EARTHQUAKE SAFETY EVALUATION OF ATATURK DAM
EARTHQUAKE SAFETY EVALUATION OF ATATURK DAM
EARTHQUAKE SAFETY EVALUATION OF ATATURK DAM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
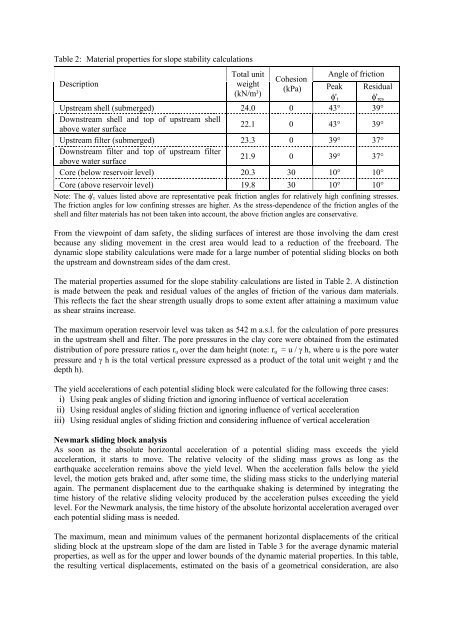
Table 2: Material properties for slope stability calculations<br />
Description<br />
Total unit<br />
weight<br />
(kN/m³)<br />
Cohesion<br />
(kPa)<br />
Angle of friction<br />
Peak Residual<br />
φ't φ'res<br />
Upstream shell (submerged) 24.0 0 43° 39°<br />
Downstream shell and top of upstream shell<br />
above water surface<br />
22.1 0 43° 39°<br />
Upstream filter (submerged) 23.3 0 39° 37°<br />
Downstream filter and top of upstream filter<br />
above water surface<br />
21.9 0 39° 37°<br />
Core (below reservoir level) 20.3 30 10° 10°<br />
Core (above reservoir level) 19.8 30 10° 10°<br />
Note: The φ't values listed above are representative peak friction angles for relatively high confining stresses.<br />
The friction angles for low confining stresses are higher. As the stress-dependence of the friction angles of the<br />
shell and filter materials has not been taken into account, the above friction angles are conservative.<br />
From the viewpoint of dam safety, the sliding surfaces of interest are those involving the dam crest<br />
because any sliding movement in the crest area would lead to a reduction of the freeboard. The<br />
dynamic slope stability calculations were made for a large number of potential sliding blocks on both<br />
the upstream and downstream sides of the dam crest.<br />
The material properties assumed for the slope stability calculations are listed in Table 2. A distinction<br />
is made between the peak and residual values of the angles of friction of the various dam materials.<br />
This reflects the fact the shear strength usually drops to some extent after attaining a maximum value<br />
as shear strains increase.<br />
The maximum operation reservoir level was taken as 542 m a.s.l. for the calculation of pore pressures<br />
in the upstream shell and filter. The pore pressures in the clay core were obtained from the estimated<br />
distribution of pore pressure ratios ru over the dam height (note: ru = u / γ h, where u is the pore water<br />
pressure and γ h is the total vertical pressure expressed as a product of the total unit weight γ and the<br />
depth h).<br />
The yield accelerations of each potential sliding block were calculated for the following three cases:<br />
i) Using peak angles of sliding friction and ignoring influence of vertical acceleration<br />
ii) Using residual angles of sliding friction and ignoring influence of vertical acceleration<br />
iii) Using residual angles of sliding friction and considering influence of vertical acceleration<br />
Newmark sliding block analysis<br />
As soon as the absolute horizontal acceleration of a potential sliding mass exceeds the yield<br />
acceleration, it starts to move. The relative velocity of the sliding mass grows as long as the<br />
earthquake acceleration remains above the yield level. When the acceleration falls below the yield<br />
level, the motion gets braked and, after some time, the sliding mass sticks to the underlying material<br />
again. The permanent displacement due to the earthquake shaking is determined by integrating the<br />
time history of the relative sliding velocity produced by the acceleration pulses exceeding the yield<br />
level. For the Newmark analysis, the time history of the absolute horizontal acceleration averaged over<br />
each potential sliding mass is needed.<br />
The maximum, mean and minimum values of the permanent horizontal displacements of the critical<br />
sliding block at the upstream slope of the dam are listed in Table 3 for the average dynamic material<br />
properties, as well as for the upper and lower bounds of the dynamic material properties. In this table,<br />
the resulting vertical displacements, estimated on the basis of a geometrical consideration, are also