ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENT 3 2-0-1& INSTRUMENTATIONCBBI-502 CONCEPTS OF BIOINFORMATICS 3 2-0-1BCBT-407 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 3 3-0-0LNG-304 PROFESSIONAL COMMUNICATION 3 3-0-0& TECHNICAL WRITINGBCBT-405 BASIC IMMUNOLOGY 3 2-0-1MCE-403INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTALBIOTECHNOLOGY 3 2-0-1MBFT-452 MICROBIAL METABOLISM 2 2-0-0MBFT-453 PRINCIPLES OF MICROBIAL GENETICS 2 2-0-0JSBB -400 TRAINING-I EVALUATION 1 0-0-1Total 23SEMESTER – VIBAM-502 MARKETING & MANAGEMENT 3 3-0-0OF BIOTECHNOLOGY PRODUCTSTIEG-503 CONCEPTS OF IN VITRO CULTURE 3 2-0-1MCE-404 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 2-0-1MCE-501 BIOSAFETY, BIOETHICS & IPR ISSUES 3 3-0-0MCE-502 RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY [MCE] 3 2-0-1JSBB-488 SEMINAR-I 1 0-0-1Total 16JSBB-500 TRAINING-II 1 0-0-2SEMESTER – VIIMOLECULAR & CELLULAR ENGINEERING (MCE)MCE-601 MOLECULAR BREEDING 3 2-0-1MCE-602 GENOMICS 3 3-0-0MCE-603 GENETICALLY MODIFIED FOODS 3 3-0-0
MCE-604 GENE CLONING AND GENE THERAPY 2 2-0-0CBBI-601 STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS 2 1-0-1JSBB-589 SEMINAR-II 1 0-0-1JSBB-500 TRAINING-II EVALUATION 1 0-0-1Total 15SEMESTER – VIIIJSBB-699 PROJECT (GE/MT/BT) 9 0-0-181 st SemesterME-304 WORKSHOP PRACTICE & TECHNOLOGY 4(2-0-2)Introduction to eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g materials and its classification, metals and itsclassification – ferrous and non-ferrous metals and its alloys, cast iron steel andalloy steelBrief <strong>in</strong>troduction – description and uses of hand tools used <strong>in</strong> carpentry shop,fitt<strong>in</strong>g shop, sheet metal work, smithy shop, plumb<strong>in</strong>g shop, weld<strong>in</strong>g shop.Weld<strong>in</strong>g –<strong>in</strong>troduction to weld<strong>in</strong>g and its classification, gas weld<strong>in</strong>g, electricweld<strong>in</strong>g, solder<strong>in</strong>g and bras<strong>in</strong>gVarious types of fasteners and fasten<strong>in</strong>g devices, threads, term<strong>in</strong>ology ofthreads, various forms of threads. Properties of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g materialsmechanicalproperties – strength elasticity, stiffness, plasticity, malleability,ductility, brittleness, toughness, hardness, impact strength , fatigue and creep
Practical1. Carpentry shop, - simple job on vertical and horizontal saw<strong>in</strong>g , plann<strong>in</strong>gand slot mak<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> wood , (ii) tomake t- lap jo<strong>in</strong>t2. Smithy shop – to make o- r<strong>in</strong>g from a given rod (ii) to prepare s- hook3. Fitt<strong>in</strong>g shop –(i) simple exercise on fil<strong>in</strong>g, v- groove and vertyical saw<strong>in</strong>g(ii) to make square from given piece of mild steel by fil<strong>in</strong>g and hack saw<strong>in</strong>g4. Weld<strong>in</strong>g shop –(i) to makle butt weld of two given mild steel pieces (ii) tomake lab weld of two given pieces (iii) solder<strong>in</strong>g and braz<strong>in</strong>g practices5. Sheet b metal shop –(I) to make book stand from given piece of sheetmetal of 18 SWG6. Introduction of lathi mach<strong>in</strong>e show<strong>in</strong>g various parts.PHY-313 APPLIED PHYSICS 3(3-0-0)Units and measurements, dimensions and dimensional analysisSpeed, velocity, acceleration, momentum, impulse, torque, k<strong>in</strong>ematics <strong>in</strong> one,two and three dimensions.Newton’s law of motion, conservation of energy and l<strong>in</strong>ear momentum, weightand mass of body, Newton’s law of universal gravitation, satellite andweightlessness, Keplers law of planetary motion, types of force <strong>in</strong> nature.Equilibrium and elasticity, stress, stra<strong>in</strong>, hookes law elastic limitMach<strong>in</strong>es and their pr<strong>in</strong>ciple, efficiency, mechanical advantage, velocity ratio,relationship between efficiency, mechanical advantage and velocity ratio , leversand their k<strong>in</strong>ds .Pressure <strong>in</strong> fluids and their laws, Pascals law, atmospheric pressure, gaugepress, measurement of press, simple barometer, buoyancy and Archimedespr<strong>in</strong>ciple, pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of floatation and it has applications. hydrometer andlactometer.Surface tension, capillary, equation of cont<strong>in</strong>uity, bernoullis equation, viscosity.
Thermometry, relationship between the scales of temperature, absolute scale oftemperature and cl<strong>in</strong>ical thermometer, specific heat, latent, conduction,conviction, radiationRectil<strong>in</strong>ear propagation and reflection of light, formation of image of a po<strong>in</strong>t objectby a plane mirrors, coloursSound, pitch, frequency, wavelength, velocity of sound echoesElectricity, simple cell, relation ship between current charge, potential, oms lawresistance, series and parellel comb<strong>in</strong>ationElectrical power, watt and KWH, household electricity.CHEM-310 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3(2-0-1)UNIT I: chemistry of carbohydratesUNIT II: am<strong>in</strong>o acid and prote<strong>in</strong>UNIT III: Benzene and its homologous, structure of benzene, aroma,nomenclature and aromatic compoundsUNITIV: General <strong>in</strong>troduction of alkaloidsUNITV: General <strong>in</strong>troduction of terpenesUNIT VI: <strong>in</strong>troduction to analytical chemistry and its branchesUNITVII: General pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of analytical chemistry, volumetric analysis, conceptof gram equivalents and method of express<strong>in</strong>g concentration of solution,preparation of primary and secondary standard solutions. Neutralization (acid –base), titration permagnometry, gravimetric analysis: pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of methodologyestimate of calciumUNIT VIII thermometric analysis the gravimetric analysis, types, <strong>in</strong>strumentation,applicationUNITIX Polarimetry
UNIT X Potentiometric titration, electrode system, ion selective membraneelectrodes, application of potentiometric titrationsPRACTICALS1. Qualitative analysis of organic compounds2. Volumetric determ<strong>in</strong>ation of Fe by KMnO 4 solution3. Polarimetric analysis4. Estimation of prote<strong>in</strong> by kjeldal method5. Estimation of calcium volumetrically.CHEM-311 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3(2-0-1)Periodic table: Mendleef periodic table, modern periodic table and table. Longand extended form of periodic table, its ma<strong>in</strong> features, merits and demerits.Periodic properties:Atomic and ionic radii: classification of atomic radii (1) covalent radii (2) metallicradii (3) vander-waal radii, ionic radii. Classification of ionic radii (1) size ofanions, size of cations, crystal coord<strong>in</strong>ation number, radius ratio, size of anions,factors <strong>in</strong>fluenz<strong>in</strong>g magnitude of ionic radii. Periodic variation of atomic and ionicradii.Ionization energy: <strong>in</strong>troduction, successive ionization energies. Factors<strong>in</strong>fluenz<strong>in</strong>g ionization energy (nuclear charge, size of atom, ion. shield<strong>in</strong>geffective nuclear charge, pr<strong>in</strong>cipal quantum number, half and full filled orbitals)trend of ionization energy <strong>in</strong> the periodic tableElectronic aff<strong>in</strong>ity: first and second electron aff<strong>in</strong>ity. Factors effect<strong>in</strong>g magnituteof electron aff<strong>in</strong>ity. Periodic variation
Radioactivity: <strong>in</strong>troduction of radioactivity, radioactive emmision ( alpla ,betaand gamma rays ). Half-life period, average life period, radioactive equilibrium.Group displacement law, atomatic and <strong>in</strong>duced radioactivity.Nuclear chemistry: nuclear fusion and nuclear fission reactions.Mass defect, b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g energy.GPT-301 MORAL AND VALUE EDUCATION 3(3-0-0)My country and my people, the many Indians, be<strong>in</strong>g and becom<strong>in</strong>g Indian,nationalism and <strong>in</strong>ternationalismSome life issues – love, sex and marriage, men and money – value of time,mean<strong>in</strong>g of work, human communication, human suffer<strong>in</strong>g, addition, ecology,women issuesUnderstand<strong>in</strong>g ones neighbor, neighborhood groups: their structure and theirfunctions patterns of social <strong>in</strong>teractions of group dynamics. Preparation for acareer, choice of vocation, motivation of study and research, and the present<strong>edu</strong>cational system: curricu8lam and syllabus, teach<strong>in</strong>g methods, exam<strong>in</strong>ationand work experienceDef<strong>in</strong>ition of value <strong>edu</strong>cation, moral and ethics, laws and morale based on TenCommandments and two great commandmentsDiscovery of self, self – awareness, growth of <strong>in</strong>tellect – mans spiritual lifeemotions, will respect the rights of life, liberty, property, truth reputationS<strong>in</strong>, orig<strong>in</strong> of s<strong>in</strong>, manifestation of s<strong>in</strong>, the result of s<strong>in</strong>, the remedy of s<strong>in</strong>, s<strong>in</strong> asan act, s<strong>in</strong> as a state, s<strong>in</strong> as a nature.
