30. Furan-Based Adhesives
30. Furan-Based Adhesives
30. Furan-Based Adhesives
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
IX. MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS OF FURAN RESINS<br />
Azimov et al. [65] compared the performances of furan resins with those of conventional<br />
phenol–formaldehyde adhesives. They used these binders to assemble aluminumto-aluminum<br />
and glass-to-glass structures and showed that furanic resins gave<br />
much higher rupture moduli in both systems studied. Rassokha and Avramenko [66]<br />
studied similar systems, but gave more information about the furan resin used. They<br />
used 5- and6-based adhesives both in the presence and absence of zeolite-based fillers,<br />
and assembled aluminum-to-aluminum and glass-to-glass structures. They showed that<br />
the use of polyethylene-co-vinylacetate as a filler dispersant gave well dispersed suspensions<br />
and consequently the best mechanical properties of the assembly. Nikolaev<br />
et al. [67] studied the thermal stability of furan resins produced by the reaction<br />
between a furfuryl ether of glycerol and 2,4-toluene diisocyanate. They showed clearly<br />
that the incorporation of this resin into conventional adhesives improved their thermal<br />
stability. The mechanical properties of steel-to-steel assemblies based on these compositions<br />
were found to follow the same tendency as that observed for the thermal<br />
properties.<br />
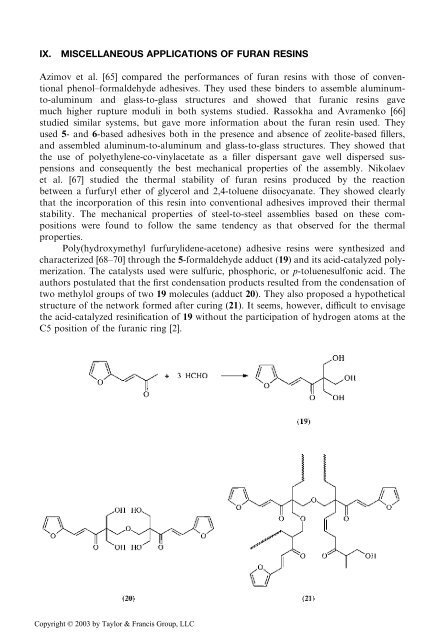
Poly(hydroxymethyl furfurylidene-acetone) adhesive resins were synthesized and<br />
characterized [68–70] through the 5-formaldehyde adduct (19) and its acid-catalyzed polymerization.<br />
The catalysts used were sulfuric, phosphoric, or p-toluenesulfonic acid. The<br />
authors postulated that the first condensation products resulted from the condensation of<br />
two methylol groups of two 19 molecules (adduct 20). They also proposed a hypothetical<br />
structure of the network formed after curing (21). It seems, however, difficult to envisage<br />
the acid-catalyzed resinification of 19 without the participation of hydrogen atoms at the<br />
C5 position of the furanic ring [2].<br />
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC