- Page 1 and 2: 1 The Evans Equations of Unified Fi
- Page 3 and 4: 3 Torsion .........................
- Page 5: 5 Standard Model with Higgs versus
- Page 8 and 9: Do keep in mind Einstein’s statem
- Page 10 and 11: postulate of general relativity. In
- Page 12 and 13: thought were incorrect. Einstein wa
- Page 14 and 15: 8 Figure I-1 Spacetime Newton’s f
- Page 16 and 17: In order to do calculations in the
- Page 18 and 19: 12 Figure I-4 The Four Forces Gravi
- Page 20 and 21: The Particles There are stable, lon
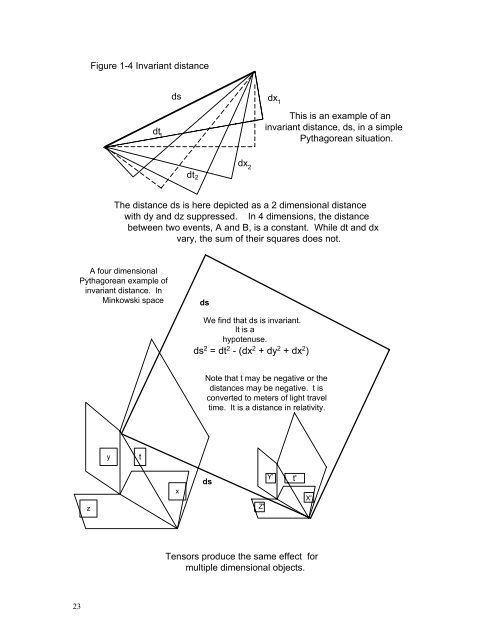
- Page 22 and 23: Chapter 1 Special Relativity 16 The
- Page 24 and 25: unnoticeable, for low velocities, b
- Page 26 and 27: The nature of spacetime is the caus
- Page 30 and 31: An example is shown in Figure 1-4.
- Page 32 and 33: There are many short form abbreviat
- Page 34 and 35: The cross product is not defined In
- Page 36 and 37: form. Given that they are discrete
- Page 38 and 39: curvature, but does not allow spinn
- Page 40 and 41: Chapter 2 General Relativity Introd
- Page 42 and 43: However, acceleration and a gravita
- Page 44 and 45: Energy density reference frames T =
- Page 46 and 47: infinity - at distances where the c
- Page 48 and 49: 42 Figure 2-4 Visualizing Curved Sp
- Page 50 and 51: Curvature Curvature is central to t
- Page 52 and 53: We showed that gravitation is curva
- Page 54 and 55: Figure 2-9 Base Manifold with Eucli
- Page 56 and 57: In Figure 2-10 at the top is the te
- Page 58 and 59: We put the object in the tangent sp
- Page 60 and 61: The metric tensor is important in g
- Page 62 and 63: Chapter 3 Quantum Theory Quantum Th
- Page 64 and 65: 1930’s when it became well establ
- Page 66 and 67: that we have such accuracy as we ha
- Page 68 and 69: spaces. The formulation is beyond t
- Page 70 and 71: frame where measurement is made.) P
- Page 72 and 73: Quantum Numbers The equations below
- Page 74 and 75: Quantum Gravity and other theories
- Page 76 and 77: x time, or momentum x distance, or
- Page 78 and 79:
72 E = pc and E = ħ ω and therefo
- Page 80 and 81:
When the Planck units are used, it
- Page 82 and 83:
76 ms is spin quantum number. It is
- Page 84 and 85:
experiments and to describe events.