BIOL- 403 LIFE SCIENCE-I 3(2-0-1)1. Orig<strong>in</strong> of Life: History of earth, theories of orig<strong>in</strong> of life nature of the earliestorganism.2. Varieties of Life: Classification, Five k<strong>in</strong>gdoms, viruses (TMV, HIV,bacteriophage), Prokaryotes (Bacteria-cell structure, nutrition, reproduction),Proyista,fungi,Plantae and animalia.3. Chemicals of life: (Biomolecules)-Carbohydrates, lipids am<strong>in</strong>o acids,prote<strong>in</strong>s, nucleic acids, identification of biomolecules <strong>in</strong> tissues.4. Histology: Meristems (apical, <strong>in</strong>tercalary, lateral) and their function simpletissues (parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma) Complex tissue(xylem andphloem); Tissue systems (epidermal, ground, vascular); primary body andgrowth(root,stem and leaf); secondary growth.Animal Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue andtheir function <strong>in</strong> body.5.Nutrition: Autotophic(photosynthesis) Pigment systems, Chloroplast, lightabsorption by chlorophyll and transfer of energy, two pigment systems,photosynthetic unit, phosphorylation and electron transfer system, Calv<strong>in</strong>-BensonCycle(C3), Hatch Slack Pathway(C4), Crassulacan Acid Metabolism(CAM),factors affect<strong>in</strong>g photosynthesis; M<strong>in</strong>eral nutrition <strong>in</strong> plants.Heterotrophic-Forms of heterotrophic nutrition, elementary canal <strong>in</strong> Humans,nervous and hormonal control of digestive systems, fate of absorbed foodmaterials; Nutrition <strong>in</strong> humans, Reference values.6.Energy Utilization: (Respiration) –Structure of mitochondria, cellularrespiration, relationship of carbohydrate metabolism to other compounds,Glycolysis, fermentation, formation of acrtyl co-A, Kreb cycle, Electron TransportSystem and Oxidative Phosphorylation, ATP, factors affect<strong>in</strong>g respiration.7.Transport : Plant water relationship Properties of watwer diffusion, osmosis,imbibitions movement of water <strong>in</strong> flower<strong>in</strong>g plants, uptake of water by roots,ascent of water <strong>in</strong> xylem. Apoplast, symplast theory, transpiration structure of lealand stomata <strong>in</strong> plants open<strong>in</strong>g and clos<strong>in</strong>g mechanism of stomata factorsaffect<strong>in</strong>g transpiration, significance of transpiration, general characteristics ofblood vascular system, development of blood systems <strong>in</strong> animals, composition ofblood, circulation <strong>in</strong> blood vessel, formation of tissue fluids, the heart, function ofmammalian blood, the immune systemSES-415 Environmental Studies I 2(2-0-0)
Unit-I The Multidiscipl<strong>in</strong>ary Nature of Environmental StudiesDef<strong>in</strong>ition, Scope and importance: Need for public awarenessUnit-II EcosystemConcept of an ecosystem, Structure and function of an ecosystem, Proc<strong>edu</strong>res,consumers and decomposers, Energy flow <strong>in</strong> the ecosystem, Ecologicalsuccession, Food ch<strong>in</strong>s, food webs and ecological pyramids, Introduction types,characteristics features, structure and function of the follow<strong>in</strong>g ecosystem:(a) Forest ecosystem (b) Grassland ecosystem (c) Desertecosystem(d) Aqatic ecosystems (ponds, streams, lakes, rivers, oceans, estuaries)Unit-III Social Issue and the EnvironmentForm Unsusta<strong>in</strong>able to Susta<strong>in</strong>able development, Urban problems related toenergy, Water conservation, ra<strong>in</strong> harvest<strong>in</strong>g, watershed management, Resettlemtand rehabilitation of people its problems and concerns. Case studies,Environmental ethics: Issues and possible solutions. Wasteland reclamation:Consumerism and waste products: Environment ethics, issues and possiblesolutions, Wasteland reclamation, Consumerism and waste products,Environment Protection Act. Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act: Water(Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act: Wildlife protection Act. ForestConservation Act: Issues <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> enforcement of environmental legislation:(Public awareness).MAS-313 Elementary Maths-I 4(4-0-0)Algebra: Theory of Quadratic equations, Partial fractions, B<strong>in</strong>omial theorem (forpositive <strong>in</strong>dex), Exponential and Logarithmic series, Elementary concepts ofPermutation and Comb<strong>in</strong>ation.
Trigonometry: Elementary concepts of Complex numbers, De-Movier’s theoremand its application.Co-ord<strong>in</strong>ate Geometry: Equation of standard curves and their identification.Differential Calculus: Function, Limit, Cont<strong>in</strong>uity and Differentiability,Differentiation of standard functions, Method of Differentiation, Trangent andNoraml, Maxima and M<strong>in</strong>ima.Integral Calculus: Indef<strong>in</strong>ite <strong>in</strong>tegration of standard functions, Integration bysubstitution, by parts, by partial fraction.Vector Analysis: Scalar and Vectors, sum and Difference of Vectors, Dot andCross product. (double, triple).BIOL-201 ELEMENTRY BIOLOGY 2(2-0-0)LIFE: Liv<strong>in</strong>g and non-liv<strong>in</strong>gOrig<strong>in</strong> of life: opar<strong>in</strong> abiotic theoryEvolution: unicellularity, multicellularity, complex tissue systemIntroduction to various systems of biologyIntroduction to botany: history of botany, brief <strong>in</strong>troduction of branches ofbotany, morphology, anatomy, taxonomy, physiology, paleobotany.Introduction to lower botany: Algae, fungi, lichen, bacteria, virus, bryophytes,pteridophytes, gymnosperms.
Introduction to zoology: Classification of animal k<strong>in</strong>gdom, adaptation ofanimals. External morphology of frog, <strong>in</strong>ternal anatomy of frog – <strong>in</strong>ternal organs,different <strong>in</strong>ternal systems.Scope: application of biology
2 nd SemesterME-301 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 3(0-0-3)Introduction to eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g draw<strong>in</strong>g, about the draw<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>strumentsDimensional, letter<strong>in</strong>g, scalesDraw<strong>in</strong>g of various geometrical curves like ellipse, parabola, cycloid.Concepts of first angle and third angle projection, projection of po<strong>in</strong>ts, l<strong>in</strong>es,planes, projection of solidsOrthographic projection of sample objects, miss<strong>in</strong>g views, sectorial viewsIsometric projection of simple objects – draw<strong>in</strong>g of isometric views from the givenorthographic projections.PHY-308 BIOPHYSICS 3(3-0-0)1. Concepts of biophysics and classification, liv<strong>in</strong>g body as a thermodynamicsystem, biological effects of radiation, radiation hazards <strong>in</strong> man.2. Biological effects of light, biophysics of vision, <strong>in</strong>teraction of UV light with liv<strong>in</strong>gsystem, <strong>in</strong>teraction of microwaves <strong>in</strong> liv<strong>in</strong>g system.3. Cronobiology, cybernetics, biomagnetism and magneto biology, bioacoustics –the ear.4.Influenze of gravity, g-force, acceleration and decelation, <strong>in</strong>fluence ofbarometric pressure and vibration, elementary idea of thermodynamics.MAS-408 TECHNICALMATHEMATICS-I 4(3-1-0)Matrices: Theory of Matrices, Types, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication,Transpore, Ad jo<strong>in</strong>t and Inverse of Matrices, Rank of Matrix, Solution ofsimultaneous equations, Eigun values, Cayley-Hamilton theorem.
