DISEASES OF MIDDLE EAR
DISEASES OF MIDDLE EAR
DISEASES OF MIDDLE EAR
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Students should be able to:<br />
<strong>DISEASES</strong> <strong>OF</strong> <strong>MIDDLE</strong> <strong>EAR</strong><br />
L<strong>EAR</strong>NING OBJECTIVES<br />
1. Recognize the clinical manifestations of diseases of middle ear and<br />
their basic management.<br />
2. Understand when to refer the patient to the concerned speciality.<br />
3. Able to follow guidelines for treatment of discharging ear.<br />
4. Discuss the management of OTITIS MEDIA<br />
ASOM,CSOM,OME,OTOSCLEROSIS<br />
OTITIS MEDIA<br />
DEFINITION<br />
Inflammation of the middle ear cleft<br />
OTITIS MEDIA - CLASSIFICATION<br />
Acute OM - rapid onset of signs & symptoms < 3 wks course<br />
Subacute OM - 3 wks to 3 months<br />
Chronic OM - 3 months or longer<br />
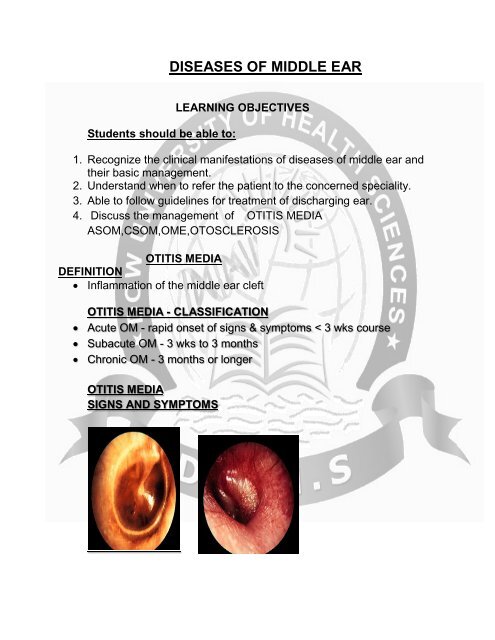
OTITIS MEDIA<br />
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
SPECIFIC SIGNS<br />
Otalgia<br />
Otorrhea<br />
Hearing Loss<br />
Vertigo<br />
NONSPECIFIC SIGN<br />
Fever<br />
Irritability<br />
Lethargy<br />
Anorexia<br />
Vomiting<br />
Diarrhea<br />
STAGES <strong>OF</strong> SUPPURATIVE AOM<br />
Stage of tubal occlusion.<br />
Stage of pre suppuration.<br />
Stage of suppuration.<br />
Stage of resolution.<br />
Stage of complication.<br />
STAGE <strong>OF</strong> TUBAL OCCLUSION<br />
SYMPTOMS:<br />
Deafness.<br />
Otalgia.<br />
No fever.
SIGNS:<br />
Retracted tympanic membrane.<br />
Prominence of lateral process of malleus<br />
Loss of light reflex<br />
STAGE <strong>OF</strong> PRESUPPURATION<br />
SYMPTOMS:<br />
Otalgia<br />
No fever<br />
SIGNS:<br />
Redness and outward bulging of pars flaccida.<br />
Dilation of blood vessels most apparent.
STAGE <strong>OF</strong> SUPPURATION<br />
SYMPTOMS:<br />
Severe otalgia<br />
Persistent fever.<br />
Conductive deafness<br />
SIGNS:<br />
Edematous TM.<br />
No landmarks seen.<br />
bulge to the point of rupture.<br />
Obvious outward
STAGE <strong>OF</strong> RESOLUTION<br />
SYMPTOMS:<br />
No otalgia.<br />
Mild hearing loss.<br />
No fever.<br />
SIGNS:<br />
Inflammation resolved.<br />
Blood stained discharge in auditory canal.<br />
SEROUS OTITIS MEDIA (OME)<br />
An effusion in the middle ear resulting from incomplete<br />
resolution of acute otitis media or obstruction of the eustachian<br />
tube
usually sterile<br />
may contain pathogenic bacteria.<br />
More common in children.<br />
Predisposing Factors:<br />
o Eustachian tube obstruction<br />
inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx<br />
allergic manifestations<br />
hypertrophic adenoids<br />
benign or malignant neoplasms.<br />
SYMPTOMS - OME<br />
Asymptomatic<br />
o or<br />
Patient may experience<br />
-ear discomfort<br />
-hearing loss<br />
-tinnitus<br />
-possibly vertigo<br />
-feeling of ear fullness<br />
SIGNS<br />
Tympanic membrane retraction--mild<br />
Displacement of the light reflex--Distorted<br />
Accentuation of the landmarks--Prominent<br />
Transudate from the blood vessels in the mucous membrane<br />
develops in the middle ear<br />
o amber or gray appearance of tympanic membrane<br />
o immobility of the tympanic membrane<br />
An air-fluid level or bubbles of air may be seen through the tympanic<br />
membrane.<br />
Conductive hearing loss occurs<br />
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS FOR SOM
Otoscopy<br />
Pneumatic otoscopy--- diagnostic clinical test<br />
Tympanometry – type B--diagnostic investigation<br />
PTA – conductive loss<br />
Type A<br />
DIAGNOSIS<br />
Acute OM<br />
o preceding URI<br />
o fever, otalgia, hearing loss, otorrhea<br />
o may have assoc. constitutional symptoms<br />
Chronic MEE (OME)<br />
o asymptomatic<br />
o hearing loss<br />
o “plugged”<br />
o “popping”<br />
The position of the tympanic membrane is a key for<br />
differentiating acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion.
