The Effect of Zr-Doping and Crystallite Size on the Mechanical ...
The Effect of Zr-Doping and Crystallite Size on the Mechanical ...
The Effect of Zr-Doping and Crystallite Size on the Mechanical ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
II. Methods <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> Instrumentati<strong>on</strong><br />
pressures. In c<strong>on</strong>trast, in <strong>the</strong> DAC, a maximum static pressure <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> ~300 GPa can be<br />
reached. At intermediate pressures, <strong>the</strong> DAC can be heated by electrical resistive<br />
heating (internal or external) to about 1000°C or internal laser heating to about 3000°C.<br />
However, sample volumes are as small as 0.0002 mm³.<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> choice <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> in-situ measurements possible is highest for DAC experiments.<br />
Diam<strong>on</strong>ds are transparent for electromagnetic radiati<strong>on</strong> in a broad energy range,<br />
allowing for optical, near-infrared <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> X-ray analytical methods. Depending <strong>on</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
design <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>the</strong> choice <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> materials, multi anvil presses can allow for in-situ X-ray<br />
diffracti<strong>on</strong>, but are limited for o<strong>the</strong>r in-situ techniques. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> pist<strong>on</strong> cylinder apparatus<br />
lacks <strong>the</strong> possibility for in-situ X-ray diffracti<strong>on</strong>.<br />
1.1. Hydro<strong>the</strong>rmal Experiments<br />
Hydro<strong>the</strong>rmal experiments were performed in cold-seal pressure vessels, at<br />
pressure <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> temperature c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s, were H2O is in <strong>the</strong> supercritical state, allowing for<br />
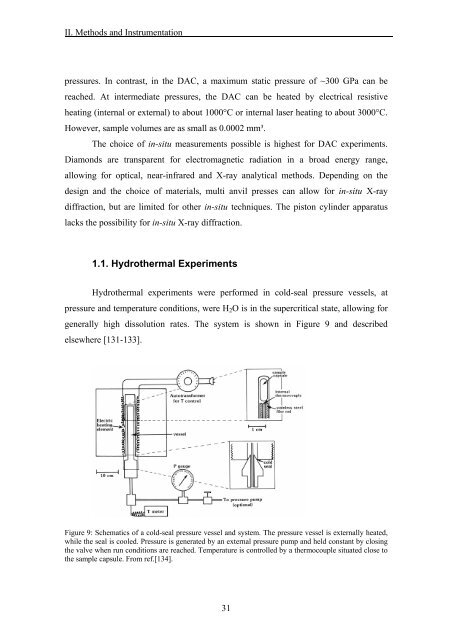
generally high dissoluti<strong>on</strong> rates. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> system is shown in Figure 9 <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> described<br />
elsewhere [131-133].<br />
Figure 9: Schematics <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> a cold-seal pressure vessel <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> system. <str<strong>on</strong>g>The</str<strong>on</strong>g> pressure vessel is externally heated,<br />
while <strong>the</strong> seal is cooled. Pressure is generated by an external pressure pump <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> held c<strong>on</strong>stant by closing<br />
<strong>the</strong> valve when run c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s are reached. Temperature is c<strong>on</strong>trolled by a <strong>the</strong>rmocouple situated close to<br />
<strong>the</strong> sample capsule. From ref.[134].<br />
31