Differential Calculus: Partial Differentiation, Euler theorem, Total differentialcoefficient, Partial higher order derivatives, Application of partial differentiation,Maxima-M<strong>in</strong>ima of function of two variables, Jacobians.Integral Calculus: Def<strong>in</strong>ite <strong>in</strong>tegrals and their properties, Application ofdeterm<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g are length, area, surface and volume. Simpson’s rule forapproximate <strong>in</strong>tegration, Mean values, Root mean square values.Differential Equations: Ord<strong>in</strong>ary differential equations their order, degree andformation, Solution of the equation of the first order, first degree, Homogenousdifferential equations, L<strong>in</strong>ear differential equations, Exact differential equations,L<strong>in</strong>ear differential equations of second order with constant coefficient,Homogenous l<strong>in</strong>ear equations, Applications.COMP-410 COMPUTER AND LANGUAGES 4(2-1-1)Introduction to computers: Computer organization and peripherals. Hardware,software concepts, term<strong>in</strong>ology. Introduction to DOS – DOS external commands,DOS <strong>in</strong>ternal commands. Introduction to w<strong>in</strong>dows- Start menu and accessories,w<strong>in</strong>dows explorer, my computer. Introduction to network<strong>in</strong>g of computers.Program development us<strong>in</strong>g BASIC- Algorithms and flow charts, variables,constants, relational logical operators, library functions, hierarchy rules foroperators and evaluations of expressions, LET, INPUT, READ……. DATA,control statements, GOTO, IF---THEN, FOR---NEXT, Introduction to array andDIM statement, Introduction to search<strong>in</strong>g, sort<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong>troduction to functions andsubrout<strong>in</strong>es. Steps <strong>in</strong> development of applications. Introduction to <strong>in</strong>formationmanagement- Data storage, retrieval, data manipulation, validation and security
of data, presentation of data and report generation. Introduction to MS-Office.Introduction to RDBMS.CHEM-312 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 3(2-0-1)Ionic equilibrium: concepts of acids and their related strength, buffer solutionand its ph, hydrolysis of salts, acids –base <strong>in</strong>dicators oswalds and qu<strong>in</strong>onoidestheory, solubility productChemical k<strong>in</strong>etics: order and molecularity, differential rate lawsand <strong>in</strong>tegratedrate laws equations for zero, 1 st , 2nd and 3 rd reactions (derivations <strong>in</strong>cluded)significance of rate constant and its evaluation, time for def<strong>in</strong>ite fractional changeof reaction, determ<strong>in</strong>ation of orderElectro chemistry: reversible and irreversible cells, EMF of a cell and freeenergy, nernst equation, equilibrium constant, standard electrode potential, typesof reversible electrodes, applications of EMFmeasurements, determ<strong>in</strong>ation ofsolubility product, ph, dissociation constant of acids, hydrolics constant solubility,soluble saltsPracticals:Analysis of <strong>in</strong>organic mixture, redox and acid base titration. Preparation andstandardization of primary and secondary standard solution, ph, buffers,chemical k<strong>in</strong>eticsand partition coefficient.BCBT- 401 Biochemistry- I 3(2-0-1)Unit I : Chemical structure of prote<strong>in</strong>s and their properties, cellular membraneand transport phenomenon.Unit II: Intermediary metabolism- concept of anabolism and catabolism,metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and am<strong>in</strong>o acids and their <strong>in</strong>terrelationship.
Unit III: Biological oxidation, electron transport system, oxidativephosphorylation, free energy changes <strong>in</strong> biochemical reactions, energy changes<strong>in</strong> biochemical reactions, energy rich compounds.Unit IV: Metabolism of nucleic acids and prote<strong>in</strong>s.Unit V: Hormones: regulation of metabolism by various hormones.Practicals :1. Specific group tests for carbohydrates2. Specific group tests for am<strong>in</strong>o acids.3. Specific tests for lipids.4. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of mil prote<strong>in</strong>, fat and lactose.5. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of acidity <strong>in</strong> sample.BIOL-404 LIFE SCIENCE-II (ZOOLOGY) 3(2-0-1)Coord<strong>in</strong>ation and control: Plant movement (tactic, tropic and Nastic) , Plantgrowth substances(aux<strong>in</strong>s, cytok<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>s, gibberell<strong>in</strong>, ABA and Etylene) ,Phytochrome and effect of light on plant development , vernalization and flower<strong>in</strong>g.Nervous system , parts of nervous system, sensory receptors, structure andfunction of receptors, endocr<strong>in</strong>e system, role of hormones <strong>in</strong> growth anddevelopment <strong>in</strong> humans.Homeostasis: Control system <strong>in</strong> biology, control of blood glucose level,temperature regulation <strong>in</strong> endothermic animals, the liver and its importance.Reproduction: Asexual reproduction - apomixis and other means of naturalvegetative reproduction (bulb, corm, rhizome, stolon, runner, tuber, tap root ,tillers),advantage and disadvantage of natural asexual reproduction. Artificialpropagation- cutt<strong>in</strong>g , graft<strong>in</strong>g budd<strong>in</strong>g , layer<strong>in</strong>g, micro propagation through tissueculture ,advantage and disadvantage of micro propagation .Sexual reproduction-life cycle of flower<strong>in</strong>g plants, the parts of a flower(dicot andmonocot), microsporogenesis, <strong>in</strong> vitro pollen culture, microgametogenesis,isolation of sperms, palynology, scope of palynology, development of ovule, typesof ovule, megasporogenesis, megagametogenesis, embryo sac, seed formation,structure of seed and its importance. Review of sexual reproduction <strong>in</strong> vertebrates,human <strong>in</strong>tervention <strong>in</strong> reproduction.
Cont<strong>in</strong>uity <strong>in</strong> Life: Chromosomes, cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis, techniques to studymitosis and meiosis.Hereditary and Variation: Mendel’s work, chromosomal basis of <strong>in</strong>heritance,modified dihybrid ratio, gene <strong>in</strong>teraction, L<strong>in</strong>kage, gene mapp<strong>in</strong>g, sexdeterm<strong>in</strong>ation, cytoplasmic <strong>in</strong>heritance, variation and mutation.Economical Importance Plants: Cereals (wheat, rice, maize), Beverages (tea,coffee, cocoa), Fibers (jute, l<strong>in</strong>en, cotton), wood (p<strong>in</strong>es, cedar, teak, sisam), rubber(Para robber), spices (turmeric, black pepper, cloves, coriander), medic<strong>in</strong>al plants(Ephedra, Taxus, C<strong>in</strong>chona, Fox glove, Belladonna, Ravolfia, neem, Hemp).SES-416 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES II 2(2-0-0)Def<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g Environment, atmosphere model: Troposphere, stratosphere,mesosphere, thermosphere, comparison of clear and dry air Hydrological cycle,components of hydrologic cycle, role of water <strong>in</strong> pollutant cycle <strong>in</strong> soils.Pollutants: Def<strong>in</strong>ition and classification, air, water and soil pollutionSoil and water pollution due to NO 3 , phosphates and heavy metals, NO 3 pollutiondue to organic matter decomposition, m<strong>in</strong>eralization, nitrogen cycle, negativeenvironmental effects of NO 3 , PO -34 and other metal ions on human health;phosphate load<strong>in</strong>g to surface water bodies through characteristic overland flow,sediment delivery ratio, runoff ratio/coefficient, enrichment ratio, water quality<strong>in</strong>deed, water quality standard, sewage treatment, water purification andmanagement water quality <strong>in</strong>dex, water quality standard, sewage treatment,water purification and management strategiesAir pollution: concept, air pollution problem <strong>in</strong> India, present status Type andsources of urban and <strong>in</strong>dustrial pollutant Responses of crops to importantphytotoxic air pollutants (SO, NO, Ozone, HF etc).
