EDU 403 Measurement and Evaluation - National Open University ...
EDU 403 Measurement and Evaluation - National Open University ...
EDU 403 Measurement and Evaluation - National Open University ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>EDU</strong> <strong>403</strong> MEASUREMENT AND EVALUATION<br />
3.0 MAIN CONTENT<br />
3.1 Cognitive domain<br />
The cognitive domain involves those objectives that deal with the<br />
development of intellectual abilities <strong>and</strong> skills. These have to do with<br />
the mental abilities of the brain. The domain is categorized into six<br />
hierarchical comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis <strong>and</strong><br />
evaluation. These levels are of hierarchical <strong>and</strong> increasing operational<br />
difficulties that achievement of a higher level of skill assumes the<br />
achievement of the previous levels. This implies that a higher level of<br />
skill could be achieved only if a certain amount of ability called for by<br />
the previous level has been achieved. For instance, you cannot apply<br />
what you do not know or comprehend, can you now underst<strong>and</strong> what it<br />
means to be hierarchical.<br />
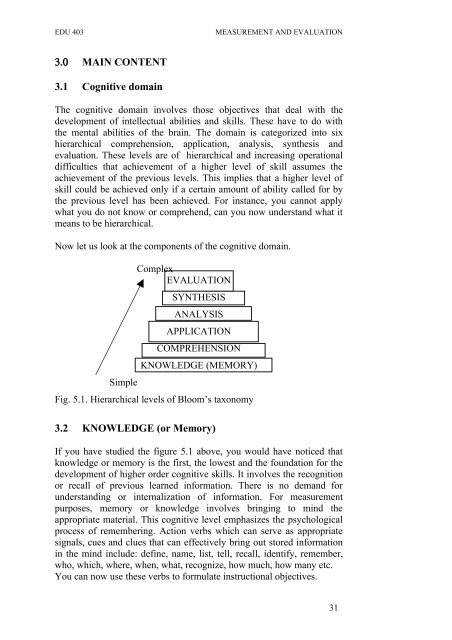
Now let us look at the components of the cognitive domain.<br />
Simple<br />
Complex<br />
EVALUATION<br />
SYNTHESIS<br />
ANALYSIS<br />
APPLICATION<br />
COMPREHENSION<br />
KNOWLEDGE (MEMORY)<br />
Fig. 5.1. Hierarchical levels of Bloom’s taxonomy<br />
3.2 KNOWLEDGE (or Memory)<br />
If you have studied the figure 5.1 above, you would have noticed that<br />
knowledge or memory is the first, the lowest <strong>and</strong> the foundation for the<br />
development of higher order cognitive skills. It involves the recognition<br />
or recall of previous learned information. There is no dem<strong>and</strong> for<br />
underst<strong>and</strong>ing or internalization of information. For measurement<br />
purposes, memory or knowledge involves bringing to mind the<br />
appropriate material. This cognitive level emphasizes the psychological<br />
process of remembering. Action verbs which can serve as appropriate<br />
signals, cues <strong>and</strong> clues that can effectively bring out stored information<br />
in the mind include: define, name, list, tell, recall, identify, remember,<br />
who, which, where, when, what, recognize, how much, how many etc.<br />
You can now use these verbs to formulate instructional objectives.<br />
31