- Page 2 and 3:
Filtration and Purification in the
- Page 4 and 5:
1. Pharmacokinetics, Milo Gibaldi a
- Page 6 and 7:
55. Radiopharmaceuticals: Chemistry
- Page 8 and 9:
107. Drug Stability: Principles and
- Page 10:
156. Pharmacogenomics: Second Editi
- Page 13:
Informa Healthcare USA, Inc. 52 Van
- Page 18:
Foreword Filtration has been used s
- Page 21 and 22:
viii Preface describing essential p
- Page 23 and 24:
x Contents 14. Extractables and Lea
- Page 25 and 26:
xii Contributors Theodore H. Meltze
- Page 27 and 28:
2 Quigley liquids. The problem can
- Page 29 and 30:
4 Quigley FIGURE 3 Diatoms in diato
- Page 31 and 32:
6 Quigley This inertial force depen
- Page 33 and 34:
8 Quigley Adsorption Activated Carb
- Page 35 and 36:
10 Quigley easier to change than a
- Page 37 and 38:
12 Quigley The graded pore size for
- Page 39 and 40:
14 Quigley FIGURE 15 Depth and memb
- Page 41 and 42:
16 Quigley The proper cake formatio
- Page 43 and 44:
18 Quigley The sterile bulk albumin
- Page 45 and 46:
20 Quigley When running a forward f
- Page 48 and 49:
2 Charge Modified Filter Media Euge
- Page 50 and 51:
Charge Modified Filter Media 25 pro
- Page 52 and 53:
Charge Modified Filter Media 27 saf
- Page 54 and 55:
Charge Modified Filter Media 29 FIG
- Page 56 and 57:
Charge Modified Filter Media 31 FIG
- Page 58 and 59:
Charge Modified Filter Media 33 FIG
- Page 60 and 61:
Charge Modified Filter Media 35 At
- Page 62 and 63:
Charge Modified Filter Media 37 FIG
- Page 64 and 65:
Charge Modified Filter Media 39 FIG
- Page 66 and 67:
Charge Modified Filter Media 41 FIG
- Page 68 and 69:
Charge Modified Filter Media 43 DNA
- Page 70 and 71:
Charge Modified Filter Media 45 Hag
- Page 72 and 73:
3 Filter Designs Suraj B. Baloda Mi
- Page 74 and 75:
Filter Designs 49 The most common 4
- Page 76 and 77:
Filter Designs 51 Multiple steps an
- Page 78 and 79:
Filter Designs 53 air filtration or
- Page 80 and 81:
Filter Designs 55 pleat pack that c
- Page 82 and 83:
Filter Designs 57 FIGURE 7 Differen
- Page 84 and 85:
Filter Designs 59 the tailoring of
- Page 86 and 87:
Filter Designs 61 measured. This gi
- Page 88 and 89:
Filter Designs 63 FIGURE 12 (A) Pil
- Page 90 and 91:
4 Pore Sizes and Distributions C. T
- Page 92 and 93:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 67 Fil
- Page 94 and 95:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 69 FIG
- Page 96 and 97:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 71 pre
- Page 98 and 99:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 73 whe
- Page 100 and 101:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 75 FIG
- Page 102 and 103:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 77 FIG
- Page 104:
Pore Sizes and Distributions 79 fil
- Page 107 and 108:
82 Meltzer and Jornitz The pore str
- Page 109 and 110:
84 Meltzer and Jornitz Pore Size Di
- Page 111 and 112:
86 Meltzer and Jornitz The dilution
- Page 113 and 114:
88 Meltzer and Jornitz per cm 2 EFA
- Page 115 and 116:
90 Meltzer and Jornitz TABLE 2 Rete
- Page 117 and 118:
