Single-Width Centrifugal Fan Performance Supplement - Greenheck
Single-Width Centrifugal Fan Performance Supplement - Greenheck
Single-Width Centrifugal Fan Performance Supplement - Greenheck
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5<br />
Engineering Data<br />
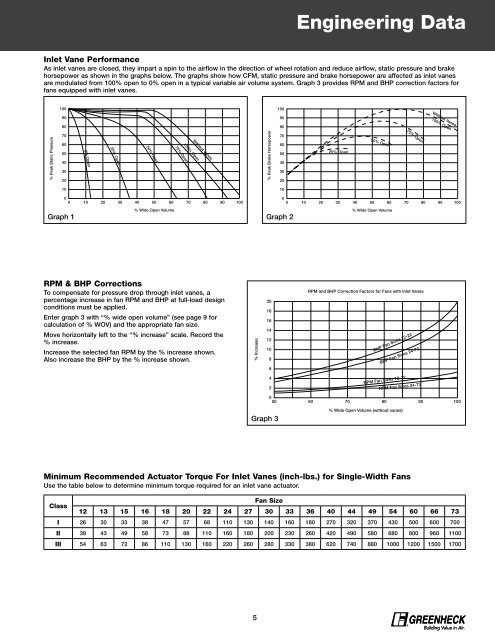
Inlet Vane <strong>Performance</strong><br />
As inlet vanes are closed, they impart a spin to the airflow in the direction of wheel rotation and reduce airflow, static pressure and brake<br />
horsepower as shown in the graphs below. The graphs show how CFM, static pressure and brake horsepower are affected as inlet vanes<br />
are modulated from 100% open to 0% open in a typical variable air volume system. Graph 3 provides RPM and BHP correction factors for<br />
fans equipped with inlet vanes.<br />
% Peak Static Pressure<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
0% Open<br />
25% Open<br />
50% Open<br />
% Wide Open Volume<br />
75% Open<br />
100% Open<br />
Without Vanes<br />
Graph 1 Graph 2<br />
RPM & BHP Corrections<br />
To compensate for pressure drop through inlet vanes, a<br />
percentage increase in fan RPM and BHP at full-load design<br />
conditions must be applied.<br />
Enter graph 3 with “% wide open volume” (see page 9 for<br />
calculation of % WOV) and the appropriate fan size.<br />
Move horizontally left to the “% increase” scale. Record the<br />
% increase.<br />
Increase the selected fan RPM by the % increase shown.<br />
Also increase the BHP by the % increase shown.<br />
% Increase<br />
% Peak Brake Horsepower<br />
Graph 3<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
25% Open<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
% Wide Open Volume<br />
50% Open<br />
75% Open<br />
RPM and BHP Correction Factors for <strong>Fan</strong>s with Inlet Vanes<br />
BHP <strong>Fan</strong> Sizes 12-22<br />
BHP <strong>Fan</strong> Sizes 24-73<br />
RPM <strong>Fan</strong> Sizes 12-22<br />
RPM <strong>Fan</strong> Sizes 24-73<br />
®<br />
Without Vanes<br />
100% Open<br />
20<br />
18<br />
16<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
% Wide Open Volume (without vanes)<br />
Minimum Recommended Actuator Torque For Inlet Vanes (inch-lbs.) for <strong>Single</strong>-<strong>Width</strong> <strong>Fan</strong>s<br />
Use the table below to determine minimum torque required for an inlet vane actuator.<br />
Class<br />
12 13 15 16 18 20 22 24<br />
<strong>Fan</strong> Size<br />
27 30 33 36 40 44 49 54 60 66 73<br />
I 26 30 33 38 47 57 68 110 130 140 160 180 270 320 370 430 500 600 700<br />
II 38 43 49 58 73 88 110 160 180 200 230 260 420 490 580 680 800 960 1100<br />
III 54 63 72 86 110 130 160 220 260 280 330 380 620 740 880 1000 1200 1500 1700