The unicellular green alga Dunaliella salina Teod. as a model - Algae
The unicellular green alga Dunaliella salina Teod. as a model - Algae
The unicellular green alga Dunaliella salina Teod. as a model - Algae
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Algae</strong> 2011, 26(1): 3-20<br />
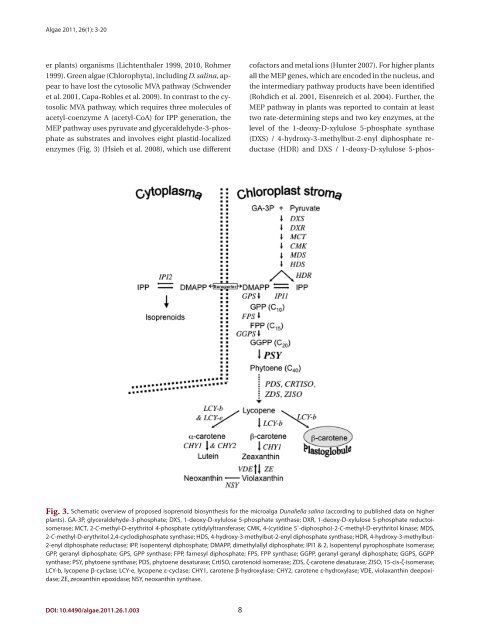
er plants) organisms (Lichtenthaler 1999, 2010, Rohmer<br />
1999). Green <strong>alga</strong>e (Chlorophyta), including D. <strong>salina</strong>, appear<br />
to have lost the cytosolic MVA pathway (Schwender<br />
et al. 2001, Capa-Robles et al. 2009). In contr<strong>as</strong>t to the cytosolic<br />
MVA pathway, which requires three molecules of<br />
acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) for IPP generation, the<br />
MEP pathway uses pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate<br />
<strong>as</strong> substrates and involves eight pl<strong>as</strong>tid-localized<br />
enzymes (Fig. 3) (Hsieh et al. 2008), which use different<br />
DOI: 10.4490/<strong>alga</strong>e.2011.26.1.003 8<br />
cofactors and metal ions (Hunter 2007). For higher plants<br />
all the MEP genes, which are encoded in the nucleus, and<br />
the intermediary pathway products have been identified<br />
(Rohdich et al. 2001, Eisenreich et al. 2004). Further, the<br />
MEP pathway in plants w<strong>as</strong> reported to contain at le<strong>as</strong>t<br />
two rate-determining steps and two key enzymes, at the<br />
level of the 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synth<strong>as</strong>e<br />
(DXS) / 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reduct<strong>as</strong>e<br />
(HDR) and DXS / 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phos-<br />
Fig. 3. Schematic overview of proposed isoprenoid biosynthesis for the micro<strong>alga</strong> <strong>Dunaliella</strong> <strong>salina</strong> (according to published data on higher<br />
plants). GA-3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; DXS, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synth<strong>as</strong>e; DXR, 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomer<strong>as</strong>e;<br />
MCT, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransfer<strong>as</strong>e; CMK, 4-(cytidine 5'-diphospho)-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kin<strong>as</strong>e; MDS,<br />
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synth<strong>as</strong>e; HDS, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate synth<strong>as</strong>e; HDR, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-<br />
2-enyl diphosphate reduct<strong>as</strong>e; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; IPI1 & 2, isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomer<strong>as</strong>e;<br />
GPP, geranyl diphosphate; GPS, GPP synth<strong>as</strong>e; FPP, farnesyl diphosphate; FPS, FPP synth<strong>as</strong>e; GGPP, geranyl geranyl diphosphate; GGPS, GGPP<br />
synth<strong>as</strong>e; PSY, phytoene synth<strong>as</strong>e; PDS, phytoene desatur<strong>as</strong>e; CrtISO, carotenoid isomer<strong>as</strong>e; ZDS, ζ-carotene desatur<strong>as</strong>e; ZISO, 15-cis-ζ-isomer<strong>as</strong>e;<br />
LCY-b, lycopene β-cycl<strong>as</strong>e; LCY-e, lycopene ε-cycl<strong>as</strong>e; CHY1, carotene β-hydroxyl<strong>as</strong>e; CHY2, carotene ε-hydroxyl<strong>as</strong>e; VDE, violaxanthin deepoxid<strong>as</strong>e;<br />
ZE, zeoxanthin epoxid<strong>as</strong>e; NSY, neoxanthin synth<strong>as</strong>e.