Drug Disposition Overview - Pharmacology and at UCSD
Drug Disposition Overview - Pharmacology and at UCSD
Drug Disposition Overview - Pharmacology and at UCSD
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
BIOM/PHAR 255 Winter 2013 Halpert - Jan. 17, 2013<br />
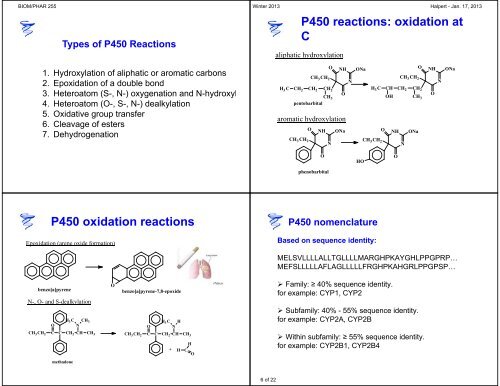
Types of P450 Reactions<br />
1. Hydroxyl<strong>at</strong>ion of aliph<strong>at</strong>ic or arom<strong>at</strong>ic carbons<br />
2. Epoxid<strong>at</strong>ion of a double bond<br />
3. Hetero<strong>at</strong>om (S-, N-) oxygen<strong>at</strong>ion <strong>and</strong> N-hydroxyl<br />
4. Hetero<strong>at</strong>om (O-, S-, N-) dealkyl<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
5. Oxid<strong>at</strong>ive group transfer<br />
6. Cleavage of esters<br />
7. Dehydrogen<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
P450 oxid<strong>at</strong>ion reactions<br />
Epoxid<strong>at</strong>ion (arene oxide form<strong>at</strong>ion)<br />
benzo[a]pyrene<br />
N-, O- <strong>and</strong> S-dealkyl<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
O<br />
H3 C CH3 N<br />
CH3CH2 C C CH2CH CH3 methadone<br />
O<br />
benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-epoxide<br />
H3C H<br />
O N<br />
CH3 CH2 C C CH2CH CH3 +<br />
H C<br />
H<br />
O<br />
6 of 22<br />
P450 reactions: oxid<strong>at</strong>ion <strong>at</strong><br />
C<br />
aliph<strong>at</strong>ic hydroxyl<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
H 3 C<br />
CH 3CH 2<br />
O<br />
CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 pentobarbital<br />
arom<strong>at</strong>ic hydroxyl<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
CH 3CH 2<br />
O<br />
phenobarbital<br />
N<br />
NH ONa<br />
O<br />
NH ONa<br />
O<br />
N<br />
HO<br />
H 3C<br />
CH 3 CH 2<br />
P450 nomencl<strong>at</strong>ure<br />
Based on sequence identity:<br />
O<br />
CH<br />
OH<br />
CH 3 CH 2<br />
CH 2<br />
N<br />
O<br />
CH2 CH3 NH ONa<br />
O<br />
NH ONa<br />
MELSVLLLLALLTGLLLLMARGHPKAYGHLPPGPRP…<br />
MEFSLLLLLAFLAGLLLLLFRGHPKAHGRLPPGPSP…<br />
Family: ≥ 40% sequence identity.<br />
for example: CYP1, CYP2<br />
Subfamily: 40% - 55% sequence identity.<br />
for example: CYP2A, CYP2B<br />
Within subfamily: ≥ 55% sequence identity.<br />
for example: CYP2B1, CYP2B4<br />
O<br />
N