Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Semi</strong>-Implicit<br />
<strong>Semi</strong>-<br />
<strong>Lagrangian</strong><br />
Time-<br />
Stepping<br />
Methods and<br />
Regularized<br />
Fluid<br />
Equations in<br />
Numerical<br />
Weather<br />
Prediction<br />
Sebastian<br />
Reich<br />
Numerical<br />
Weather<br />
Prediction<br />
Basic Facts<br />
Unified Model<br />
Towards a<br />
New Dynamic<br />
Core<br />
Model System and<br />
Basic Ideas<br />
Results<br />
General<br />
Methodology<br />
Concluding<br />
Remarks<br />
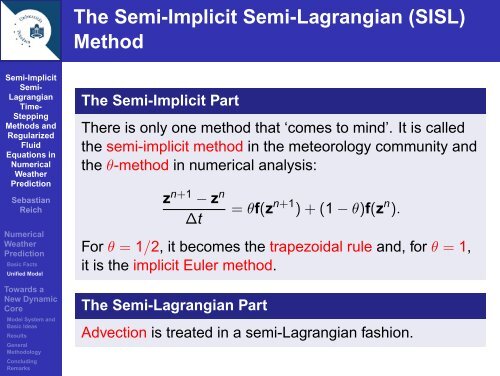
The <strong>Semi</strong>-Implicit <strong>Semi</strong>-<strong>Lagrangian</strong> (SISL)<br />
Method<br />
The <strong>Semi</strong>-Implicit Part<br />
There is only one method that ‘comes to mind’. It is called<br />
the <strong>semi</strong>-<strong>implicit</strong> method in the meteorology community and<br />
the θ-method in <strong>numerical</strong> analysis:<br />
z n+1 − z n<br />
∆t<br />
= θf(z n+1 ) + (1 − θ)f(z n ).<br />
For θ = 1/2, it becomes the trapezoidal rule and, <strong>for</strong> θ = 1,<br />
it is the <strong>implicit</strong> Euler method.<br />
The <strong>Semi</strong>-<strong>Lagrangian</strong> Part<br />
Advection is treated in a <strong>semi</strong>-<strong>Lagrangian</strong> fashion.