- Page 86 and 87:
are the same space; this is a mathe
- Page 88 and 89:
82 If a curve is described by y = a
- Page 90 and 91:
Scalar, or Inner Product The dot pr
- Page 92 and 93:
Figure 4-5 Cross Product a 86 The v
- Page 94 and 95:
product produces surfaces that cut
- Page 96 and 97:
4-Vectors and the Scalar Product An
- Page 98 and 99:
definite - it is a real distance. I
- Page 100 and 101:
Einstein is the tensor defined as G
- Page 102 and 103:
With some operations one must add t
- Page 104 and 105:
Alternately, a set of basis matrice
- Page 106 and 107:
Figure 4-12 100 0 2 1 3 q can repre
- Page 108 and 109:
Contravariant and covariant vectors
- Page 110 and 111:
The scalars, whether real or imagin
- Page 112 and 113:
106 2 _ 1 ∂ 2 c 2 ∂ t 2 can be
- Page 114 and 115:
Covariant Exterior Derivative D ∧
- Page 116 and 117:
Chapter 5 Well Known Equations Intr
- Page 118 and 119:
V = IR. A circuit is a completed ci
- Page 120 and 121:
The standard definition of magnetic
- Page 122 and 123:
Another way of stating this is that
- Page 124 and 125:
Figure 5-4 Ampere's and Faraday’s
- Page 126 and 127:
Newton’s law of gravitation 120 A
- Page 128 and 129:
Figure 5-6 Fields Poisson’s Equat
- Page 130 and 131:
This is a differential operator use
- Page 132 and 133:
The Evans equations indicate that R
- Page 134 and 135:
Compton and de Broglie wavelengths
- Page 136 and 137:
Here ħ = h / 2π = Planck’s cons
- Page 138 and 139:
Mathematics and Physics To a certai
- Page 140 and 141:
Chapter 6 The Evans Field Equation
- Page 142 and 143:
Then the wave equation was develope
- Page 144 and 145:
138 q ab µν = q a µq b ν q ab
- Page 146 and 147:
From the basic structure of equatio
- Page 148 and 149:
142 Rµν - ½ Rgµν = kTµν Eins
- Page 150 and 151:
original vector - its orientation i
- Page 152 and 153:
The electromagnetic and weak fields
- Page 154 and 155:
In more mechanical terms, energy an
- Page 156 and 157:
Figure 6-8 Abstract Fiber Bundle an
- Page 158 and 159:
The other three fields - electromag
- Page 160 and 161:
Figure 6-9 The spin connection and
- Page 162 and 163:
Evans Field Equation Extensions R =
- Page 164 and 165:
The real physical solutions the wav
- Page 166 and 167:
160 Another way to look at the equa
- Page 168 and 169:
determined by geometry. This makes
- Page 170 and 171:
index, it is generally covariant -
- Page 172 and 173:
It is also possible to represent bo
- Page 174 and 175:
Electromagnetism 168 The B (3) fiel
- Page 176 and 177:
Strong force If tetrad index “a
- Page 178 and 179:
neutron into other more stable curv
- Page 180 and 181:
explanation for the Aharonov-Bohm a
- Page 182 and 183:
ORIGIN Einstein / Hilbert (1915) Ev
- Page 184 and 185:
then we found it and used it to des
- Page 186 and 187:
Very Strong Equivalence Principle T
- Page 188 and 189:
Figure 8-2 Separation of Forces PRI
- Page 190 and 191:
Note that physics texts often say t
- Page 192 and 193:
criteria for dark matter. We know t
- Page 194 and 195:
Figure 8-5 Spinning Spacetime The s
- Page 196 and 197:
this gives the influence of gravita
- Page 198 and 199:
In all the forms of the tetrad, the
- Page 200 and 201:
Spacetime curvature in and around p
- Page 202 and 203:
The Evans Wave Equation Figure 8-8
- Page 204 and 205:
λ is the wavelength. It can be app
- Page 206 and 207:
λde B = ħ / p = ħ / mv (6) where
- Page 208 and 209:
where ψ a µ is a tetrad. Therefor
- Page 210 and 211:
The components of R = -kT originati
- Page 212 and 213:
Relationship between r and λ Profe
- Page 214 and 215:
Figure 9-4 Curvature and Wavelength
- Page 216 and 217:
One may tentatively assume that the
- Page 218 and 219:
The first gives us the Principle of
- Page 220 and 221:
Chapter 10 Replacement of the Heise
- Page 222 and 223:
p b µ = ћ κ b µ (2) The positio
- Page 224 and 225:
The volumes here are derived from V
- Page 226 and 227:
The Heisenberg uncertainty principl
- Page 228 and 229:
Chapter 11 The Evans B (3) Spin Fie
- Page 230 and 231:
where g = e/ћ for one photon; e is
- Page 232 and 233:
Figure 11-3 shows the circle turnin
- Page 234 and 235:
the curvature very slight at the ea
- Page 236 and 237:
The magnetic field components are r
- Page 238 and 239:
The B (3) field is the fundamental
- Page 240 and 241:
The present standard model uses con
- Page 242 and 243:
Using Einstein’s index contracted
- Page 244 and 245:
unnecessary and it has been shown t
- Page 246 and 247:
Figure 12-4 Momentum Exchange p 3 p
- Page 248 and 249:
Figure 12-6 Equations in the Tangen
- Page 250 and 251:
were still unknown. However it is o
- Page 252 and 253:
Consider an experiment where a beam
- Page 254 and 255:
Here κ is wave number, ds is the i
- Page 256 and 257:
the Evans unified field theory. Sim
- Page 258 and 259:
Figure 13-6 Ordinary Stokes is a ci
- Page 260 and 261:
Chapter 14 Geometric Concepts Intro
- Page 262 and 263:
where φ is the gravitational poten
- Page 264 and 265:
Just what equation will be found to
- Page 266 and 267:
where e is the charge of the electr
- Page 268 and 269:
have quantization of general relati
- Page 270 and 271:
The scalar curvature, R, is defined
- Page 272 and 273:
Chapter 15 A Unified Viewpoint Intr
- Page 274 and 275:
Asymmetry is a combination of symme
- Page 276 and 277:
We know energy density increase is
- Page 278 and 279:
G q a µ = kT q a µ. Is one formul
- Page 280 and 281:
unknowable measurements. ħ is the
- Page 282 and 283:
and their respective ratios was,
- Page 284 and 285:
It seems inevitable that we will fi
- Page 286 and 287:
Quantum mechanics presented us with
- Page 288 and 289:
Evans’ equations the electromagne
- Page 290 and 291:
A naïve description would be that
- Page 292 and 293:
Note that we are still missing some
- Page 294 and 295:
Oscillatory Universe The equation m
- Page 296 and 297:
We do not have a definite mechanica
- Page 298 and 299:
Glossary There are some terms here
- Page 300 and 301:
AIAS Alpha Institute for Advanced S
- Page 302 and 303:
The B (3) field and O(3) electrodyn
- Page 304 and 305:
The calculations to get coordinates
- Page 306 and 307:
Connections Circular Basis The equa
- Page 308 and 309:
Elie Cartan worked out an approach
- Page 310 and 311:
A covariant component is a physical
- Page 312 and 313:
Covariant derivative operator (∇
- Page 314 and 315:
Curvature at a given point P has a
- Page 316 and 317:
Dimension While mathematically well
- Page 318 and 319:
Einstein Field Equation The equatio
- Page 320 and 321:
Euclidean spacetime Flat geometric
- Page 322 and 323:
Fields explain “action at a dista
- Page 324 and 325:
Fundamental Particle A particle wit
- Page 326 and 327:
Geometric units Conversion of mass
- Page 328 and 329:
describes electrodynamics. It is no
- Page 330 and 331:
Index Typically Greek letters are u
- Page 332 and 333:
Isomorphism A 1:1 correspondence. J
- Page 334 and 335:
Local A very small region of spacet
- Page 336 and 337:
Another use is with the Dirac and o
- Page 338 and 339:
We want a real number to define the
- Page 340 and 341:
Time invariance (or symmetry under
- Page 342 and 343:
Dual vectors = one forms = covector
- Page 344 and 345:
Meson - Any of a family of subatomi
- Page 346 and 347:
The Evans phase law is: This is app
- Page 348 and 349:
Quantum gravity Quantum gravity is
- Page 350 and 351:
Riemann tensor Riemann calculates t
- Page 352 and 353:
Schrodinger's Equation ∇ 2 Ψn =
- Page 354 and 355:
The spin connection may be best des
- Page 356 and 357:
α angular acceleration; fine struc
- Page 358 and 359:
Rotation and reflection of a triang
- Page 360 and 361:
Next is O(3) electrodynamics which
- Page 362 and 363:
Rank is indicated by the number of
- Page 364 and 365:
A spin structure is locally a tetra
- Page 366 and 367:
q a µ can be defined in terms of a
- Page 368 and 369:
The torsion of a curve is a measure
- Page 370 and 371:
our real four dimensional spacetime
- Page 372 and 373:
Wave or Quantum Mechanics Study of