ROOM ACOUSTIC PREDICTION MODELLING - Odeon
ROOM ACOUSTIC PREDICTION MODELLING - Odeon
ROOM ACOUSTIC PREDICTION MODELLING - Odeon
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
dimensions of the reflecting surface (Christensen & Rindel, 2005). Both can be described by a frequency<br />
dependent scattering coefficient, ss and sd.<br />
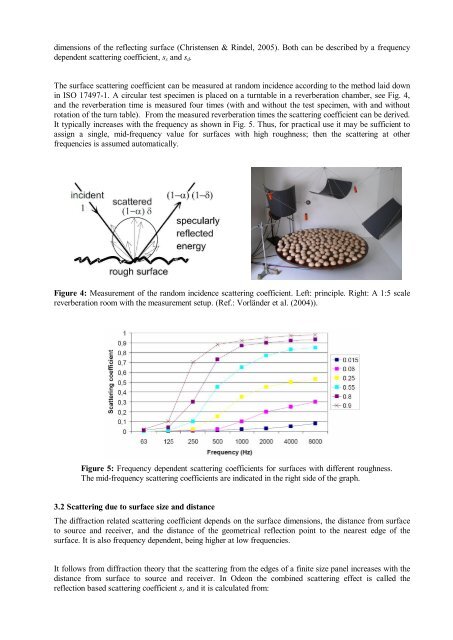
The surface scattering coefficient can be measured at random incidence according to the method laid down<br />
in ISO 17497-1. A circular test specimen is placed on a turntable in a reverberation chamber, see Fig. 4,<br />
and the reverberation time is measured four times (with and without the test specimen, with and without<br />
rotation of the turn table). From the measured reverberation times the scattering coefficient can be derived.<br />
It typically increases with the frequency as shown in Fig. 5. Thus, for practical use it may be sufficient to<br />
assign a single, mid-frequency value for surfaces with high roughness; then the scattering at other<br />
frequencies is assumed automatically.<br />
Figure 4: Measurement of the random incidence scattering coefficient. Left: principle. Right: A 1:5 scale<br />
reverberation room with the measurement setup. (Ref.: Vorländer et al. (2004)).<br />
Figure 5: Frequency dependent scattering coefficients for surfaces with different roughness.<br />
The mid-frequency scattering coefficients are indicated in the right side of the graph.<br />
3.2 Scattering due to surface size and distance<br />
The diffraction related scattering coefficient depends on the surface dimensions, the distance from surface<br />
to source and receiver, and the distance of the geometrical reflection point to the nearest edge of the<br />
surface. It is also frequency dependent, being higher at low frequencies.<br />
It follows from diffraction theory that the scattering from the edges of a finite size panel increases with the<br />
distance from surface to source and receiver. In <strong>Odeon</strong> the combined scattering effect is called the<br />
reflection based scattering coefficient sr and it is calculated from: