The Effect of Zr-Doping and Crystallite Size on the Mechanical ...
The Effect of Zr-Doping and Crystallite Size on the Mechanical ...
The Effect of Zr-Doping and Crystallite Size on the Mechanical ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
I. Introducti<strong>on</strong><br />
1.3. Energetics <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Nanocrystalline <str<strong>on</strong>g>Zr</str<strong>on</strong>g>O2 <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> TiO2 Phases<br />
In microscale particles, <strong>on</strong>ly a negligible amount <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> atoms is situated <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
surface, whereas <strong>the</strong> bulk mass <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> atoms is surrounded by o<strong>the</strong>r bulk atoms. With a<br />
decrease <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> crystallite size to <strong>the</strong> nanometer range, <strong>the</strong> relative amount <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> atoms <strong>on</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> surface increases. Atoms <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong> surface exhibit a surface structure, different from<br />
<strong>the</strong> bulk material due to unsaturated b<strong>on</strong>dings <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> atoms. Energetics are <strong>the</strong>refore<br />
very different compared to <strong>the</strong> bulk mass <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> in most cases, H2O is adsorbed <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
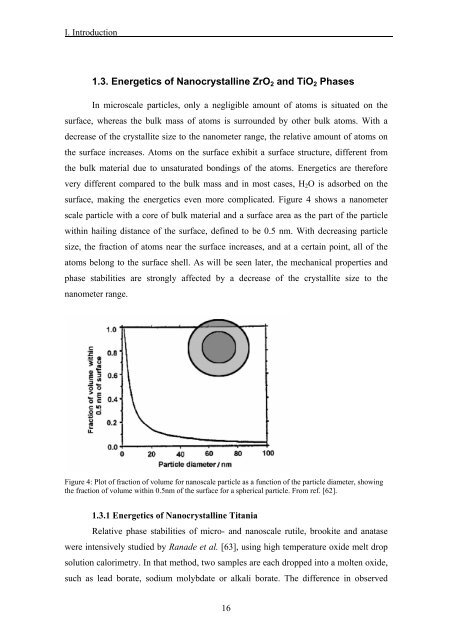
surface, making <strong>the</strong> energetics even more complicated. Figure 4 shows a nanometer<br />
scale particle with a core <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> bulk material <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> a surface area as <strong>the</strong> part <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> particle<br />
within hailing distance <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> surface, defined to be 0.5 nm. With decreasing particle<br />
size, <strong>the</strong> fracti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> atoms near <strong>the</strong> surface increases, <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> at a certain point, all <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong><br />
atoms bel<strong>on</strong>g to <strong>the</strong> surface shell. As will be seen later, <strong>the</strong> mechanical properties <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
phase stabilities are str<strong>on</strong>gly affected by a decrease <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> crystallite size to <strong>the</strong><br />
nanometer range.<br />
Figure 4: Plot <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> fracti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> volume for nanoscale particle as a functi<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> particle diameter, showing<br />
<strong>the</strong> fracti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> volume within 0.5nm <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> surface for a spherical particle. From ref. [62].<br />
1.3.1 Energetics <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Nanocrystalline Titania<br />
Relative phase stabilities <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> micro- <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> nanoscale rutile, brookite <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> anatase<br />
were intensively studied by Ranade et al. [63], using high temperature oxide melt drop<br />
soluti<strong>on</strong> calorimetry. In that method, two samples are each dropped into a molten oxide,<br />
such as lead borate, sodium molybdate or alkali borate. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> difference in observed<br />
16