Intervertebral Disk Replacement - Keivan Anbarani's Electronic ...
Intervertebral Disk Replacement - Keivan Anbarani's Electronic ...
Intervertebral Disk Replacement - Keivan Anbarani's Electronic ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
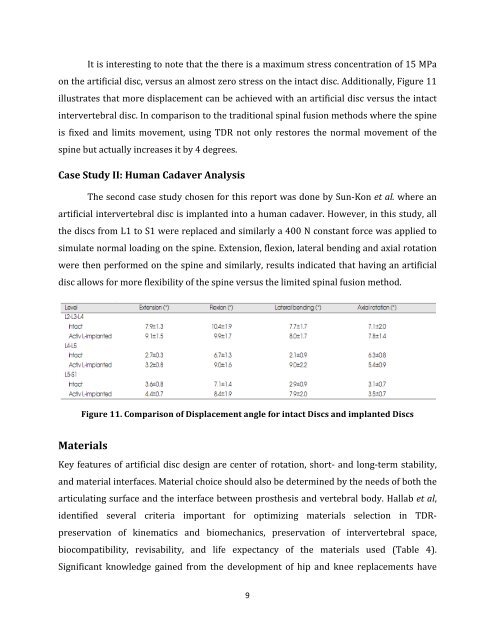
It is interesting to note that the there is a maximum stress concentration of 15 MPa<br />
on the artificial disc, versus an almost zero stress on the intact disc. Additionally, Figure 11<br />
illustrates that more displacement can be achieved with an artificial disc versus the intact<br />
intervertebral disc. In comparison to the traditional spinal fusion methods where the spine<br />
is fixed and limits movement, using TDR not only restores the normal movement of the<br />
spine but actually increases it by 4 degrees.<br />
Case Study II: Human Cadaver Analysis<br />
The second case study chosen for this report was done by Sun-‐Kon et al. where an<br />
artificial intervertebral disc is implanted into a human cadaver. However, in this study, all<br />
the discs from L1 to S1 were replaced and similarly a 400 N constant force was applied to<br />
simulate normal loading on the spine. Extension, flexion, lateral bending and axial rotation<br />
were then performed on the spine and similarly, results indicated that having an artificial<br />
disc allows for more flexibility of the spine versus the limited spinal fusion method.<br />
Figure 11. Comparison of Displacement angle for intact Discs and implanted Discs<br />
Materials<br />
Key features of artificial disc design are center of rotation, short-‐ and long-‐term stability,<br />
and material interfaces. Material choice should also be determined by the needs of both the<br />
articulating surface and the interface between prosthesis and vertebral body. Hallab et al,<br />
identified several criteria important for optimizing materials selection in TDR-‐<br />
preservation of kinematics and biomechanics, preservation of intervertebral space,<br />
biocompatibility, revisability, and life expectancy of the materials used (Table 4).<br />
Significant knowledge gained from the development of hip and knee replacements have<br />
9