92 Meltzer and Jornitz FIGURE 9 B.
- Page 119 and 120:
94 Meltzer and Jornitz Viscosity Vi
- Page 121 and 122:
96 Meltzer and Jornitz TABLE 5 Rete
- Page 123 and 124:
98 Meltzer and Jornitz fluid in its
- Page 125 and 126:
100 Meltzer and Jornitz TABLE 7 Flu
- Page 127 and 128:
102 Meltzer and Jornitz THE MODELIN
- Page 129 and 130:
104 Meltzer and Jornitz FIGURE 12 P
- Page 131 and 132:
106 Meltzer and Jornitz the mechani
- Page 133 and 134:
108 Meltzer and Jornitz filters in
- Page 135 and 136:
110 Meltzer and Jornitz particles f
- Page 137 and 138:
112 Meltzer and Jornitz from the el
- Page 139 and 140:
114 Meltzer and Jornitz modified to
- Page 141 and 142:
116 Meltzer and Jornitz This finds
- Page 143 and 144:
118 Meltzer and Jornitz The hydroge
- Page 145 and 146:
120 Meltzer and Jornitz Solvating E
- Page 147 and 148:
122 Meltzer and Jornitz filter’s
- Page 149 and 150:
124 Meltzer and Jornitz bonding of
- Page 151 and 152:
126 Meltzer and Jornitz and strongl
- Page 153 and 154:
128 Meltzer and Jornitz bacteria ne
- Page 155 and 156:
130 Meltzer and Jornitz The Electri
- Page 157 and 158:
132 Meltzer and Jornitz namely VDW
- Page 159 and 160:
134 Meltzer and Jornitz (non-flowin
- Page 161 and 162:
136 Meltzer and Jornitz hydrocarbon
- Page 163 and 164:
138 Meltzer and Jornitz neutralized
- Page 165 and 166:
140 Meltzer and Jornitz Interesting
- Page 167 and 168:
142 Meltzer and Jornitz the endotox
- Page 169 and 170:
144 Meltzer and Jornitz (1) The equ
- Page 171 and 172:
146 Meltzer and Jornitz Bowman FW,
- Page 173 and 174:
148 Meltzer and Jornitz Ridgway HF.
- Page 176 and 177:
6 Microbiological Considerations in
- Page 178 and 179:
Microbiological Considerations 153
- Page 180 and 181:
Microbiological Considerations 155
- Page 182 and 183:
Microbiological Considerations 157
- Page 184 and 185:
Microbiological Considerations 159
- Page 186:
Microbiological Considerations 161
- Page 189 and 190:
164 Meltzer and Jornitz some lower
- Page 191 and 192:
166 Meltzer and Jornitz taken that
- Page 193 and 194:
168 Meltzer and Jornitz 8. Initial
- Page 195 and 196:
170 Meltzer and Jornitz flow decrea
- Page 197 and 198:
172 Meltzer and Jornitz FIGURE 3 Pa
- Page 199 and 200:
174 Meltzer and Jornitz FIGURE 5 Se
- Page 201 and 202:
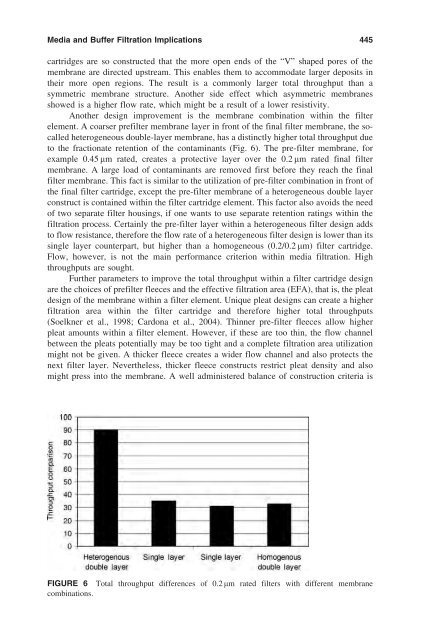
176 Meltzer and Jornitz Homogeneous
- Page 203 and 204:
178 Meltzer and Jornitz Prefilter A
- Page 205 and 206:
180 Meltzer and Jornitz upon the us
- Page 207 and 208:
182 Meltzer and Jornitz obtained by
- Page 209 and 210:
184 Meltzer and Jornitz published.
- Page 211 and 212:
186 Meltzer and Jornitz If flow dec
- Page 213 and 214:
188 Meltzer and Jornitz effect, the
- Page 215 and 216:
190 Meltzer and Jornitz differentia
- Page 217 and 218:
192 Meltzer and Jornitz Trotter AM,
- Page 219 and 220:
194 Bardo We will survey key aspect
- Page 221 and 222:
196 Bardo corrosion cracking, inclu
- Page 223 and 224:
198 Bardo were to skip any of the m
- Page 225 and 226:
200 Bardo stainless steel and other
- Page 227 and 228:
202 Bardo all the obligations requi
- Page 229 and 230:
204 Bardo built into the top plate,
- Page 231 and 232:
206 Bardo often called domes or she
- Page 233 and 234:
208 Bardo FIGURE 3 T-style sanitary
- Page 235 and 236:
210 Bardo In multi-round sanitary h
- Page 237 and 238:
212 Bardo FIGURE 6 (A) 222- and (B)
- Page 239 and 240:
214 Bardo Cartridge replacement. St
- Page 241 and 242:
216 Bardo ever larger. As the bioph
- Page 243 and 244:
218 Bardo n Difficult to scale-up n
- Page 245 and 246:
220 Bardo that is free of many of t
- Page 247 and 248:
222 Bardo TABLE 3 Comparison of Sta
- Page 249 and 250:
224 Bardo From this productive amal
- Page 251 and 252:
226 Bardo n integrity testing, n va
- Page 253 and 254:
228 Bardo CONCLUSION The evolution
- Page 256 and 257:
9 Stainless Steel Application and F
- Page 258 and 259:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 260 and 261:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 262 and 263:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 264 and 265:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 266 and 267:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 268 and 269:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 270 and 271:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 272 and 273:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 274 and 275:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 276 and 277:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 278 and 279:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 280:
Stainless Steel Application and Fab
- Page 283 and 284:
258 Meltzer operational mechanism (
- Page 285 and 286:
260 Meltzer adsorptive interactions
- Page 287 and 288:
262 Meltzer surfaces to which they
- Page 289 and 290:
264 Meltzer matter, the bovine seru
- Page 291 and 292:
266 Meltzer FIGURE 2 Outer coats of
- Page 293 and 294:
268 Meltzer molecular arrangements
- Page 295 and 296:
270 Meltzer Extents of adsorption d
- Page 297 and 298:
272 Meltzer Qualitative Measurement
- Page 299 and 300:
274 Meltzer albumin solution, etc.
- Page 301 and 302:
276 Meltzer hydrophobic bonding. An
- Page 303 and 304:
278 Meltzer network. Thus, the mole
- Page 305 and 306:
280 Meltzer FIGURE 8 The hydrogen b
- Page 307 and 308:
282 Meltzer TABLE 4 Flu-Vaccine Fil
- Page 309 and 310:
284 Meltzer feedstream. At this poi
- Page 311 and 312:
286 Meltzer FIGURE 10 Different pro
- Page 313 and 314:
288 Meltzer factors, the short rang
- Page 315 and 316:
290 Meltzer plotted trace signals b
- Page 317 and 318:
292 Meltzer instead of flat membran
- Page 319 and 320:
294 Meltzer Characklis WG. Microbia
- Page 322 and 323:
11 The Filter Integrity Tests Theod
- Page 324 and 325:
The Filter Integrity Tests 299 befo
- Page 326 and 327:
The Filter Integrity Tests 301 side
- Page 328 and 329:
The Filter Integrity Tests 303 the
- Page 330 and 331:
The Filter Integrity Tests 305 supe
- Page 332 and 333:
The Filter Integrity Tests 307 thes
- Page 334 and 335:
The Filter Integrity Tests 309 Data
- Page 336 and 337:
The Filter Integrity Tests 311 The
- Page 338 and 339:
The Filter Integrity Tests 313 FIGU
- Page 340 and 341:
The Filter Integrity Tests 315 may
- Page 342 and 343:
The Filter Integrity Tests 317 pres
- Page 344 and 345:
The Filter Integrity Tests 319 FIGU
- Page 346 and 347:
The Filter Integrity Tests 321 Due
- Page 348 and 349:
The Filter Integrity Tests 323 Log
- Page 350 and 351:
The Filter Integrity Tests 325 Pres
- Page 352 and 353:
The Filter Integrity Tests 327 filt
- Page 354 and 355:
The Filter Integrity Tests 329 are
- Page 356 and 357:
The Filter Integrity Tests 331 the
- Page 358 and 359:
The Filter Integrity Tests 333 the
- Page 360 and 361:
The Filter Integrity Tests 335 test
- Page 362 and 363:
The Filter Integrity Tests 337 Is t
- Page 364 and 365:
The Filter Integrity Tests 339 (Tro
- Page 366 and 367:
The Filter Integrity Tests 341 an i
- Page 368 and 369:
The Filter Integrity Tests 343 FIGU
- Page 370 and 371:
