Ch 12 Answers
Ch 12 Answers
Ch 12 Answers
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Ch</strong>apter <strong>12</strong> continued<br />
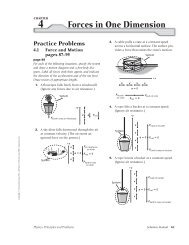
59. Water Heater A 3.010 2 -W electric<br />
immersion heater is used to heat a cup<br />
of water, as shown in Figure <strong>12</strong>-20. The<br />
cup is made of glass, and its mass is<br />
3.0010 2 g. It contains 250 g of water at<br />
15°C. How much time is needed to bring<br />
the water to the boiling point? Assume<br />
that the temperature of the cup is the<br />
same as the temperature of the water at<br />
all times and that no heat is lost to the air.<br />
Q m G C G T G m W C W T W<br />
but T G T W ,so<br />
Q (m G C G m W C W )T<br />
((0.300 kg)(840 J/kg°C) (0.250 kg)(4180 J/kg°C))(100.0°C 15°C)<br />
1.110 5 J<br />
Now P E<br />
Q<br />
t t ,so<br />
t Q<br />
P 1.<br />
1105<br />
J<br />
<br />
3. 00102<br />
J/s<br />
370 s 6.1 min<br />
60. Car Engine A 2.5010 2 -kg cast-iron car engine contains water as a coolant.<br />
Suppose that the engine’s temperature is 35.0°C when it is shut off, and the air<br />
temperature is 10.0°C. The heat given off by the engine and water in it as they cool<br />
to air temperature is 4.4010 6 J. What mass of water is used to cool the engine?<br />
Q m W C W T m i C i T<br />
Q mi<br />
mW <br />
CW Ci<br />
T<br />
T (4.410<br />
<br />
6 J) ((2.50102 kg)(450 J/kg°C)(35.0°C 10.0°C))<br />
<br />
(4180 J/kg°C)(35.0°C 10.0°C)<br />
15 kg<br />
<strong>12</strong>.2 <strong>Ch</strong>anges of State and the Laws of Thermodynamics<br />
page 337<br />
Level 1<br />
61. Years ago, a block of ice with a mass of about 20.0 kg was used daily in a home<br />
icebox. The temperature of the ice was 0.0°C when it was delivered. As it melted,<br />
how much heat did the block of ice absorb?<br />
Q mH f (20.0 kg)(3.3410 5 J/kg) 6.6810 6 J<br />
62. A 40.0-g sample of chloroform is condensed from a vapor at 61.6°C to a liquid at<br />
61.6°C. It liberates 9870 J of heat. What is the heat of vaporization of chloroform?<br />
Q mHv Hv 2.47105 Q 9870 J<br />
<br />
J/kg<br />
m 0.0400 kg<br />
280 Solutions Manual Physics: Principles and Problems<br />
250 g<br />
15°C<br />
3.0010 2 g<br />
3.0010 2 W<br />
■ Figure <strong>12</strong>-20<br />
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.