Acid ra<strong>in</strong>: causes and consequences with special references to crops. Nuclearpollution and consequences. Air pollution control and alternate strategies. Riskassessment and warn<strong>in</strong>gMBFT 349 Introductory Microbiology 3(2-0-1)• Def<strong>in</strong>ition, Scope and History of Microbiology<strong>Cellular</strong> organization of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells• Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells• General characteristics and nature of Bacteria, Mycoplasma, Rickettsiae,Chlamydiae, Act<strong>in</strong>omycetes, Protozoa, Fungi, Algae & VirusesPracticalFamiliarity with equipment to be used <strong>in</strong> Microbiology Laboratory.Clean<strong>in</strong>g, wash<strong>in</strong>g and sterilization of glass waresObservation of permanent slides to study the structural characteristics of commonbacteria , fungi, algae & protozoa
3 rd SemesterME-305 FLUID MECHANICS & TRANSPORT PROCESS 3(3-0-0)Introduction to pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g and units: classification of unitoperation and transport process and basic system of units, methods ofexpress<strong>in</strong>g temperature and composition gas law and vapour pressure,conservation of mass and material balances, energy and heat unit, conservationof heat energy and heat balancesPr<strong>in</strong>ciples of momentum transfer: <strong>in</strong>troduction, fluid statics, and viscosity offluid s, mass energy and momentum balances, and non-Newtonian fluidsPr<strong>in</strong>ciples of steady state heat transfer: Introduction and mechanism of heattransfer, conduction, conduction through solid <strong>in</strong> series, forced convection heat,transfer <strong>in</strong> fluids, natural convection heat transfer and heat transfer of nonNewtonian fluidsPr<strong>in</strong>ciple of mass transfer: Introduction the mass transfer and diffusion,molecular diffusion <strong>in</strong> gas and liquid biological solution and cells, mass transfer <strong>in</strong>cellular systemsMAS-488 TECHNICAL MATHEMATICS-II 4(3-1-0)Differential calculus: partial differentiation, Euler theorem, total differentialcoefficient, partial higher order derivatives, application of partial differentiationapproximation problems, error determ<strong>in</strong>ation, maxima – m<strong>in</strong>ima functions of twovariables, Jacobeans
Integral calculus: def<strong>in</strong>ite <strong>in</strong>tegrals and their properties, their application <strong>in</strong>determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g arc length and surface area, Simpson rule for approximation,<strong>in</strong>tegration, mean values and root mean square values. Multiple <strong>in</strong>tegrals –double and triple <strong>in</strong>tegrals, their application <strong>in</strong> determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g area and volumeDifferential equations :Ord<strong>in</strong>ary differential equations, their order degree andformation, solution of the equations of the first order and first degree.Homogenous and differential equations, l<strong>in</strong>ear differential equations, exactdifferential equations, l<strong>in</strong>ear differential equation of second order with constantequations, homogenous l<strong>in</strong>ear equations.Vector calculus: vector differentiation, gradient, divergence and curl, theirphysical <strong>in</strong>terpretation directional and normal derivatives vector <strong>in</strong>tegration, l<strong>in</strong>esurface and volume <strong>in</strong>tegrals, green theorem, gauss theorem and stoke stheoremFourier series: periodic functions, fouriers series fourier series and theircoefficients and their determ<strong>in</strong>ation ( euler formula ) ,change of <strong>in</strong>terval , halfrange s<strong>in</strong>e and cos<strong>in</strong>e series.MAS-511 STATISTICAL METHODS 3(2-0-1)Def<strong>in</strong>ition and application of statistics, geographical representation of frequencydistribution, measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, standarderror of mean, coefficient of variation
Probability: def<strong>in</strong>ition and applications, numerical problemsSimple correlation between two variables (def<strong>in</strong>ition, properties and numericals)Regression l<strong>in</strong>es: def<strong>in</strong>itions and uses, methods of least square, concept ofregression coefficient.CHEM-330 ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY 3(2-0-1)Introduction to Analytical chemistry and its branches.General pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of analytical chemistry: Volumetric analysis.Concept of gram equivalents and method of express<strong>in</strong>g , Concentration ofsolutionpreparation of primary and secondary, Standard solution Neutralized (Acid-Base), Titration, Permagnometry. Gravimetric analysis & methodology. Estimateof calcium.Thermometric analysis: The gravimetric Analysis – types, Instrumentation,Application.Polarimetry.Potentiometer titration: Electrode system, Ion selective membraneElectrodes, Application of potentiometer titrationsBCBT- 403 Biochemistry – II 3 (2-0-1)Unit I: Prote<strong>in</strong> Chemistry: Structure of prote<strong>in</strong>s, methods for determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the 3Dstructure of a prote<strong>in</strong> – X-ray diffraction, NMR, Mass spectrometry, prote<strong>in</strong>homology among species, prote<strong>in</strong> denaturation and fold<strong>in</strong>g, assisted fold<strong>in</strong>g,edman degradation, glycoprote<strong>in</strong>, lipoprote<strong>in</strong>s, proteoglycans, phosphor prote<strong>in</strong>s,chromoprote<strong>in</strong>, bacterial and viral prote<strong>in</strong> (HIV, HBV, tox<strong>in</strong>s, etc.)Unit II: Biomembranes: <strong>Molecular</strong> constituents of membranes, movement ofmolecules through membranes, energetics of membrane transport system,biosignall<strong>in</strong>g, voltage gated ion channels, transporters and group translocationwith examples.
Unit III: Sensory systems: Olfaction, taste, vision, hear<strong>in</strong>g and touch with theirbiochemical mechanisms.Unit IV: Physiochemical properties of nucleic acids: Hydrogen bond<strong>in</strong>g, bondlength, tautomerism and its significance <strong>in</strong> nitrogen bases, DNA denom<strong>in</strong>ation,and factor responsible for hypochromicity. Renaturation of DNA, anneal<strong>in</strong>g,walloce’s rule, hybridization, ionization, enzymatic of nucleic acids, effect ofacids and alkalis on nucleic acids, DNA super coil<strong>in</strong>g and nucleic acid mutations.Practicals:1. Fractionation of egg prote<strong>in</strong>s.2. Detection of alpha – amylase activity <strong>in</strong> saliva.3. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of sugar/glucose I ur<strong>in</strong>e (Benedict’s Tritrimetric method).4. Identification of blood constitution.5. Extraction of total nucleic acid from plant tissues.6. Extraction of RNA from yeast.7. Assay of prote<strong>in</strong> by Biuret’s method.MBGE-302 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 3(2-0-1)Unit 1: Introduction: Development of molecular biology. Historical perspectives.Concepts <strong>in</strong> molecular biology.Unit 2: Structure and properties of nucleic acids: Structure of nucleotides, DNAdouble helix, helical conformations and DNA topology. Types of DNA and RNA- A,B, Z forms of DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, hnRNA, snRNA. Physical and chemicalproperties of DNA.Unit 3: DNA prote<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>teraction: <strong>Molecular</strong> aspects of prote<strong>in</strong>-nucleic acid b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g.DNA b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g motifs <strong>in</strong> prote<strong>in</strong>s- Helix- turn - helix, Z<strong>in</strong>c f<strong>in</strong>ger motifs, Leuc<strong>in</strong>e zipper,HMG box, etc.Unit 4: Gene organization: Gene structure and architecture, gene clusters, splitgenes, overlapp<strong>in</strong>g genes, pseudogenes, operon, open read<strong>in</strong>g frames,transposons, oncogenes.Range of genome size. C value and gene numbers.Reassociation k<strong>in</strong>etics, Repetitive DNA -satellite DNA.MCE 401 BASICS OF MOLECULAR GENETICS 3 (2-0-1)Unit 1. Introduction: Basic concepts <strong>in</strong> molecular genetics. Prokaryotic andEukaryoticgenome. Concept of gene and central dogma.Unit 2. Transcription: Mechanism of transcription <strong>in</strong> prokaryotes and eukaryotes.Transcription of prote<strong>in</strong> cod<strong>in</strong>g genes- mRNA. Post transcriptional modifications - 5_capp<strong>in</strong>g, poly A tail<strong>in</strong>g and mRNA splic<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> eukaryotes.
Unit 3. Translation: Introduction to prote<strong>in</strong> synthesis. The nature of genetic code.Mechanism of translation <strong>in</strong> prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Post translationalmodification ofprote<strong>in</strong>s.Unit 4. Regulation of gene expression: Gene regulation <strong>in</strong> prokaryotes - lac andtrp operons as model systems. Gene regulation <strong>in</strong> eukaryotes – Transcriptional levelcontrol, RNA process<strong>in</strong>g level control, translational level control, post translationallevel control.Unit 5. Gene mutation: Mutagenesis. Causes of mutation – spontaneous and<strong>in</strong>duced. Types of mutagens - physical and chemical. Classification of mutations.<strong>Molecular</strong> basis of gene mutation.PracticalsStructural elucidation of nucleotides and nucleic acids.Study of DNA and RNA modelsExtraction of prote<strong>in</strong>s from plant tissuesEstimation of prote<strong>in</strong>s by Lowry and Bradford methodsMCE 303 INTRODUCTORY BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 (3-0-0)Unit 1. Introduction: Historical development of biotechnology. Basic concepts ofbiotechnology. Def<strong>in</strong>ition and descriptions of some important term<strong>in</strong>ology <strong>in</strong>biotechnology.Unit 2. Branches of biotechnology: Study of various branches of <strong>Biotechnology</strong><strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g Plant, Animal, Medical, Industrial, Environmental, Mar<strong>in</strong>e <strong>Biotechnology</strong>,Bio<strong>in</strong>formatics, etc.Unit 3. <strong>Biotechnology</strong> <strong>in</strong> India: <strong>Biotechnology</strong> and develop<strong>in</strong>g world- concerns andconsequences. Role of biotechnology <strong>in</strong> Indian <strong>in</strong>dustry. Impact on agriculturalsector.Unit 4. <strong>Biotechnology</strong> and other discipl<strong>in</strong>es: <strong>Biotechnology</strong>- an <strong>in</strong>terdiscipl<strong>in</strong>arypursuit, a three component central core, product safety. New trends <strong>in</strong> biotechnology.Unit 5. Applications and scope of biotechnology: Practice of biotechnology <strong>in</strong>medic<strong>in</strong>e, <strong>in</strong>dustry, agriculture, live stock improvement and environment. Futureperspectives.