The Filter Integrity Tests 345 The
- Page 372 and 373:
The Filter Integrity Tests 347 EMEA
- Page 374:
The Filter Integrity Tests 349 Waib
- Page 377 and 378:
352 Jornitz For this reason vendors
- Page 379 and 380:
354 Jornitz Nevertheless, the vendo
- Page 381 and 382:
356 Jornitz meaning every step requ
- Page 383 and 384:
358 Jornitz successes will also ens
- Page 385 and 386:
360 Jornitz components are required
- Page 387 and 388:
362 Jornitz API WFI Higher Risk or
- Page 389 and 390:
364 Jornitz FIGURE 9 Typical flow d
- Page 391 and 392:
366 Jornitz is supplied to assure a
- Page 393 and 394:
368 Jornitz FIGURE 12 Validation sc
- Page 396 and 397:
13 Validation of the Filter and of
- Page 398 and 399:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 400 and 401:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 402 and 403:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 404 and 405:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 406 and 407:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 408 and 409:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 410 and 411:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 412:
Validation of the Filter and of the
- Page 415 and 416:
390 Colton and Bestwick FIGURE 1 Cr
- Page 417 and 418:
392 Colton and Bestwick such as pol
- Page 419 and 420: 394 Colton and Bestwick Filters use
- Page 421 and 422: 396 Colton and Bestwick 3. Composit
- Page 423 and 424: 398 Colton and Bestwick Another con
- Page 425 and 426: 400 Colton and Bestwick This experi
- Page 427 and 428: 402 Colton and Bestwick and leachab
- Page 429 and 430: 404 Colton and Bestwick The mass fr
- Page 431 and 432: 406 Colton and Bestwick through the
- Page 433 and 434: 408 Colton and Bestwick Alternative
- Page 435 and 436: 410 Colton and Bestwick Modeling Le
- Page 438 and 439: 15 Endotoxin, Limulus Amebocyte Lys
- Page 440 and 441: Endotoxin, Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
- Page 442 and 443: Endotoxin, Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
- Page 444 and 445: Endotoxin, Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
- Page 446 and 447: Endotoxin, Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
- Page 448: Endotoxin, Limulus Amebocyte Lysate
- Page 451 and 452: 426 Gould thousand to roughly 25,00
- Page 453 and 454: 428 Gould different endotoxin prepa
- Page 455 and 456: 430 Gould Because turbidity can be
- Page 457 and 458: 432 Gould ERROR OF THE LAL TEST The
- Page 459 and 460: 434 Gould qualification of the LAL
- Page 461 and 462: 436 Gould promotes adsorption and d
- Page 463 and 464: 438 Gould Twohy CW, Nierman ML, Dur
- Page 465 and 466: 440 Jornitz and Meltzer form a high
- Page 467 and 468: 442 Jornitz and Meltzer Another imp
- Page 469: 444 Jornitz and Meltzer commonly sh
- Page 473 and 474: 448 Jornitz and Meltzer FIGURE 10 F
- Page 475 and 476: 450 Jornitz and Meltzer filter devi
- Page 477 and 478: 452 Jornitz and Meltzer filter (600
- Page 479 and 480: 454 Jornitz and Meltzer FIGURE 15 F
- Page 481 and 482: 456 Jornitz and Meltzer the end use
- Page 484 and 485: 18 Downstream Processing Uwe Gottsc
- Page 486 and 487: Downstream Processing 461 medium wi
- Page 488 and 489: Downstream Processing 463 explore s
- Page 490 and 491: Downstream Processing 465 (A) (B) S
- Page 492 and 493: Downstream Processing 467 impuritie
- Page 494 and 495: Downstream Processing 469 TABLE 1 D
- Page 496 and 497: Downstream Processing 471 (A) (B) S
- Page 498 and 499: Downstream Processing 473 n flux us
- Page 500 and 501: Downstream Processing 475 Feed Resi
- Page 502 and 503: Downstream Processing 477 TABLE 2 S
- Page 504 and 505: Downstream Processing 479 Chromatog
- Page 506 and 507: Downstream Processing 481 TABLE 3 S
- Page 508 and 509: Downstream Processing 483 crystalli
- Page 510 and 511: Downstream Processing 485 presents
- Page 512 and 513: Downstream Processing 487 and react
- Page 514 and 515: Downstream Processing 489 The chall
- Page 516 and 517: Downstream Processing 491 Jagschies
- Page 518: Downstream Processing 493 Zhou JX,
- Page 521 and 522:
496 Dosmar and Pinto Pore size (mic
- Page 523 and 524:
498 Dosmar and Pinto Flux (ml/min/c
- Page 525 and 526:
500 Dosmar and Pinto APPLICATIONS I
- Page 527 and 528:
502 Dosmar and Pinto In instances w
- Page 529 and 530:
504 Dosmar and Pinto TABLE 1 The Th
- Page 531 and 532:
506 Dosmar and Pinto 40% respective
- Page 533 and 534:
508 Dosmar and Pinto The polysulfon
- Page 535 and 536:
