30. Furan-Based Adhesives
30. Furan-Based Adhesives
30. Furan-Based Adhesives
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
a few furanic monomers and resins are involved, namely: 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6, as well as liquid<br />
oligomers of 2 (poly2) and3 (poly3). The properties of these monomers together with<br />
the mechanisms of their resinification and the composition of poly2 and poly3 will<br />
be briefly dealt with before discussing their use in the manufacture of resins for binders<br />
and adhesives.<br />
II. PROPERTIES OF FURANIC MONOMERS<br />
The relevant properties of furanic compounds covered in this review are summarized in<br />
Table 1.<br />
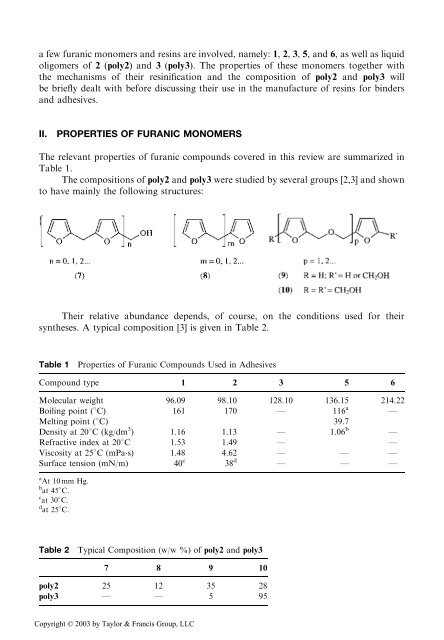
The compositions of poly2 and poly3 were studied by several groups [2,3] and shown<br />
to have mainly the following structures:<br />
Their relative abundance depends, of course, on the conditions used for their<br />
syntheses. A typical composition [3] is given in Table 2.<br />
Table 1 Properties of <strong>Furan</strong>ic Compounds Used in <strong>Adhesives</strong><br />
Compound type 1 2 3 5 6<br />
Molecular weight 96.09 98.10 128.10 136.15 214.22<br />
Boiling point ( C) 161 170 — 116 a<br />
—<br />
Melting point ( C) 39.7<br />
Density at 20 C (kg/dm 3 ) 1.16 1.13 — 1.06 b<br />
—<br />
Refractive index at 20 C 1.53 1.49 — —<br />
Viscosity at 25 C (mPa s) 1.48 4.62 — — —<br />
Surface tension (mN/m) 40 c<br />
38 d<br />
— — —<br />
a At 10 mm Hg.<br />
b at 45 C.<br />
c at 30 C.<br />
d at 25 C.<br />
Table 2 Typical Composition (w/w %) of poly2 and poly3<br />
7 8 9 10<br />
poly2 25 12 35 28<br />
poly3 — — 5 95<br />
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC