Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Semi</strong>-Implicit<br />
<strong>Semi</strong>-<br />
<strong>Lagrangian</strong><br />
Time-<br />
Stepping<br />
Methods and<br />
Regularized<br />
Fluid<br />
Equations in<br />
Numerical<br />
Weather<br />
Prediction<br />
Sebastian<br />
Reich<br />
Numerical<br />
Weather<br />
Prediction<br />
Basic Facts<br />
Unified Model<br />
Towards a<br />
New Dynamic<br />
Core<br />
Model System and<br />
Basic Ideas<br />
Results<br />
General<br />
Methodology<br />
Concluding<br />
Remarks<br />
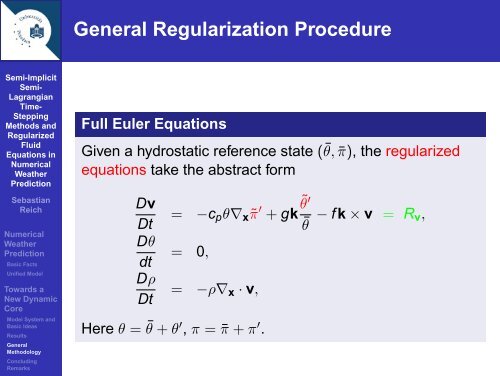
General Regularization Procedure<br />
Full Euler Equations<br />
Given a hydrostatic reference state (¯θ, ¯π), the regularized<br />
equations take the abstract <strong>for</strong>m<br />
Dv<br />
Dt = −cpθ∇x˜π ′ ˜θ ′<br />
+ gk<br />
¯θ<br />
Dθ<br />
dt<br />
= 0,<br />
Dρ<br />
Dt = −ρ∇x · v,<br />
Here θ = ¯ θ + θ ′ , π = ¯π + π ′ .<br />
− f k × v = Rv,