510 Dosmar and Pinto 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.
- Page 537 and 538:
512 Dosmar and Pinto Flux (mL/min/c
- Page 539 and 540:
514 Dosmar and Pinto interface. The
- Page 541 and 542:
516 Dosmar and Pinto Permeate port
- Page 543 and 544:
518 Dosmar and Pinto layer is on th
- Page 545 and 546:
520 Dosmar and Pinto TABLE 4 Factor
- Page 547 and 548:
522 Dosmar and Pinto If the tempera
- Page 549 and 550:
524 Dosmar and Pinto Excessive TMP
- Page 551 and 552:
526 Dosmar and Pinto Permeate Flow
- Page 553 and 554:
528 Dosmar and Pinto rate, identify
- Page 555 and 556:
530 Dosmar and Pinto shown) at any
- Page 557 and 558:
532 Dosmar and Pinto TABLE 6 Casset
- Page 559 and 560:
534 Dosmar and Pinto to the feed ta
- Page 561 and 562:
536 Dosmar and Pinto TABLE 8 Biolog
- Page 563 and 564:
538 Dosmar and Pinto TABLE Adsorpti
- Page 565 and 566:
540 Dosmar and Pinto MWCO Abbreviat
- Page 567 and 568:
542 Dosmar and Pinto Marshall AD, M
- Page 569 and 570:
544 Aranha were directed at selecti
- Page 571 and 572:
546 Aranha CONTROL OF PRODUCTION PR
- Page 573 and 574:
548 Aranha There are several availa
- Page 575 and 576:
550 Aranha TABLE 4 Risk Minimizatio
- Page 577 and 578:
552 Aranha proteins from chromatogr
- Page 579 and 580:
554 Aranha side of the filter is ta
- Page 581 and 582:
556 Aranha If the size of the prote
- Page 583 and 584:
558 Aranha Regulatory guidelines (C
- Page 585 and 586:
560 Aranha vary depending on the un
- Page 587 and 588:
562 Aranha the virus, it cannot be
- Page 589 and 590:
564 Aranha Steps that require dilut
- Page 591 and 592:
566 Aranha TABLE 10 Categorization
- Page 593 and 594:
568 Aranha TABLE 12 Main Characteri
- Page 595 and 596:
570 Aranha rederivatization. CBER h
- Page 597 and 598:
572 Aranha also virus removal filte
- Page 599 and 600:
574 Aranha every single reported ca
- Page 601 and 602:
576 Aranha Golker CF, Whiteman MD,
- Page 604 and 605:
21 A Rapid Method for Purifying Esc
- Page 606 and 607:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 608 and 609:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 610 and 611:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 612 and 613:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 614 and 615:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 616 and 617:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 618 and 619:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 620 and 621:
A Rapid Method for Purifying Escher
- Page 622 and 623:
22 Membrane Chromatography Jeffrey
- Page 624 and 625:
Membrane Chromatography 599 contami
- Page 626 and 627:
Membrane Chromatography 601 the cyl
- Page 628 and 629:
Membrane Chromatography 603 Even so
- Page 630 and 631:
Membrane Chromatography 605 TABLE 2
- Page 632 and 633:
Membrane Chromatography 607 TABLE 4
- Page 634 and 635:
Membrane Chromatography 609 Isoelec
- Page 636 and 637:
Membrane Chromatography 611 validat
- Page 638 and 639:
Membrane Chromatography 613 C/CO 1
- Page 640 and 641:
Membrane Chromatography 615 TABLE 6
- Page 642 and 643:
Membrane Chromatography 617 spiked
- Page 644 and 645:
23 Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene
- Page 646 and 647:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 648 and 649:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 650 and 651:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 652 and 653:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 654 and 655:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 656 and 657:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 658 and 659:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 660 and 661:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 662 and 663:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 664 and 665:
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Me
- Page 666 and 667:
24 Air Filtration Applications in t
