Film Extrusion Guide.pmd - LyondellBasell
Film Extrusion Guide.pmd - LyondellBasell
Film Extrusion Guide.pmd - LyondellBasell
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
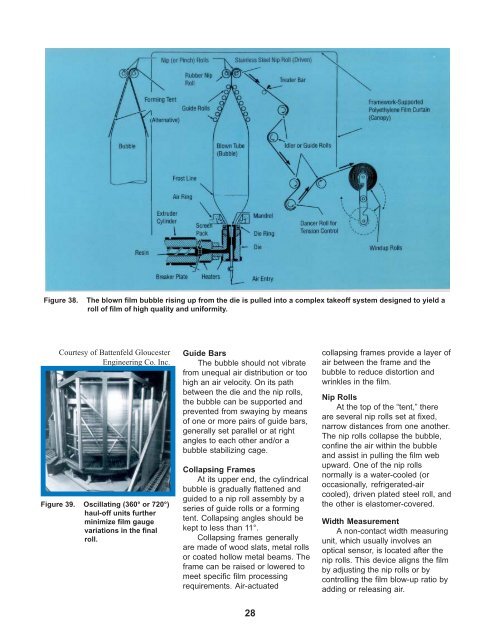
Figure 38. The blown film bubble rising up from the die is pulled into a complex takeoff system designed to yield a<br />
roll of film of high quality and uniformity.<br />
Courtesy of Battenfeld Gloucester<br />
Engineering Co. Inc.<br />
Figure 39. Oscillating (360° or 720°)<br />
haul-off units further<br />
minimize film gauge<br />
variations in the final<br />
roll.<br />
<strong>Guide</strong> Bars<br />
The bubble should not vibrate<br />
from unequal air distribution or too<br />
high an air velocity. On its path<br />
between the die and the nip rolls,<br />
the bubble can be supported and<br />
prevented from swaying by means<br />
of one or more pairs of guide bars,<br />
generally set parallel or at right<br />
angles to each other and/or a<br />
bubble stabilizing cage.<br />
Collapsing Frames<br />
At its upper end, the cylindrical<br />
bubble is gradually flattened and<br />
guided to a nip roll assembly by a<br />
series of guide rolls or a forming<br />
tent. Collapsing angles should be<br />
kept to less than 11°.<br />
Collapsing frames generally<br />
are made of wood slats, metal rolls<br />
or coated hollow metal beams. The<br />
frame can be raised or lowered to<br />
meet specific film processing<br />
requirements. Air-actuated<br />
28<br />
collapsing frames provide a layer of<br />
air between the frame and the<br />
bubble to reduce distortion and<br />
wrinkles in the film.<br />
Nip Rolls<br />
At the top of the “tent,” there<br />
are several nip rolls set at fixed,<br />
narrow distances from one another.<br />
The nip rolls collapse the bubble,<br />
confine the air within the bubble<br />
and assist in pulling the film web<br />
upward. One of the nip rolls<br />
normally is a water-cooled (or<br />
occasionally, refrigerated-air<br />
cooled), driven plated steel roll, and<br />
the other is elastomer-covered.<br />
Width Measurement<br />
A non-contact width measuring<br />
unit, which usually involves an<br />
optical sensor, is located after the<br />
nip rolls. This device aligns the film<br />
by adjusting the nip rolls or by<br />
controlling the film blow-up ratio by<br />
adding or releasing air.