4 th SemesterME-420 INTRODUCTION TO HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER 3(3-0-0)Mass Transfer Operation: Classification of mass transfer operation, choice ofoperation method, methods of conduct<strong>in</strong>g the mass transfer operation, unitsystemsDiffusion <strong>in</strong> solids: Ficks law diffusion, types of solid diffusion Equipment forgas liquid operations: L.gas dispersed –sparged vessel (bubble columns),mechanically agitated vessels, mechanical agitation of s<strong>in</strong>gle phase liquids, gasliquid contract, tray tower, liquid dispersed –venturi scrubbers, wetted wall tower,spray tower and spray chamber, packed tower. Concurrent tower gas and liquid,end effect and artificial and tray mix<strong>in</strong>g, tray tower vs. packed towers.Humidification operationsDistillation: Vapors liquid equilibria, s<strong>in</strong>gle stage operation (flash vaporization)differential or simple distillation, cont<strong>in</strong>uous rectification (b<strong>in</strong>ary system)multistage tray towers, cont<strong>in</strong>uous contact equipment (packed towers)multicomponent systems, low-pressure distillation.Dry<strong>in</strong>g: Dry<strong>in</strong>g operation, batch dry<strong>in</strong>g, mechanism of batch dry<strong>in</strong>g, cont<strong>in</strong>uousdry<strong>in</strong>g, leech<strong>in</strong>g.EEE-301 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 4(2-1-2)UNIT I: Electrical circuits and circuit parameters, voltage, current, power energy,basic circuit components – resistance, <strong>in</strong>ductance, capacitance, ohms law, seriesand parallel comb<strong>in</strong>ation of resistance, voltage and current division <strong>in</strong> series andparallel circuits, voltage and current sources <strong>in</strong> series and parallel circuits,voltage and current sources, source transformation, kirchoffs current law,electrical circuit analysis us<strong>in</strong>g KVL & KCL.
UNITII: Fundamental of ac circuits: impedance admittance reactance andcomplex power real reactive power analysis of circuits us<strong>in</strong>g Maxwell’s loop,current method and Maxwell nodal method of voltage, average, rms, form factorof s<strong>in</strong>usoidal wave form.UNITIII: network theorems a) theven<strong>in</strong>s theorem b) Norton theorem c)superposition theorem d) maximum power transfer theorem.UNIT IV: polyphase system three-phase system l<strong>in</strong>e phase l<strong>in</strong>e voltage. Phasecurrent, phase voltage of three phase stare or delta connected systems relationbetween the current and phase current and l<strong>in</strong>e voltage and phase voltage <strong>in</strong>three phase star and delta connected system, balanced and unbalanced threephase system. Three phase electrical power measurement us<strong>in</strong>g two-watt metermethod.UNIT V: Measurement and measur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments. Measurement of electriccurrent voltage power energy construction and work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of ammetervoltmeter wattmeter energy meterMagnetic circuit and transformer b-h curves magneto motive force (MMF) fluxreluctance <strong>in</strong> a magnetic circuit relation between electric and magnetic circuits,basic pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of a s<strong>in</strong>gle phase transformer EMF equation, transformation ratioand equivalent circuit of transformer, open circuit test and short circuit test <strong>in</strong> as<strong>in</strong>gle phase transformer, losses and efficiency.UNIT VI: electric mach<strong>in</strong>es dc mach<strong>in</strong>es – construction and work<strong>in</strong>g of dcgenerator, dc series, dc shunt and dc compound generators and motors, the<strong>in</strong>ternal characteristics of dc generators, charecteristic of dc motors, work<strong>in</strong>g andconstructions, application of dc motors <strong>in</strong> field of biotechnology. AC mach<strong>in</strong>es –<strong>in</strong>duction motor, work<strong>in</strong>g and construction, equivalent circuit, slip, synchronousspeed. S<strong>in</strong>gle phase and three phase <strong>in</strong>duction motor. Synchronous mach<strong>in</strong>e –<strong>in</strong>troduction to construction and work<strong>in</strong>g, application <strong>in</strong> field of biotechnology.UNITVIII: Introduction to power system, power system components, protection ofpower system, per unit system, safety device fuse.COMP-510 FOUNDATION OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 4(2-1-2)Introduction to w<strong>in</strong>dows: Start menu and accessories, w<strong>in</strong>dows explorer, mycomputer. Introduction to network<strong>in</strong>g of computers.Internet-<strong>in</strong>ternet, TCP/IP, IP address, Basic C and C++,Oracle.
Information networks: Internet, world wide web, web browsers, HTTP, HTMLand URLS, EMB.BCBT-408 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS 3(3-0-0)Introduction To Thermodynamics Terms (System, surround<strong>in</strong>g, boundariesetc.) open and closed loop systems, isolated systems, thermodynamic variables,extensive and <strong>in</strong>tensive properties.Thermodynamic process- lost thermal, adiabatic process, isobaric, isochoric,cyclic and irreversible processes.Laws of thermodynamics- thermal equilibrium, zero law, first law, second law ofthermodynamics, energy concept, law of conservation of energy, concept ofenthalpy, entropy.Reactive systems, degree of reaction, reaction equilibrium, laws of mass action,Gibbs functional change heat of reaction, fugacity + reactivity, construction,enthalpy of formation, laws for reaction systems. Air cycle, Otto cycle, work done<strong>in</strong> cycles, thermal efficiency.Refrigeration- Introduction to pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of vapors compression cyclBCBT-404 ENZYMOLOGY & ENZYME TECHNOLOGY 3(2-0-1)Unit1: Introduction of enzymes: General properties and significance,classification and nomenclature. Terms and def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>in</strong> enzymology: enzymeactivity, specific activity, turnover number, active site, isoenzyme, marker enzymeMultienzyme complex, extracellular enzymes, extremozymes, abzymes,ribozymes, <strong>in</strong>duced enzyme etcUnit 2: Factor affect<strong>in</strong>g enzyme activity: pH, Temperature, substrateconcentration etc. Isolation, purification and localization of enzyme, techniques<strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> enzyme assays.Unit 3: Enzyme k<strong>in</strong>etics: steady rate k<strong>in</strong>etics, Derivation of Michaelis-Mentenequation us<strong>in</strong>g steady state/equilibrium k<strong>in</strong>etics, plots of L<strong>in</strong>eweaver- Bruke etc.machanism of substrate and multi-substrate enzyme catalyzed reaction.Unit 4: Regulation of enzyme activity: Covalent modification, enzyme <strong>in</strong>hibitionand k<strong>in</strong>etics. Allostearic enzyme: feed back <strong>in</strong>hibition, allostearic modelconcerted and sequential, co-operativity.
Unit 5: Mechanism of enzyme action and concept of active site: Vis-a-vislysozyme, chymotryps<strong>in</strong>, alcohol dehydrogenase, glycerldehyde 3 phosphatedehydrogenase, proteases.Unit 6:Enzyme <strong>Tech</strong>nology: Commercial production of enzymes, preference ofextracted enzymes over whole organism, immobilization of enzymes, example ofenzyme eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, application of enzyme(therapeutic uses, analytical uses,manipulated uses etc.), uses of enzyme <strong>in</strong> solutions, enzyme reactors, biphasicsystem, Bi and poly functional enzymes, solvent eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g.Practical:1. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of prote<strong>in</strong>2. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of salivary amylase3. Activity of effect of salt on salivary amylase4. Detection of effect of pH on enzyme activity5. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of Acid/Alkal<strong>in</strong>e phosphatase6. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of enzyme k<strong>in</strong>etics7. Separation of prote<strong>in</strong> by PAGE8. Identification of extra cellular enzymes like protease, oxidase, urease,catalaseandGPB-412 GENETICS 3(2-0-1)Mendels law of heritability, mono, di hybrids ratiosL<strong>in</strong>kage: types, l<strong>in</strong>kage maps, l<strong>in</strong>klage groups, coefficient of co<strong>in</strong>cidence,coefficient of <strong>in</strong>terferenceCross<strong>in</strong>g over, cytological basis of cross<strong>in</strong>g over, factors effect<strong>in</strong>g cross<strong>in</strong>g over,estimation of recomb<strong>in</strong>ation frequency from f2 data.Practicals:Simple and compound microscope, cell culture. Monohybrid and dihybrid ratios,test cross, back cross, epistatic <strong>in</strong>teractions, practice of mitotic and meiotic cell
division, study of special chromosomes, probality, chi square and cross<strong>in</strong>g over,two po<strong>in</strong>t test, cross l<strong>in</strong>kage analysis, three po<strong>in</strong>t test, cross l<strong>in</strong>kage analysis.MCE-406MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES AND INSTRUMENTATION3(2-0-1)Unit l. <strong>Molecular</strong> biology techniques: Cell fractionation. Isolation and purification ofgenomic DNA. Polymerase Cha<strong>in</strong> Reaction. Nucleic acid blott<strong>in</strong>g. DNA sequenc<strong>in</strong>gtechniques.Unit 2. Instrumentation <strong>in</strong> biotechnology: Work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples, <strong>in</strong>strumentation andapplications of pH meter, centrifuge, colorimeter, spectrophotometer, autoclave,distillation unit, lyophilizer, flame photometer.Unit 3. Methods for separation of macromolecules: Chromatography- column, th<strong>in</strong>layer, paper, ion exchange, gel filtration, aff<strong>in</strong>ity. Electrophoresis- agarose gelelectrophoresis and poly acrilamide gel electrophoresis.UNIT 4. Microscopy: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and applications of microscopy - simple, compound,phase contrast and electron microscopy. Yeast-2 Hybrid system, MS, tandem MSand MS imag<strong>in</strong>gPracticalsMeasurement of hydrogen ion concentration of a given solutionSeparation techniques-centrifugation and electrophoresisStudy of work<strong>in</strong>g pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and operation of some important equipments used <strong>in</strong>biotechnologylaboratory viz., spectrophotometer, pH meter, centrifuge, electrophoresis apparatus(AGE andPAGE), PCR mach<strong>in</strong>e, Distillation unit, autoclaves etc.MCE 402 INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 (2-0-1)Unit 1. Introduction to plant biotechnology: Def<strong>in</strong>ition. History and developmentof plant biotechnology. Modern trends <strong>in</strong> plant biotechnology.Unit 2. Gene transfer <strong>in</strong> plants us<strong>in</strong>g Agrobacterium: Ti plasmids, transfer of T-DNA, construction of b<strong>in</strong>ary and co-<strong>in</strong>tegrate vector systems. Agrobacteriummediated leaf disc transformation.