- Page 668 and 669:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 670 and 671:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 672 and 673:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 674 and 675:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 676 and 677:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 678 and 679:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 680 and 681:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 682 and 683:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 684 and 685:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 686 and 687:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 688 and 689:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 690 and 691:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 692 and 693:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 694 and 695:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 696 and 697:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 698 and 699:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 700 and 701:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 702 and 703:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 704 and 705:
Air Filtration Applications in the
- Page 706 and 707:
25 Sterility Testing by Filtration
- Page 708 and 709:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 710 and 711:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 712 and 713:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 714 and 715:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 716 and 717:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 718 and 719:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 720 and 721:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 722:
Sterility Testing by Filtration in
- Page 725 and 726:
700 Mittelman phospholipids surroun
- Page 727 and 728:
702 Mittelman 1. Trace organics, wh
- Page 729 and 730:
704 Mittelman from chemical treatme
- Page 731 and 732:
706 Mittelman Flow Effects In the s
- Page 733 and 734:
708 Mittelman TREATMENT Inactivatio
- Page 735 and 736:
710 Mittelman TABLE 3 Chemical Trea
- Page 737 and 738:
712 Mittelman Khoury AE, Lam K, Ell
- Page 739 and 740:
714 Mittelman Richards GK, Gagnon R
- Page 742 and 743:
27 Steam Sterilization of Filters S
- Page 744 and 745:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 719
- Page 746 and 747:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 721
- Page 748 and 749:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 723
- Page 750 and 751:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 725
- Page 752 and 753:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 727
- Page 754 and 755:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 729
- Page 756 and 757:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 731
- Page 758 and 759:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 733
- Page 760 and 761:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 735
- Page 762 and 763:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 737
- Page 764 and 765:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 739
- Page 766 and 767:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 741
- Page 768 and 769:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 743
- Page 770 and 771:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 745
- Page 772 and 773:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 747
- Page 774 and 775:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 749
- Page 776:
Steam Sterilization of Filters 751
- Page 779 and 780:
754 Manfredi TABLE 1 List of Organo
- Page 781 and 782:
756 Manfredi Based upon its unstabl
- Page 783 and 784:
758 Manfredi Ozone, unlike chlorine
- Page 785 and 786:
760 Manfredi FIGURE 3 Tubular coron
- Page 787 and 788:
762 Manfredi Ozone monitors, for bo
- Page 789 and 790:
764 Manfredi ultraviolet decomposit
- Page 791 and 792:
766 Manfredi entering the vessel ma
- Page 793 and 794:
768 Manfredi d[O 3] = dt k o3 [M] [
- Page 795 and 796:
770 Manfredi pressure, although the
- Page 797 and 798:
772 Manfredi Ozone. 9 September 200
- Page 799 and 800:
774 Index [Air filtration applicati
- Page 801 and 802:
776 Index [Charge-modified filters]
- Page 803 and 804:
778 Index [ePTFE] lyophilization, 6
- Page 805 and 806:
780 Index [Filter validation/filter
- Page 807 and 808:
782 Index [Integrity tests] redunda
- Page 809 and 810:
784 Index Optimum TMP, definition,
- Page 811 and 812:
786 Index [Product capture/purifica
- Page 813 and 814:
788 Index [Steam sterilization of f
- Page 815:
790 Index Wetted membrane, rate of