X - UWSpace - University of Waterloo
X - UWSpace - University of Waterloo
X - UWSpace - University of Waterloo
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
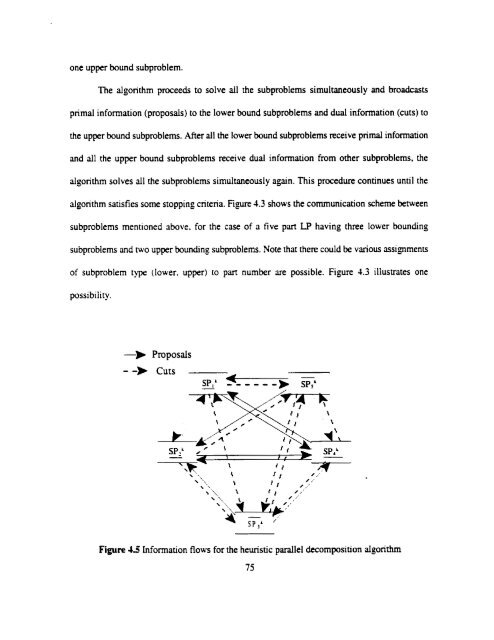
one upper bound subproblem.<br />
The algorithm proceeds to solve ail the subproblems simultaneously and broadcasts<br />
prima1 information (proposais) to the lower bound subproblems and duai information (cuts) 10<br />
the upper bound subproblems. After ail the lower bound subproblems receive pnmal information<br />
and ail the upper bound subproblems receive duai information from other subproblems. the<br />
algorithm solves ail the subproblems simultaneousl y again. This procedm continues until the<br />
algorithm satisfies some stopping criteria. Figure 1.3 shows the communication scheme between<br />
subproblems mentioned sbove. for the case <strong>of</strong> a five part LP having the lower bounding<br />
subproblems and two upper bounding subproblems. Note that there could be various assignments<br />
<strong>of</strong> subproblem type (lower. upper) to pan number are possible. Figure 4.3 illustrates one<br />
possibility.<br />
Figure 4.3 Information Bows for the heuristic parailel decomposition algondun<br />
75