Acute OM<br />
o Bulging<br />
o Thickened<br />
o yellow middle ear effusion<br />
Chronic MEE (OME)<br />
o typically retracted or in the neutral position<br />
o Thickened<br />
o Amber or grayish middle ear effusion<br />
Acute OM<br />
Chronic MEE (OME)<br />
MANAGEMENT <strong>OF</strong> OTITIS MEDIA<br />
TREATMENT<br />
Medical<br />
Aural toilet<br />
Suction Cleaning<br />
Topical Antibiotics<br />
Systemic Antibiotics<br />
o depending on the culture and sensitivity<br />
DECONGESTANTS<br />
ANALGESICS AND ANTIPYRETICS
MANEUVERS TO OPEN ET<br />
VALSALVA MANOEUVRE<br />
It is a simple method in which the patient closes his nostrils & mouth<br />
at the same time & attempts to exhale forcefully.<br />
In this way the ends of Eustachian tubes where they connect with<br />
throat can be opened.<br />
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT<br />
Myringotomy with or without ventilation tube insertion.<br />
Laser assisted myringotomy / tympanostomy<br />
Mastoidectomy and related procedures.<br />
Myringoplasty or tympanoplasty.<br />
GROMMET / VENTILATION /TYMPANOSTOMY TUBES
INDICATIONS <strong>OF</strong> MYRINGOTOMY/ VENTILATION TUBE<br />
INSERTION<br />
Impending rupture of TM.<br />
Infection not responding to medical treatment.<br />
Infection in immature or immuno-compromised host.<br />
Pain or vertigo.<br />
Prolonged serious hearing loss which may compromise speech and<br />
IQ development.<br />
Recurrent otitis media.<br />
COMPLICATIONS<br />
Injury to incudostapedial joint or stapes.<br />
Injury to jugular bulb with profuse bleeding.<br />
Middle ear infection.<br />
Failure to resolve the ear infection.<br />
Persistent perforation after the tube falls out of the ear drum.<br />
Chronic ear drainage.<br />
Infection.<br />
Hearing loss.<br />
Scarring of the ear drum.<br />
Foreign body reaction to the tube itself.<br />
MASTOIDECTOMY & RELATED PROCEDURES<br />
MASTOIDECTOMY<br />
-The purpose of these procedures is to eradicate DISEASE present in<br />
the inaccessible parts of the temporal bone.<br />
- Middle ear.<br />
- Mastoid.<br />
- Attic/Antrum.<br />
-Increase the Air Reservior<br />
Adenoidectomy and/or tonsillectomy<br />
for the treatment of otitis media with effusion is controversial, some<br />
studies support it while others do not.
OTOSCLEROSIS<br />
INTRODUCTION<br />
7-10% Caucasian temporal bones<br />
1% Caucasians with symptoms<br />
Other races lesser incidence<br />
Otosclerosis is an autosomal dominant disorder of the otic capsule,<br />
limited to the temporal bone.<br />
Has simple autosomal dominant inheritence with incomplete<br />
penetrance. - 70%<br />
Age of onset of hearing loss ranges from teens to the forties<br />
Pregnancy can accelerate the otosclerotic process.<br />
Mostly Involves Foot Plate of Stapes- Fistula Ante Fenestrum<br />
CLINICAL FEATURES<br />
Slowly progressive hearing loss
Bilateral, asymmetric<br />
Ages 15 to 45<br />
Women 2:1<br />
o pregnancy/estrogen therapy<br />
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION<br />
Otomicroscopy<br />
o normal<br />
o Schwartze’s sign<br />
Tuning forks<br />
o 512 Hz Conductive Deafness<br />
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS<br />
Tympanosclerosis<br />
Incus/malleus fixation<br />
ossicular discontinuity<br />
congenital footplate fixation<br />
Middle ear pathology causing CD
AUDIOLOGIC EVALUATION SHOULD INCLUDE<br />
Impedance audiometry<br />
Pure tone audiogram<br />
Speech audiometry
IMPEDANCE AUDIOMETRY DIAGNOSTIC<br />
MANAGEMENT
Amplification<br />
- Refuse surgery<br />
- Poor surgical candidate<br />
- Following improvement of CHL<br />
Medical therapy<br />
- Sodium fluoride<br />
- Vitamin D<br />
- Calcium carbonate<br />
Stapes surgery<br />
STAPES SURGERY<br />
Stapedotomy/ Stapedectomy<br />
Insertion of prosthesis
THANK YOU