Unit 3. Direct gene transfer <strong>in</strong> plants: Physical (Particle gun delivery,electroporation, micro<strong>in</strong>jection, macro<strong>in</strong>jection, electro<strong>in</strong>jection, fiber mediated DNAdelivery, Laser <strong>in</strong>duced DNA uptake, Sonication) and Chemical methods of genetransfer (Poly ethylene glycol, Poly v<strong>in</strong>yl alcohol, Calcium phosphate)Unit 4. Applications of plant biotechnology: Improv<strong>in</strong>g agronomic traits - geneticmanipulation of plants for salt resistance, herbicide resistance, fungi and virusresistance, <strong>in</strong>sect and other pest resistance. Modification of production traits -delayed fruit ripen<strong>in</strong>g, improv<strong>in</strong>g seed storage prote<strong>in</strong>s.PracticalsSafety aspects and precautions to be taken <strong>in</strong> <strong>Biotechnology</strong> LaboratoryPreparation of reagents, stock solutions and buffers for plant DNA isolation.Study of Labwares used for isolation of DNAIsolation of genomic DNA from plant tissues by CTAB method.Purification of crude DNA samples.JSBB 400 TRAINING I I (0-0-1)
5 th SemesterECE-430 ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENTATION 3(2-0-1)Semiconductors: energy band theory of solids, concept of solids, concept offorbidden gaps, <strong>in</strong>sulators and semiconductors. Transport phenomenon <strong>in</strong>semiconductors, <strong>in</strong>stridic, and extr<strong>in</strong>sic semiconductorsJunction diode p-n junction diode vi characteristics, diode application as arectifier (half wave and full wave) breakdown mechanism –se4len and Avalenchecharacteristics, zener diode and its applications LED and its applicationsBijunction transistor, CE, CB Configuration, characteristics, curves, requirementof bias<strong>in</strong>g, stability, small signal equivalent ckt, h- parameter model, transistor asan amplifier, frequency response of amplifiers, negative feed back, ga<strong>in</strong> bandwidth product, oscillators and condition for oscillationOther semiconductor devices: <strong>in</strong>troduction of JFET, MOSFET, and CMOSSwitch<strong>in</strong>g theory and logic gates number systems, Boolean algebra, logic gates,flip flop and ICSA/D and D/A converters <strong>in</strong>troduction, methods of conversion A/D, D/AQuantities of measurements: <strong>in</strong>troduction, performance characteristics, staticcharacteristic, error <strong>in</strong> measurement, types of error, and source of error, dynamiccharacteristicElectronic <strong>in</strong>struments: ammeter, voltmeter, ohm meter, VOM, Q meterCRO block diagram and work<strong>in</strong>gTransducers and measurements of electrical and non electric quanta ties:measurement of liquid level, flow temperature, stra<strong>in</strong>, pressure, force, torque,power, displacement, vibration, acceleration due to transducers. Measurement ofresistance, <strong>in</strong>ductance, capacitance us<strong>in</strong>g DC (Wheatstone bridge) and AC(MAXWELL Bridge, WEINBRIDGE) bridges.List of Practicals:Study of diode characteristics
Study of half wave and full wave rectifier with and without capacitor filter anddeterm<strong>in</strong>e ripple factor.CBBI-502 Concepts of Bio<strong>in</strong>formatics 3 (2-0-1)Unit 1Bio<strong>in</strong>formatics and Internet: Internet Basics, FTP, www, connect<strong>in</strong>g to Internet,Electronic mail, <strong>in</strong>ternet resources.Unit 2Information Retrieval from Biological Databases: Integrated <strong>in</strong>formation Retrieval(Entrez System), Retriev<strong>in</strong>g database entries.Unit 3The NCBI data model: Introduction, Seq-id, Sequence, collection of sequence,annotation of sequence, Describ<strong>in</strong>g sequence.Unit 4GenBank Sequence Database: Introduction to structure, Primary and secondarydatabase, Format vs Content: Computer vs. Human, Databases, Genbank Flatfile, GCG.Unit 5Sequence Alignment And Database Search<strong>in</strong>g : Introduction , EvolutionaryBasis of Sequence Alignment, Optimal alignment method , Substitution Scoreand Gap Penalty , Statistical Significance of Alignment, Database similaritysearch<strong>in</strong>g , FASTA , BLAST , Database search<strong>in</strong>g Artifacts , Position SpecificScor<strong>in</strong>g Matrices.Unit 6Multiple Sequence Alignment: What is MSA, Structural or EvolutionaryAlignment, how to align Sequences, Tools.Unit 7Phylogenetic Analysis: Fundamental of Phylogenetic model, Tree <strong>in</strong>terpretation –Paralogues and orthologues, Tree build<strong>in</strong>g and tree evaluation, Phylogeneticsoftware.Unit 8Predictive Method us<strong>in</strong>g Nucleotide Sequence: Introduction, Mark<strong>in</strong>g repetitiveDNA, Database search, Codon bias detection, detect<strong>in</strong>g functional site <strong>in</strong> DNA.Unit 9Predictive Method us<strong>in</strong>g Prote<strong>in</strong> Sequence : Prote<strong>in</strong> identification based oncomposition , Physical properties based on sequence , Motif and pattern ,
Secondary structure and fold<strong>in</strong>g classes, specialized structure or features ,Tertiary structures.Unit 10Structure Database : Introduction to Structure , PDB , MMDB , Structure fileformat , visualiz<strong>in</strong>g structure <strong>in</strong>formation , Structure viewers , structure similaritysearch<strong>in</strong>g , Advanced structure model<strong>in</strong>g.Unit 11Comparative Genome Analysis: Introduction, application, genome analysis andannotation.Practicals:1. Understand<strong>in</strong>g L<strong>in</strong>ux Operat<strong>in</strong>g System and Commands.2. Introduction to NCBI.3. Us<strong>in</strong>g Entrez to search Literature Databases.4. Retriev<strong>in</strong>g DNA sequence from GenBank and analyz<strong>in</strong>g various formats of thedata stored.5. Retriev<strong>in</strong>g Prote<strong>in</strong> sequence from GenPept (NCBI) and Expasy.6. Analyz<strong>in</strong>g Prote<strong>in</strong> Sequences.7. Analyz<strong>in</strong>g DNA sequence.8. Sequence alignment us<strong>in</strong>g BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool).9. Sequence alignment us<strong>in</strong>g FASTA.10. Multiple sequence alignment us<strong>in</strong>g ClustalW.11. Introduction to the structure database PDB.12. Visualization of the prote<strong>in</strong> structure us<strong>in</strong>g VMD.13. Secondary structure prediction us<strong>in</strong>g GOR algorithm.BCBT- 407 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING 3(3-0-0)Mix<strong>in</strong>g : Types of agitator, flow pattern and power consumptionSteady state conduction: Fourier’s laws, concept of resistance to heat transfer, critical<strong>in</strong>sulation thickness, conduction with heat generation.Convection : Film theory and concept of heat transfer coefficient. Heat transfer <strong>in</strong>Lam<strong>in</strong>ar and turbulent flows.Heat exchanger: Siz<strong>in</strong>g of shell and tube heat exchanger. Heat transfer <strong>in</strong> agitatedvessel.
Boil<strong>in</strong>g and condensation: Heat transfer to boil<strong>in</strong>g liquids and from condens<strong>in</strong>g vapors.Fundamentals of mass transfer: <strong>Molecular</strong> diffusion <strong>in</strong> fluids and solids, concept ofmass transfer coefficient. Equilibrium stage, Multistage and cont<strong>in</strong>uous contractors withapplication to gas absorption, calculation of NTU, HTU and no. of stages. Psychrometricchart and its application.LNG-304 Professional Communication and <strong>Tech</strong>nical Writ<strong>in</strong>g 3(3-0-0)Language:1. Concerned (Subject, Verb Agreement)2. Antectents (Noun, Pronoun Agreement)3. Modifiers (Adjectives, Adverbs, Participle)4. Prepositions (Usage)5. Inflection (Noun, Verb)6. Determ<strong>in</strong>ers (General, Specific)7. Word enrichment (Antonyms, Synonyms, Homonyms, Acronyms,Orthography)8. VoiceCommunications:1. K<strong>in</strong>ds2. Different Speeches (Welcome Speech, Voice of thanks)<strong>Tech</strong>nical Writ<strong>in</strong>g:1. Importance2. Objectives3. Audience4. Methods5. Essentials (Documentation, Visuals, Sentences, Punctuation)6. Process7. Curriculum Vitae8. Interview9. Letter (Components, Format, 5 K<strong>in</strong>ds)10. Memos (Adm<strong>in</strong>istrative, Bus<strong>in</strong>ess)11. Report (Format, Style, Periodical and Miscellaneous Reports)Speech:1. Stress2. Intonation3. Accent4. Rhythm
BCBT- 405 BASIC IMMUNOLOGY 3(2-0-1)Unit I: Basic term<strong>in</strong>ology: Infection, pathogen, antigen, antibody, bacterial andviral antigens, haptens, adjuvants, immunogens <strong>in</strong>terferons, epitopes, paratopes,lymphok<strong>in</strong>esSpecific and non-specific immune response: cellular basis of immunity,humoral and cell mediated immunity, biochemistry of immunoglobul<strong>in</strong>s (structure,types, property and function),cells of immune system: cells <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> adaptive immune response i.e. B andT cells, cells <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>nate immune response- macrophages, dendritic cells,phagoytes, mast cells granulocytes, etc.Unit II: Organs of immune system: primary lymphoid and secondary lymphoidoragans, their structure and function. Major Histo Compatibility complex (MHCclass I and class II), their structure and function. Chemistry of antigen-antibody<strong>in</strong>teractions, precipitation and agglut<strong>in</strong>ation.Unit III: Structure of T-cell receptors and their comparison with analogousantibody molecule. Natural Killer cell, Their structure and function. Superantigensand Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).Unit IV: Immunodeficiency diseases: Primary B and T cell deficiency diseases,Autoimmunity, Hypersensitivity. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of RIA, ELISA andimmunoelectrophoresis (Rocket immunoelectrophoresis), use of monoclonalantibodies <strong>in</strong> immunodiagnosis and immunotherapy.Practical:1. To prepare blood smear.2. Separation of serum and plasma from blood.3. Qualitative tests of important constituents of plasma and serum.4. Separation of plasma prote<strong>in</strong>s (i.e. Fibr<strong>in</strong>ogen, globul<strong>in</strong>, and album<strong>in</strong>).5. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of E.S.R. of any blood sample.6. Preparation of antigen from blood.7. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the blood group.8. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of the haematocrit value of the blood sample.9. Use of widal kit for rapid quantitative slide test.10. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of density of blood.11. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of bleed<strong>in</strong>g and clott<strong>in</strong>g time of blood.12. Preparation of haemat<strong>in</strong> crystals
MCE 403 INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL 3 (3-0-0)BIOTECHNOLOGYUnit 1. Introduction to environmental biotechnology: Importance of biotechnology <strong>in</strong>environmental protection. Biodiversity, ecosystem and population diversity. Environmentalhazards.Unit 2. Biomass utilization: Bioremediation, bioleach<strong>in</strong>g, biodegradation, biostimulation,bioaccumulation, bioaugmentation, biomagnification.Unit 3. Biotechnological methods of pollution detection: Bioassay, biosensors andbiological <strong>in</strong>dicators. Sewage and soil waste management.Unit 4. Global environment issues: Ozone depletion, green house effect, acid ra<strong>in</strong>, sea levelrise, global warm<strong>in</strong>g.MBFT 452 MICROBIAL METABOLISM 2(2-0-0)Bacterial Enzymes: Classification, Properties, Factors affect<strong>in</strong>g enzyme activity,Inhibition of enzyme action, Regulation of enzymes.Carbohydrate metabolism: Anabolism- Photosynthesis (oxygenic andanoxygenic). Catabolism- EMP pathway, Pentose pathway, Kreb’s cycle,Fermentation Electron transport system, ATP productionMetabolism of prote<strong>in</strong>s: Metabolic pathways of nitrogen utilization, Urea cycle,Prote<strong>in</strong> synthesis.Catabolism of lipids.MBFT 451 PRINCIPLES OF MICROBIAL GENETICS 3(2-0-1)History-Experiments of Hershey Chase and Griffith; DNA as geneticmaterial; Discovery of DNA structure, RNA as genetic material, Genetic code.Organization and function of genetic material-Bacterial and ViralBrief account of plasmids-Structure and types.Replication of DNA- Roll<strong>in</strong>g circle model; Replication of RNA- Reversetranscriptase.Concept of genes-Lac operon, Tryptophan operon; Attenuation control-Promoters- Repressors- Gene Expression and control.Gene transfer mechanisms- Conjugation, Transformation, Transduction.Mutagenesis-Mutation, Mutants, IS elements, Transposons, Repairmechanisms
PracticalIsolation of antibiotic resistant stra<strong>in</strong>s; Replica plate technique for isolationof mutantsIsolation and purification of chromosomal and plasmid DNA and RNAChemical mutation, Non-ioniz<strong>in</strong>g radiation UVR, its effects on morphologyand Biochemical analysisJSBB-400 TRAINING I EVALUATION 1(0-0-1)6 th SemesterBAM-502 MARKETING & MANAGEMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGYPRODUCTS 3(3-0-0)Concept of Market<strong>in</strong>gCustomer Satisfaction and Buyer Behavior.Market<strong>in</strong>g MixAnalyz<strong>in</strong>g Consumer Markets of Biotechnological products.Pric<strong>in</strong>g-strategies and methods of pric<strong>in</strong>g of Biotechnological productsIdentify<strong>in</strong>g Markets Segments and Select<strong>in</strong>g Target Markets for Biotechnologicalproducts.Position<strong>in</strong>g the Market Offer<strong>in</strong>g Through the Product Life Cycle
Distribution ChannelPromotion of Biotechnological Products.TE- 503 Concepts of In vitro Culture 3 (2-0-1)UNIT 1: Introduction to Plant Tissue Culture: Historic view, organizationof tissue culture laboratory, aspectic techniques, media formulation, clonalpropagation vs tissue culture, totipotency.Unit 2: Animal Tissue Culture: Basic techniques, media formulation foranimal cell, <strong>in</strong>itiation of cell culture, evolution & ma<strong>in</strong>tenance of cell l<strong>in</strong>es,suspension culture & immobilized culture.UNIT 3: Types of <strong>in</strong> vitro cultures: Axillary bud proliferation,Organogenesis, Embryogenesis, organ culture, anther culture, suspensionculture.UNIT 4: Applications of tissue culture techniques: Somaclonal andgametoclonal variation, protoplast fusion and somatic hybridization,haploid and monopliod production, cybridizaiton, preservation of geneticresources, cryporeseration.Practicals:• Media preparation for animal & plant tissue culture• Sterilization techniques of different explants• Callus <strong>in</strong>duction• Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of Growth Curve <strong>in</strong> Suspension Culture• Development of cell l<strong>in</strong>es from chicken embryoMCE 404 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 (2-0-1)Unit 1. Introduction to animal biotechnology: Def<strong>in</strong>ition, history, importance andscope ofanimal biotechnology. Applications of animal biotechnology.Unit 2. Gene manipulation of animals: Animal viral genome, animal clon<strong>in</strong>g vectors.Genetransfer methods <strong>in</strong> eukaryotic systems - retroviral vector method, DNA micro<strong>in</strong>jectionmethod,eng<strong>in</strong>eered embryonic stem cell method. Selection of clones by us<strong>in</strong>g different methods.Unit 3. Transgenic animals: Production of transgenic mice, rabbits, fish, sheep, goat,cattle, pig,etc.
