Research Report - Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Zentrum für Molekulare Medizin
Research Report - Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Zentrum für Molekulare Medizin
Research Report - Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Zentrum für Molekulare Medizin
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The mechanism of this transdifferentiation process remains to be elucidated. We<br />
have preliminary evidence that after opening of the chondrocyte lacunae by<br />
osteoclasts hypertrophic chondrocytes de-differentiate to bone marrow stem cells<br />
which may then differentiate into osteoblasts precursor cells and other<br />
mesenchymal cells. Studies to confirm this hypothesis are under investigation.<br />
Fig.3 Fig. 4<br />
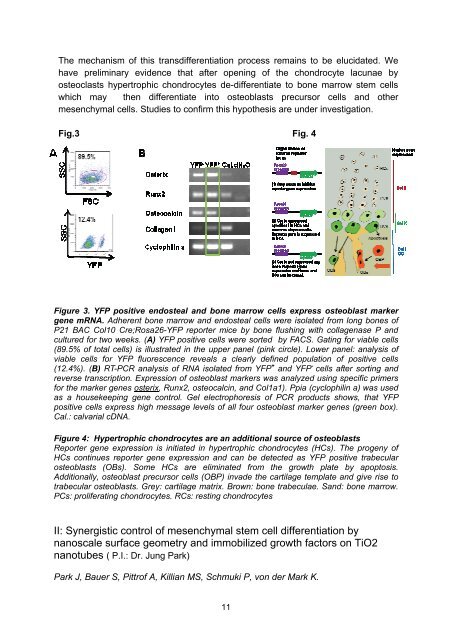
Figure 3. YFP positive endosteal and bone marrow cells express osteoblast marker<br />
gene mRNA. Adherent bone marrow and endosteal cells were isolated from long bones of<br />
P21 BAC Col10 Cre;Rosa26-YFP reporter mice by bone flushing with collagenase P and<br />
cultured for two weeks. (A) YFP positive cells were sorted by FACS. Gating for viable cells<br />
(89.5% of total cells) is illustrated in the upper panel (pink circle). Lower panel: analysis of<br />
viable cells for YFP fluorescence reveals a clearly defined population of positive cells<br />
(12.4%). (B) RT-PCR analysis of RNA isolated from YFP + and YFP - cells after sorting and<br />
reverse transcription. Expression of osteoblast markers was analyzed using specific primers<br />
for the marker genes osterix, Runx2, osteocalcin, and Col1a1). Ppia (cyclophilin a) was used<br />
as a housekeeping gene control. Gel electrophoresis of PCR products shows, that YFP<br />
positive cells express high message levels of all four osteoblast marker genes (green box).<br />
Cal.: calvarial cDNA.<br />
Figure 4: Hypertrophic chondrocytes are an additional source of osteoblasts<br />
<strong>Report</strong>er gene expression is initiated in hypertrophic chondrocytes (HCs). The progeny of<br />
HCs continues reporter gene expression and can be detected as YFP positive trabecular<br />
osteoblasts (OBs). Some HCs are eliminated from the growth plate by apoptosis.<br />
Additionally, osteoblast precursor cells (OBP) invade the cartilage template and give rise to<br />
trabecular osteoblasts. Grey: cartilage matrix. Brown: bone trabeculae. Sand: bone marrow.<br />
PCs: proliferating chondrocytes. RCs: resting chondrocytes<br />
II: Synergistic control of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by<br />
nanoscale surface geometry and immobilized growth factors on TiO2<br />
nanotubes ( P.I.: Dr. Jung Park)<br />
Park J, Bauer S, Pittrof A, Killian MS, Schmuki P, von der Mark K.<br />
11