Sponsoren und Aussteller - Life Science Nord
Sponsoren und Aussteller - Life Science Nord
Sponsoren und Aussteller - Life Science Nord
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
tests, determining the joint’s workspace and movement tracking were performed using an AURORA<br />
electromagnetic localization system; a 6 DoF localization probe was fixed on the tip of the joint. Data<br />
analysis has been elaborated in MATLAB.<br />
R e s u l t s<br />
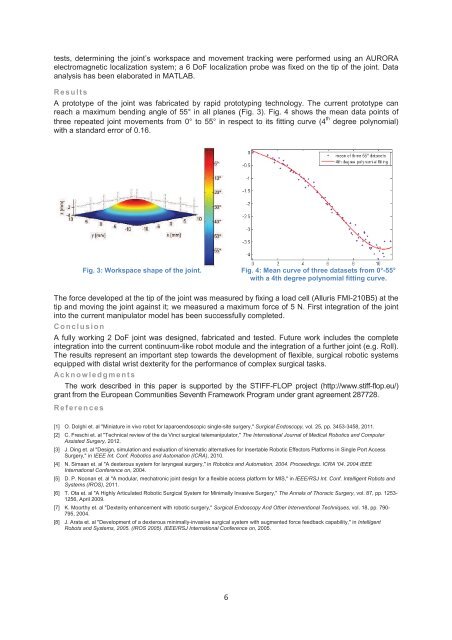
A prototype of the joint was fabricated by rapid prototyping technology. The current prototype can<br />
reach a maximum bending angle of 55° in all planes (Fig. 3). Fig. 4 shows the mean data points of<br />
three repeated joint movements from 0° to 55° in respect to its fitting curve (4 th degree polynomial)<br />
with a standard error of 0.16.<br />
Fig. 3: Workspace shape of the joint. Fig. 4: Mean curve of three datasets from 0°-55°<br />
with a 4th degree polynomial fitting curve.<br />
The force developed at the tip of the joint was measured by fixing a load cell (Alluris FMI-210B5) at the<br />
tip and moving the joint against it; we measured a maximum force of 5 N. First integration of the joint<br />
into the current manipulator model has been successfully completed.<br />
C o n c l u s i o n<br />
A fully working 2 DoF joint was designed, fabricated and tested. Future work includes the complete<br />
integration into the current continuum-like robot module and the integration of a further joint (e.g. Roll).<br />
The results represent an important step towards the development of flexible, surgical robotic systems<br />
equipped with distal wrist dexterity for the performance of complex surgical tasks.<br />
Ac k n o w l e d g m e n t s<br />
The work described in this paper is supported by the STIFF-FLOP project (http://www.stiff-flop.eu/)<br />
grant from the European Communities Seventh Framework Program <strong>und</strong>er grant agreement 287728.<br />
R e f e r e n c e s<br />
[1] O. Dolghi et. al "Miniature in vivo robot for laparoendoscopic single-site surgery," Surgical Endoscopy, vol. 25, pp. 3453-3458, 2011.<br />
[2] C. Freschi et. al "Technical review of the da Vinci surgical telemanipulator," The International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer<br />
Assisted Surgery, 2012.<br />
[3] J. Ding et. al "Design, simulation and evaluation of kinematic alternatives for Insertable Robotic Effectors Platforms in Single Port Access<br />
Surgery," in IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2010.<br />
[4] N. Simaan et. al "A dexterous system for laryngeal surgery," in Robotics and Automation, 2004. Proceedings. ICRA '04. 2004 IEEE<br />
International Conference on, 2004.<br />
[5] D. P. Noonan et. al "A modular, mechatronic joint design for a flexible access platform for MIS," in IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and<br />
Systems (IROS), 2011.<br />
[6] T. Ota et. al "A Highly Articulated Robotic Surgical System for Minimally Invasive Surgery," The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, vol. 87, pp. 1253-<br />
1256, April 2009.<br />
[7] K. Moorthy et. al "Dexterity enhancement with robotic surgery," Surgical Endoscopy And Other Interventional Techniques, vol. 18, pp. 790-<br />
795, 2004.<br />
[8] J. Arata et. al "Development of a dexterous minimally-invasive surgical system with augmented force feedback capability," in Intelligent<br />
Robots and Systems, 2005. (IROS 2005). IEEE/RSJ International Conference on, 2005.