Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Semi-implicit semi-Lagrangian methods for numerical weather ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Semi</strong>-Implicit<br />
<strong>Semi</strong>-<br />
<strong>Lagrangian</strong><br />
Time-<br />
Stepping<br />
Methods and<br />
Regularized<br />
Fluid<br />
Equations in<br />
Numerical<br />
Weather<br />
Prediction<br />
Sebastian<br />
Reich<br />
Numerical<br />
Weather<br />
Prediction<br />
Basic Facts<br />
Unified Model<br />
Towards a<br />
New Dynamic<br />
Core<br />
Model System and<br />
Basic Ideas<br />
Results<br />
General<br />
Methodology<br />
Concluding<br />
Remarks<br />
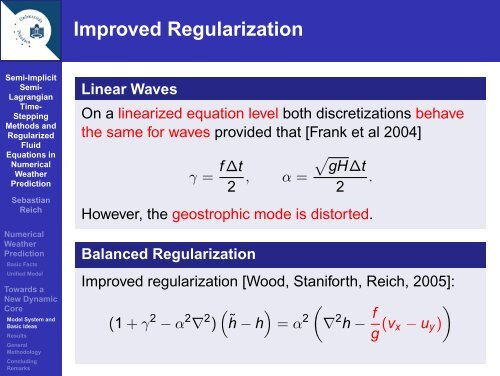
Improved Regularization<br />
Linear Waves<br />
On a linearized equation level both discretizations behave<br />
the same <strong>for</strong> waves provided that [Frank et al 2004]<br />
<br />
f ∆t<br />
gH∆t<br />
γ = , α = .<br />
2 2<br />
However, the geostrophic mode is distorted.<br />
Balanced Regularization<br />
Improved regularization [Wood, Stani<strong>for</strong>th, Reich, 2005]:<br />
(1 + γ 2 − α 2 ∇ 2 <br />
) ˜h − h = α 2<br />
<br />
∇ 2 h − f<br />
g (vx<br />
<br />
− uy)