Unit 4. Application of animal biotechnology: Transgenic animals as bioreactorsrecomb<strong>in</strong>antprote<strong>in</strong>s produced by animal bioreactors. Transgenic animals as models of humandiseases.Xenotransplantation. Embryo transfer technologies <strong>in</strong> cattle and its application.PracticalsHandl<strong>in</strong>g of laboratory animals - mice, rabbits etc.Isolation and purification of DNA from blood samplesIsolation and enumeration of bacterial population from meat samplesDevelopment of Cell L<strong>in</strong>es from Egg EmbryoScreen<strong>in</strong>g of UV mutation <strong>in</strong> E. coliMCE 501 BlOSAFETY, BIOETHICS AND INTELECTUAL PROPERTYRIGHTS IN BIOTECHNOLOGY 3 (3-0-0)Unit 1. The legal and socioeconomic impact of biotechnology, public <strong>edu</strong>cation ofthe process of biotechnology <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> generat<strong>in</strong>g new forms of life for <strong>in</strong>formeddecision mak<strong>in</strong>g,biosafety regulation and national and <strong>in</strong>ternational guidel<strong>in</strong>es, r-DNA guidel<strong>in</strong>es,experimental protocol approvals, levels of conta<strong>in</strong>ment, regulatory bodies <strong>in</strong>biotechnology, biosafety committee.Unit 2. Ethical issues, moral values on experimental animals, ethical implications ofbiotechnological products and techniques.Unit 3. Intellectual property rights, WTO, TRIPS, International conventions, patentsand copy rights, patent claims, methods of applications of patents.Unit 4. Legal implications, biodiversity and farmers right. Beneficial application anddevelopment of research focus to the need of the poor, identification of directions foryield effect <strong>in</strong> agriculture, aquaculture etc.MCE 502 RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY 3 (3-0-0)Unit 1. Biology of clon<strong>in</strong>g vectors: Plasmids, lambda bacteriophage, cosmids,M13 bacteriophage, phagemid, Agrobacterium tumifaciens- b<strong>in</strong>ary and co<strong>in</strong>tegrationvector strategy.Unit 2. Enzymes used <strong>in</strong> genetic eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g: Exonucleases, endonucleases - S1nuclease, restriction endonucleases; ligases, polymerases, reverse transcriptase,term<strong>in</strong>al deoxy nucleotidyl transferases, k<strong>in</strong>ases, alkal<strong>in</strong>e phosphatase.Unit 3. Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of recomb<strong>in</strong>ant DNA technology: Construction of recomb<strong>in</strong>antDNA, rDNA expression, genomic and complimentary DNA (cDNA) libraries,detect<strong>in</strong>g expression
of foreign genes.Unit 4. Application of r-DNA technology: Medic<strong>in</strong>e, <strong>in</strong>dustry, agriculture, live stockimprovement, environmental protection, etc.JSBB-488 SEMINAR 1(0-0-2JSBB 500 TRAINING II I (0-0-2)
7 th SemesterMCE 601 MOLECULAR BREEDING 3 (2-0-2)Unit 1. Introduction to markers: Different k<strong>in</strong>ds of markers- morphological,biochemical and molecular markers.Unit 2. <strong>Molecular</strong> marker systems: PCR based approaches - RAPD, SSR, AFLP,AP-PCR; targeted PCR, STS, SCAR; and non-PCR based approach (RFLP).Unit 3. Marker assisted selection (MAS): Development of markers, generation ofmapp<strong>in</strong>g population, bulk segregate analysis, use of NILS for tagg<strong>in</strong>g genes,selection of QTLS for MAS.Unit 4. <strong>Molecular</strong> markers <strong>in</strong> plant breed<strong>in</strong>g: Uses of molecular markersresistancebreed<strong>in</strong>g, gene <strong>in</strong>terogression, gene pyramid<strong>in</strong>g, antibiotic resistance,improvement of qualitative characters, fertility restorer genes and hybrid vigour.PracticalsExtraction of prote<strong>in</strong>s from plant tissuesProte<strong>in</strong> profil<strong>in</strong>g of crop plants by Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresisStudy of Labwares used <strong>in</strong> PCR analysisPCR amplification of DNA samplesElectrophoretic separation of PCR productsSta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g, visualization and scor<strong>in</strong>g of PCR productsMCE 602 GENOMICS 3 (3 - 0- 0)Unit 1. Introduction: Basic concepts of genomics. Structural and functionalgenomics. Proteomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics and phenomics.Unit 2. Genome: Physico-chemical properties of genome, genome size andsequence components, gene structure and higher order genome organization.Unit 3. Genome analysis: DNA sequenc<strong>in</strong>g, DNA Micro array, gene f<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g,genome databases and data m<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g. Structural, functional and comparativegenomics.Unit 4. Genome mapp<strong>in</strong>g: Basic concepts, model organisms, genome projects,genetic and l<strong>in</strong>kage map, cytogenetic maps, physical maps, comparative genomemapp<strong>in</strong>g.MCE 603 GENETICALLY MODIFIED FOODS 3 (3-0-0)
Unit 1. Introduction to GM foods: History and development of GM food / crops.Currently exist<strong>in</strong>g GM foods/ crops.Unit 2. Cultivation of GM crops: Grow<strong>in</strong>g of GM food crops. Countries cultivat<strong>in</strong>gGM food crops.Unit 3. Debate on GM foods around the world. Criticisms aga<strong>in</strong>st GM foods.Biosafety concerns and regulators of GM foods. GM food criteria <strong>in</strong> India. GM foodlabell<strong>in</strong>g and GM labell<strong>in</strong>g. Consumer acceptance and market forces.Unit 4. Economical and political effects of GM foods. Future developments.MCE 604 GENE CLONING AND GENE THARAPY 3 (2-0-2)Unit: 1 Gene clon<strong>in</strong>g: Introduction to gene clon<strong>in</strong>g, basic events of gene clon<strong>in</strong>g,selection stratergies for a clone of a specific gene.Unit: 2 Expression of cloned gene: Expression of cloned genes <strong>in</strong> cultured cells,production of prote<strong>in</strong>s from cloned genes, production of recomb<strong>in</strong>antpharmaceuticals - <strong>in</strong>sul<strong>in</strong>, human growth hormone, hepatitis B virus vacc<strong>in</strong>e, tissueplasm<strong>in</strong>ogen activator (tPA).Unit: 3 Gene therapy: Introduction and approaches to gene therapy. Types of genetherapy – germl<strong>in</strong>e gene therapy, somatic cell gene therapy, augmentation therapy,ex vivo gene therapy, <strong>in</strong> vivo gene therapy. Viral gene delivery systems – retrovirusand adenovirus vector systems.Unit: 4 Applications of gene therapy: Correction of gene defects and disorders,Cystic fibrosis, Human adenos<strong>in</strong>e deam<strong>in</strong>ase deficiency, Duchenne musculardystrophy. Ethical issues raised by gene therapy.PracticalsPreparation of Buffers for Genomic and Plasmid DNA IsolationIsolation of Bacterial Genomic DNAEstimation of DNA by Diphenylam<strong>in</strong>e MethodRestriction Digestion of λ DNA with Eco R1 Restriction EnzymeLigation of λ Eco R1 Digest us<strong>in</strong>g T4 DNA LigaseCBBI-601 Structural Bio<strong>in</strong>formatics 2 (1-0-1)Unit 1
Introduction: Def<strong>in</strong>ition of Bio<strong>Molecular</strong> model<strong>in</strong>g, Prote<strong>in</strong> Structure – Primary,Secondary and tertiary, Structure of RNA, Nucleotide, am<strong>in</strong>o acids.Unit 2Biological Databases: Types of databases and their <strong>in</strong>troduction. Primary,Secondary, Structure, Ligand Databases.Unit 3Prote<strong>in</strong> Structure determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g methods: X-Ray, NMR, RNA Structure Prediction.Unit 4In silico methods of prote<strong>in</strong> structure prediction: Thread<strong>in</strong>g, Ab-<strong>in</strong>itio, homologyModel<strong>in</strong>g.Unit 5Evaluation of modeled prote<strong>in</strong> structure: Ramachandran plot, What Check,ProCheck, Verify 3-D.Unit 6Model<strong>in</strong>g Prote<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>teraction: Prote<strong>in</strong> – Prote<strong>in</strong> Interaction, Prote<strong>in</strong> – LigandInteraction, Software.Unit 7Application of Bio<strong>Molecular</strong> model<strong>in</strong>g.Practicals:1. Introduction to the structure database PDB.2. Visualization of the prote<strong>in</strong> structure us<strong>in</strong>g VMD.3. Secondary structure prediction us<strong>in</strong>g GOR algorithm.4. Tertiary structure prediction us<strong>in</strong>g SWISS-MODEL, ModWeb and Geno3D.5. Us<strong>in</strong>g Modeller for homology model<strong>in</strong>g.6. Prote<strong>in</strong> Structure validation us<strong>in</strong>g SAVS server.7. Prote<strong>in</strong> active site prediction us<strong>in</strong>g CastP and Pocket F<strong>in</strong>der.8. Chemical file format conversion us<strong>in</strong>g Open Babel.9. Automated dock<strong>in</strong>g us<strong>in</strong>g PATCH DOCK webserver.10. Structural alignment us<strong>in</strong>g DaliLite and SSAP.JSBB-589 SEMINAR 1(0-0-1)JSBB-500 TRAINING II EVALUATION 1(0-0-1)
B. <strong>Tech</strong>. <strong>Biotechnology</strong> (MCE/IM/BPT)- 8 th SemesterJSBB PROJECT (MCE/IM/BPT) 9(0-0-18)