Lexically conditioned variation in Harmonic Grammar
Lexically conditioned variation in Harmonic Grammar
Lexically conditioned variation in Harmonic Grammar
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
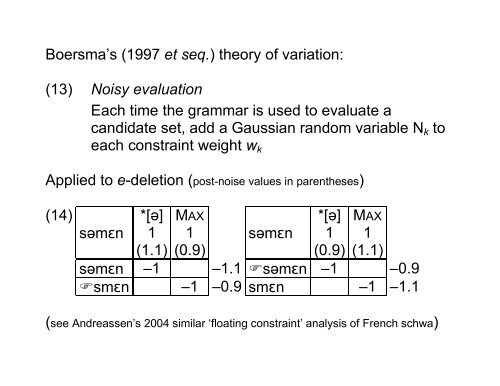
Boersma’s (1997 et seq.) theory of <strong>variation</strong>:<br />
(13) Noisy evaluation<br />
Each time the grammar is used to evaluate a<br />
candidate set, add a Gaussian random variable Nk to<br />
each constra<strong>in</strong>t weight wk<br />
Applied to e-deletion (post-noise values <strong>in</strong> parentheses)<br />
(14)<br />
sәmɛn<br />
*[ә]<br />
1<br />
(1.1)<br />
MAX<br />
1<br />
(0.9)<br />
sәmɛn<br />
*[ә]<br />
1<br />
(0.9)<br />
MAX<br />
1<br />
(1.1)<br />
sәmɛn –1 –1.1 sәmɛn –1 –0.9<br />
smɛn –1 –0.9 smɛn –1 –1.1<br />
(see Andreassen’s 2004 similar ‘float<strong>in</strong>g constra<strong>in</strong>t’ analysis of French schwa)